Free PESTLE Analysis Templates and Actionable Guide
43% of HR professionals don’t have a future of work strategy. Without a strategy, you won’t be able to anticipate future work, company, or talent needs based on external market factors.

HR professionals today constantly face the challenge of anticipating and adapting to external factors that shape their organization’s future. That’s when a PESTLE analysis comes in handy. PESTLE is a powerful strategic tool that helps you assess current and future events by examining key external factors impacting your industry, organization, employees, and customers.
A PESTLE analysis can provide valuable insights into external market dynamics, enabling you to proactively align your HR strategies with broader factors and internal business goals to address emerging challenges.
Contents
What is a PESTLE analysis?
The 6 factors of a PESTLE analysis
Why use a PESTLE analysis?
SWOT vs. PESTLE analysis
How to conduct a PESTLE analysis
PESTLE analysis templates
A PESTLE analysis in action
What is a PESTLE analysis?
A PESTLE analysis (sometimes called PESTEL analysis) is a strategic tool that organizations (and Human Resources) can use to identify and analyze the external factors that impact their operations and decision-making processes.
The acronym PESTLE stands for:
- Political
- Economic
- Social
- Technological
- Legal, and;
- Environmental factors.
This comprehensive analysis helps you to understand the broader environment in which you operate, allowing you to anticipate changes and adapt your strategies accordingly.
As an HR professional, you can use a PESTLE analysis to better understand your market, labor changes, and regulatory requirements.
The 6 factors of a PESTLE analysis
External forces driven by government and politics
External forces driven by the economy
External forces driven by culture and social dynamics
- Changes in taxation, such as corporate tax rates, VAT, and other tax incentives or burdens
- Government stability impacting employment policies
- Government policies on employment, such as initiatives to reduce unemployment, support for specific sectors, and promote diversity and inclusion
- Economic growth or recession affecting hiring budgets
- Wage inflation impacting salary structures
- Unemployment rates influencing talent availability
- Demographic changes affecting workforce composition
- Work-life balance expectations shaping company policies
- Cultural trends influencing employee engagement strategies
External forces driven by technology
External forces driven by the law
External forces driven by the environment
- Advancements in HR technology (e.g., AI for recruitment)
- Remote work technologies influencing flexible work arrangements
- Data security measures to protect employee information
- Changes in labor laws and employment regulations
- Compliance with health & safety standards & local regulations
- Keeping up to date with immigration & work visa regulations
- Sustainability initiatives affecting company practices
- Environmental regulations impacting operational processes
- Corporate social responsibility (CSR) influencing employer branding
The PESTLE analysis factors explained
Let’s take a look at each of the six factors in a PESTLE analysis.
1. Political factors
Political factors include government policies, political stability, and organizational regulatory changes. In the HR environment, political factors might include changes in labor laws, such as new regulations on minimum wage, working hours, or employee benefits.
For example, a government mandate increasing the minimum wage would require HR to adjust compensation structures and possibly re-evaluate staffing budgets.
2. Economic factors
Economic factors relate to the broader economic environment and its influence on your business. These factors typically include changes in the job market, inflation rates, and economic downturns.
While an economic recession could lead to budget cuts and require layoffs or hiring freezes, the cost of living also directly impacts employees and candidates. In this case, HR would need to develop strategies for maintaining morale and productivity during tough economic times.
3. Social factors
Social factors examine societal trends, cultural norms, and demographic changes that impact organizations. These factors could include shifting workforce demographics, such as an aging population or increasing diversity.
An aging workforce, for example, might prompt you to focus on succession planning and knowledge transfer. Increasing diversity could lead to the development of inclusive hiring practices and diversity training programs.
4. Technological factors
Technological factors focus on technological advancements and innovations. For example, the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation in HR will require further digital transformation.
Adapting to new technologies is important for remaining competitive and attracting top talent.
As an HR professional, you may not be the decision maker when it comes to investing in new tech, but you can make a business case for HR to stay ahead of the technology game. For example, you can ensure employees are adequately and continuously trained in the use of generative AI.
5. Legal factors
Legal factors encompass the laws and regulations that govern organizational operations. In HR, legal factors include compliance with employment laws, health and safety regulations, and labor standards.
For example, new data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), require HR to ensure that employee data is securely managed and that privacy policies are strictly followed to avoid legal repercussions.
6. Environmental factors
Environmental factors involve ecological and environmental considerations that can affect organizations. HR typically includes corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives and sustainability practices.
As an HR professional, you might develop programs to promote remote working to reduce the company’s carbon footprint or implement policies encouraging recycling and waste reduction.
Why use a PESTLE analysis?
Anticipate changes in the external environment
One of the primary benefits of PESTLE analysis is its ability to help HR professionals anticipate changes in the external environment. For example, new labor laws or economic downturns can significantly impact staffing and training programs.
By conducting a PESTLE analysis, HR can identify potential legislative changes and economic trends early, allowing them to prepare and adapt their strategies accordingly. This foresight helps mitigate risks and ensures the organization is not caught off guard by external shifts.
Align HR strategy with business goals
PESTLE analysis also aids in aligning HR strategies with overall business goals. If you have a macro view of the factors affecting your organization, you can develop initiatives that support and enhance the company’s strategic objectives.
An example of this in action is understanding technological advancements and their potential impact on your industry and business, which can guide training programs, recruiting skilled talent, and adopting new HR-related tech.
Enhance decision-making
You can use a PESTLE analysis to enhance your decision-making processes. The data gathered from analyzing the six key factors offers valuable insights that can inform HR decisions. Whether planning for workforce expansion, developing employee retention strategies, or implementing new technologies, understanding the external factors at play ensures that HR decisions are well-informed and strategic, leading to more effective and sustainable HR practices.
Here are a few other key reasons why you should regularly conduct a PESTLE analysis:
- Recognize and proactively address threats early
- Capitalize on identified opportunities
- Enhance organizational resilience through dynamic and responsive strategies
- Look beyond internal metrics and consider external influences that impact your workforce
- Promote a holistic view of the HR environment
- Develop well-rounded HR policies and practices.
SWOT vs. PESTLE analysis
A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) is an established strategic tool organizations use to identify risk and growth areas within the business. While both are strategic tools, they differ from each other.
Let’s examine where SWOT and PESTLE analyses overlap and differ and how you can leverage both to increase your value within your organization, solve key challenges, and unlock opportunities.
Feature SWOT analysis PESTLE analysis Combining both for HR Purpose Identifies internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. Examines external factors impacting the organization, including political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors. Provides a holistic view of internal and external factors, enabling more robust strategic planning. Focus Internal and external factors, but with a stronger emphasis on internal analysis. External macro-environmental factors that could affect the organization. Combines internal insights from SWOT with external insights from PESTLE for a balanced perspective. Factors Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats. Political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental. Integrates internal strengths and weaknesses with external opportunities and threats for comprehensive planning. Use case in HR Helps HR identify internal capabilities and challenges, such as talent strengths, skills gaps, and areas for improvement. Helps HR understand external factors like labor laws, economic conditions, societal trends, and technological advancements. Enables HR to develop strategies informed by internal capabilities and external influences. Outcome Strategic insights into leveraging strengths, addressing weaknesses, seizing opportunities, and mitigating threats. Strategic insights into adapting to external changes and preparing for future trends and regulations. A comprehensive strategic plan that aligns HR initiatives with both internal strengths and external realities. In action Identifying a strong leadership team (Strength), skill gaps (Weakness), market expansion opportunities (Opportunity), and competitive pressures (Threat). Understanding the impact of new labor laws (political), economic downturns (economic), demographic shifts (social), AI advancements (technological), compliance requirements (legal), and sustainability trends (environmental). HR can use SWOT to focus on internal training programs and employee development while using PESTLE to adapt to external legal changes and technological advancements.
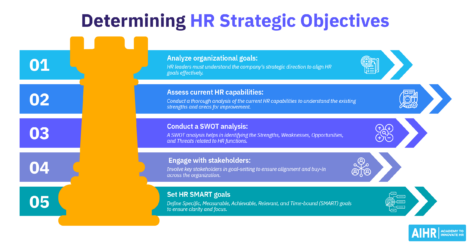
How to conduct a PESTLE analysis
Step 1: Identify the purpose and scope
Before beginning the PESTLE analysis, clearly define the purpose and scope. Determine what you want to achieve and which specific aspects of the business or HR strategy will be analyzed. This step ensures that the analysis remains focused and relevant.
→ Do this: Define the HR objectives you want to address with the PESTLE analysis, such as improving employee retention, planning workforce expansion, or adapting to new regulations.
Step 2: Gather relevant information
Collect data and information on each of the six PESTLE factors: political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental. Use reliable sources such as government reports, industry analyses, market research, and expert opinions.
→ Do this: Use HR analytics tools and external sources to gather data on workforce trends, such as changes in labor laws, economic forecasts, and technological advancements. This includes recruitment, candidate and employee reports, and surveys from respected sources.
Step 3: Analyze each PESTLE factor
Examine the data collected for each PESTLE factor. Identify how each factor might impact the organization and, specifically, the HR function. Consider both current influences and potential future trends.
→ Do this: Create a list of potential impacts on HR per factor in your PESTLE analysis template. Some factors may be more urgent and topical than others. You don’t need to address all six factors at once.
Step 4: Identify opportunities and threats
Based on the analysis, identify the opportunities and threats posed by each PESTLE factor. Again, there may not be an urgent opportunity or risk per factor. As you become more familiar with using your PESTLE analysis, you can prioritize which factors should be addressed now and which are longer-term focus areas (as discussed in step 5).
→ Do this: Develop a matrix for HR opportunities and threats. For instance, an opportunity might be the availability of advanced HR software, while a threat could be new data protection regulations requiring changes in HR data management.
Step 5: Prioritize the factors
Assess the significance of each PESTLE factor and prioritize them based on their potential impact on the organization and the HR function. Focus on the most critical factors that require immediate attention or present the greatest opportunities.
→ Do this: Rank the identified opportunities and threats based on their potential impact on HR objectives. Prioritize those significantly affecting workforce planning, employee engagement, or compliance.
Step 6: Develop strategic responses
Develop action plans that leverage the opportunities and mitigate the threats you have identified, ensuring that HR strategies are adaptable to external changes.
→ Do this: Create specific HR action plans for high-priority factors. For example, if technological advancements are a priority, plan for HR technology investments and employee training programs to enhance digital skills.
Step 7: Monitor and review
Monitor the external environment regularly and review the PESTLE analysis to ensure it remains current and relevant. Update the analysis to reflect any new information or changes in external factors.
→ Do this: Establish a schedule for periodic reviews of the PESTLE analysis, such as quarterly or bi-annually, to ensure HR strategies remain aligned with the latest external trends and developments. The world of work moves far quicker than previously. Strategies are only as relevant as the current economic, social, and legislative environment – not to mention the acceleration of technology.
PESTLE analysis templates
These free downloadable PESTLE analysis templates in Word and Excel formats are designed to assist you in evaluating the external factors that may influence your business operations.
PESTLE analysis template: Excel
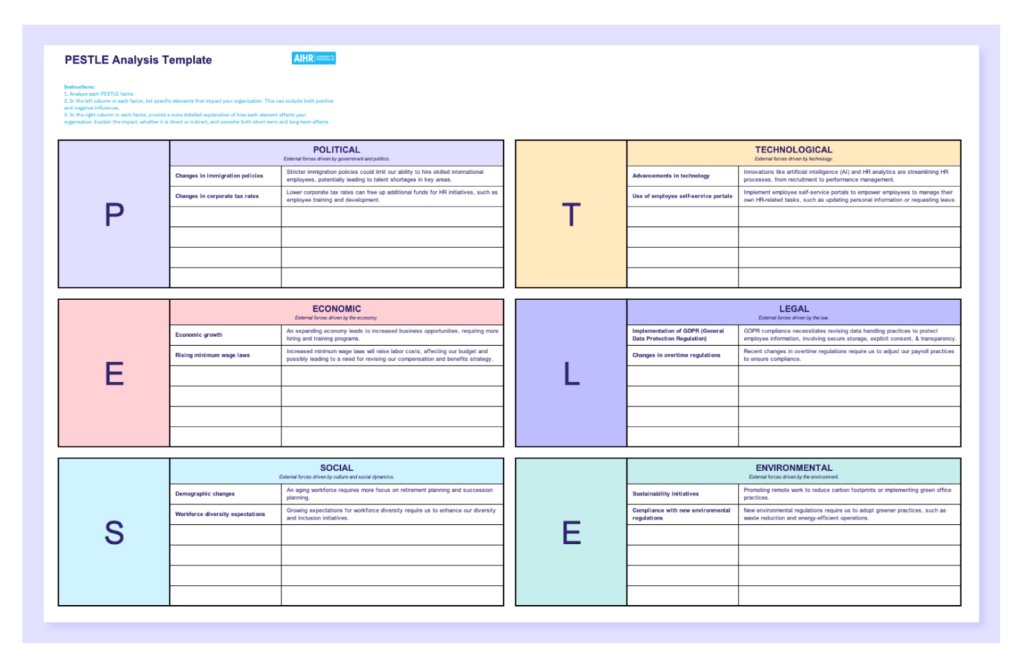
PESTLE analysis template: Word

A PESTLE analysis in action
Let’s now look at a hypothetical example of a PESTLE analysis performed by HR.
Political factors
- Government initiatives aimed at reducing unemployment, such as subsidies for hiring unemployed individuals or tax incentives for creating new jobs, can positively impact recruitment efforts.
- The local government is stable and provides a conducive environment for business growth. However, upcoming elections may result in policy changes.
HR’s focus: Monitor the political environment regularly and update HR policies accordingly. Develop contingency plans to address potential labor policy changes.
Economic factors
- An expanding economy leads to increased business opportunities, requiring more hiring and training programs.
- Low unemployment rates, linked to a growing economy, have led to talent shortages, requiring HR to enhance recruitment strategies and employee retention efforts.
HR’s focus: Invest in employee development to retain talent during competitive job markets. Focus on proactive recruitment to meet the demands of a growing business.
Social factors
- An aging workforce requires more focus on retirement planning and succession planning.
- Shifts in societal values, such as the growing emphasis on work-life balance. Growing societal calls for improved Diversity and Inclusion in the workplace have influenced the expectations of younger employees and workplace culture.
HR’s focus: Promote a culture of continuous learning and development to accommodate different career stages and a transfer of knowledge that supports succession planning. Implement inclusive policies and programs that cater to diverse employee needs.
Technological factors
- Advancements in HR Technology: Innovations like artificial intelligence (AI) and HR analytics are streamlining HR processes, from recruitment to performance management.
- The rise of remote work technologies has transformed the workplace, making it essential for HR to manage remote teams effectively.
HR’s focus: Invest in cutting-edge HR technologies to enhance efficiency and data-driven decision-making. Develop robust remote work policies and provide training for employees to adapt to new technologies.
Legal factors
- Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) require stringent data protection measures, impacting how HR manages employee information.
HR’s focus: Conduct training sessions for HR staff on the latest legal requirements and data protection practices regarding personally identifiable information (PII) that impact how employee data is collected, stored, and archived.
Environmental factors
- Promoting remote work to reduce carbon footprints or implementing green office practices.
- At the same time, increasing environmental disruptions, such as floods and large-scale wildfires, disrupt workflows.
HR’s focus: Develop and promote sustainability initiatives within the organization. Create emergency preparedness plans to ensure business continuity and employee safety during environmental disruptions.
Getting started
A well-structured and regularly conducted PESTLE analysis is not just a strategic tool; it is a game-changer for organizational growth and the strategic importance of the HR department. By systematically examining political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors with a PESTLE analysis template, HR professionals can proactively address external challenges and seize emerging opportunities.
This foresight lets you align HR initiatives with broader business objectives, ensuring that the organization is agile, resilient, and prepared for the future. The insights gained from a thoughtful PESTLE analysis can empower you to make data-driven decisions, enhance employee engagement, and support a culture of continuous improvement.
Ultimately, HR professionals should use a PESTLE analysis to elevate the HR department from a support function to a strategic partner, driving the organization’s long-term success and sustainability.
Weekly update
Stay up-to-date with the latest news, trends, and resources in HR
Learn more
Related articles
Are you ready for the future of HR?
Learn modern and relevant HR skills, online