HR Strategic Objectives: The Ultimate FAQ for HR Leaders
Culture reigns supreme: Seven out of 10 employees wouldn’t work for a top company with a poor culture. HR strategic objectives are designed to develop a happy, high-performing workforce that supports the overall business strategy. That’s what sparks innovation and drives growth.

Companies are increasingly recognizing that HR strategic objectives are essential for maintaining a competitive edge. By setting actionable, measurable strategic HR objectives, HR leaders can ensure that every HR initiative is purposefully designed to develop a high-performing workforce, support the overall business strategy, and drive growth.
This strategic alignment is crucial in addressing the changing expectations of the workforce and leveraging HR practices to build an innovative, inclusive, and efficient organizational environment.
Contents
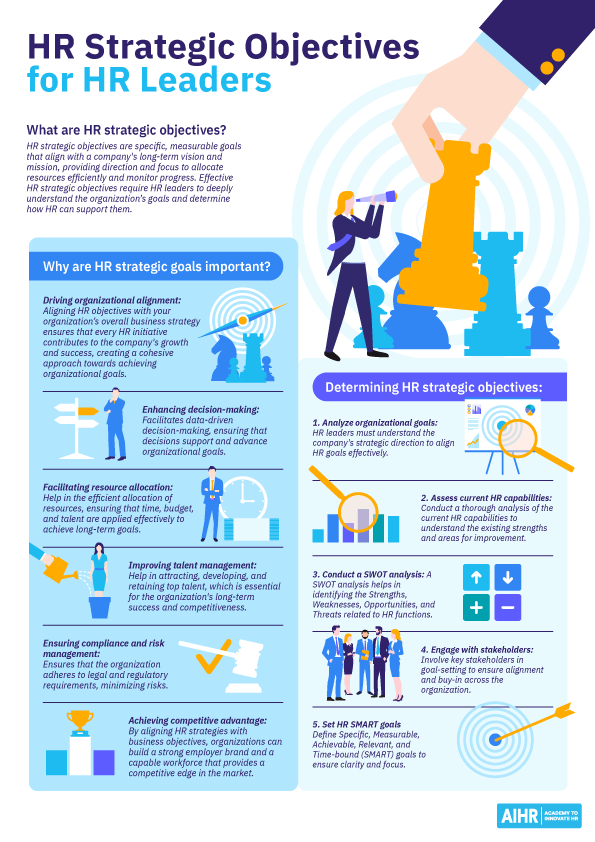
What are HR strategic objectives?
What is strategic HR management?
Why are HR strategic goals important?
How can HR leaders determine HR goals and objectives?
7 HR strategic objectives examples
What are HR strategic objectives?
HR strategic objectives are specific, measurable goals that align with a company’s long-term vision and mission, providing direction and focus to allocate resources efficiently and monitor progress. Effective HR strategic objectives require HR leaders to deeply understand the organization’s goals and determine how HR can support them.
Some areas of focus when identifying HR strategic objectives include:
- Workforce planning: Involves analyzing the current workforce, predicting future needs, and developing strategies such as aligning workforce capabilities with business needs, succession planning, and flexible workforce management.
- Employer branding: Aims to create a positive company image to attract top talent and enhance employee engagement and reputation.
- Talent management: Covers the entire employee life cycle, focusing on developing talent, performance management, and career development.
- Compensation and benefits: Ensure competitive pay structures, incentive programs, and optimized benefits packages.
- Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Belonging: DEIB initiatives promote diverse hiring practices, an inclusive culture, equitable opportunities, and a sense of belonging.
- Objectives in employee relations and engagement: Include enhancing communication, conflict resolution, and employee recognition.
- Organizational development: Focuses on change management, process improvement, and leadership development.
By setting and pursuing strategic HR objectives in these areas, HR leaders can significantly contribute to the organization’s overall success and long-term sustainability.
What is strategic HR management?
Strategic HR management (SHRM) is the proactive alignment of human resources with your organization’s long-term goals and objectives. Unlike traditional HR, which focuses on administrative tasks and daily operations, SHRM emphasizes the strategic role of HR in driving organizational success. This requires planning and implementing HR policies and practices that support the overall business strategy to ensure that HR functions are integrated with the business’s mission and vision.
Key components of strategic HR management include alignment with organizational goals, long-term planning, and comprehensive HR policies and practices. It also includes creating HR policies that support strategic objectives, adopting industry best practices, and managing talent effectively.
This involves attracting and selecting individuals who fit the strategic needs, investing in employee development, and implementing performance management systems. Additionally, SHRM focuses on enhancing employee engagement, creating a positive organizational culture, and promoting diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging (DEIB).
The benefits of strategic HR management are substantial. It improves talent management by attracting and retaining top talent and developing capable leaders. Higher employee engagement and retention are achieved through strategic HR initiatives, leading to a more engaged workforce and a positive work culture. Also, SHRM equips organizations with the agility to adapt to changing business environments, ensuring sustainability and maintaining a competitive advantage over time.
Why are HR strategic goals important?
- Driving organizational alignment: Aligning HR objectives with your organization’s overall business strategy ensures that every HR initiative contributes to the company’s growth and success, creating a cohesive approach toward achieving organizational goals.
- Enhancing decision-making: Clearly defined HR objectives facilitate data-driven decision-making, ensuring that decisions support and advance organizational goals.
- Facilitating resource allocation: Strategic objectives help in the efficient allocation of resources, ensuring that time, budget, and talent are applied effectively to achieve long-term goals.
- Improving talent management: Strategic HR goals help attract, develop, and retain top talent, which is essential for the organization’s long-term success and competitiveness.
- Boosting employee engagement: Clear HR objectives focused on employee engagement lead to a more motivated and productive workforce, directly impacting organizational performance.
- Ensuring compliance and risk management: Setting strategic HR goals related to compliance ensures that the organization adheres to legal and regulatory requirements and minimizes risks.
- Supporting organizational change: HR strategic goals facilitate effective change management by preparing and equipping the workforce to adapt to new business strategies and market conditions.
- Promoting a positive organizational culture: Strategic HR goals focused on culture help build a positive work environment that aligns with the company’s values and mission, enhancing overall employee satisfaction and retention.
- Improving performance management: Strategic HR goals help establish robust performance management systems that align individual performance with organizational objectives, driving overall business success.
- Encouraging continuous improvement: Setting and reviewing HR strategic goals promotes a culture of constant improvement within the HR function, ensuring that HR practices remain relevant and effective in supporting organizational goals.
- Driving innovation: Strategic HR goals can encourage innovation within the HR function and across the organization by promoting new ideas and practices that drive business growth.
- Achieving competitive advantage: By aligning HR strategies with business objectives, organizations can build a strong employer brand and a capable workforce that provides a competitive edge in the market.
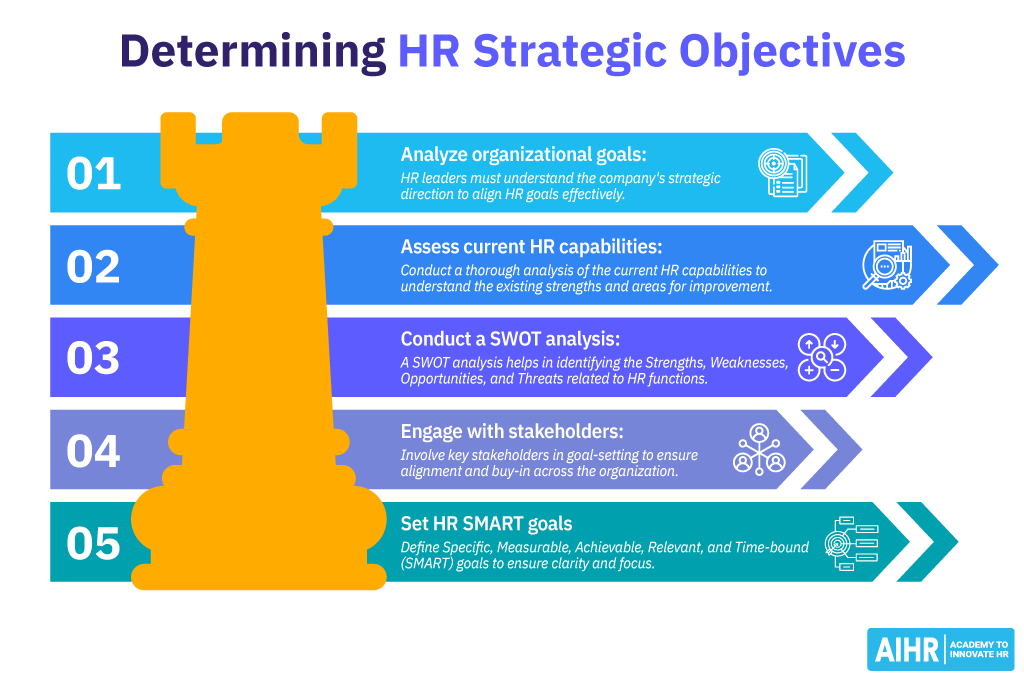
How can HR leaders determine HR goals and objectives?
1. Analyze organizational goals
Understanding the broader business objectives is the first step. HR leaders must understand the company’s strategic direction to align HR goals effectively.
Steps to analyze organizational goals
- Review strategic plans: Go through the company’s mission, vision, and strategic plans.
- Understand key initiatives: Identify key business initiatives and areas of focus.
- Identify critical success factors: Determine what factors are crucial for the company’s success.
Example
IBM’s strategic realignment toward a more agile and technology-centric structure required massive upskilling of its staff to support new technology initiatives. HR leaders at IBM needed to align their objectives with these strategic goals to ensure the workforce could support the company’s transformation.
2. Assess current HR capabilities
Conduct a thorough analysis of the current HR capabilities to understand the existing strengths and areas for improvement.
Steps to assess current HR capabilities
- Conduct a skills gap analysis: Identify the skills currently available and compare them with the skills needed.
- Evaluate HR processes: Review existing HR processes and systems for efficiency and effectiveness.
- Assess workforce demographics: Understand the current workforce composition, including diversity and inclusion metrics.
Example
Analyzing IBM’s current HR capabilities would involve identifying existing technology skills within the workforce and determining the gap between current skills and those required for future initiatives.
3. Conduct a SWOT analysis
A SWOT analysis helps in identifying the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to HR functions.
Steps to conduct a SWOT analysis
- Strengths: Identify internal HR strengths, such as strong leadership or advanced HR technology.
- Weaknesses: Recognize internal HR weaknesses, like outdated training programs or high turnover rates.
- Opportunities: Look for external opportunities, such as emerging HR trends or new recruitment channels.
- Threats: Identify external threats, such as labor market shortages or regulatory changes.
Example
For IBM, the SWOT analysis might reveal strong existing technical training programs (strength), a shortage of advanced AI skills (weakness), the opportunity to leverage online learning platforms (opportunity), and the threat of rapid technological changes outpacing workforce capabilities (threat).
4. Engage with stakeholders
Involve key stakeholders in goal-setting to ensure alignment and buy-in across the organization.
Steps to engage stakeholders
- Identify key stakeholders: Include senior leadership, department heads, and employee representatives.
- Facilitate discussions: Organize workshops or meetings to discuss HR goals and their alignment with business objectives.
- Gather feedback: Collect input and feedback from stakeholders to refine HR objectives.
Example
Engaging stakeholders at IBM would involve discussions with technology leaders, department heads, and employee groups to understand their needs and perspectives on upskilling and reskilling initiatives.
5. Set HR SMART goals
Define Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) goals to ensure clarity and focus.
Steps to set HR SMART goals
- Specific: Clearly define what the goal aims to achieve.
- Measurable: Set criteria to track progress and success.
- Achievable: Ensure the goal is feasible and attainable.
- Relevant: Align the goal with broader business objectives.
- Time-bound: Establish a clear timeline for achieving the goal.
Example
For IBM, a SMART goal could be: “Upskill 50% of the workforce in advanced AI and machine learning techniques within 18 months to support the company’s new technology initiatives.”
5 HR strategic objectives examples
Example 1: IBM’s 2024 strategy
IBM’s recent layoffs in its marketing and communications division were part of a broader strategic realignment toward a more agile and technology-centric organizational structure. IBM CEO Arvind Krishna emphasized the importance of massively upskilling employees to leverage AI effectively. This shift necessitated the upskilling of employees on AI to ensure they could support the company’s new technological initiatives.
The HR objective: Upskilling and reskilling employees
Objective: To enhance the current workforce’s skills to meet future business needs and stay competitive in a rapidly changing market.
Example 2: How Google reduced turnover
Google’s successful employee engagement strategies have resulted in a low turnover rate despite the tech industry’s high job-hopping trend. Google prioritizes psychological safety and employee needs, creating an inclusive environment where ideas are freely shared.
Career advancement is supported through internal job boards and growth courses, helping employees envision a long-term future at the company. These efforts have earned Google industry recognition, low turnover rates, and high rankings in “Best Places to Work” lists.
The HR objective: Enhancing employee engagement and retention
Objective: To develop a highly engaged workforce that is committed to the organization, reducing turnover rates and increasing productivity.
Example 3: Microsoft’s DEIB initiatives
Microsoft has implemented numerous DEIB initiatives. Over the past five years, the representation of women and various racial and ethnic minority groups at all levels of Microsoft’s workforce has increased. The company focuses on inclusive hiring practices, employee resource groups, and continuous learning on unconscious bias.
The HR Objective: Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Belonging (DEIB)
Objective: To build a diverse and inclusive workplace where all employees feel valued and have equal opportunities.
Example 4: Unilever’s HR digital transformation
Unilever has embraced digital HR tools to streamline recruitment, onboarding, and performance management processes. By leveraging AI and machine learning, Unilever has enhanced its talent acquisition and employee engagement strategies.
The HR objective: Implementing advanced HR technology
Objective: To streamline HR processes and improve efficiency through the adoption of advanced HR technologies.
Example 5: General Electric (GE) leadership programs
GE has a long history of investing in leadership development through programs like the Experienced Commercial Leadership Program (ECLP) and its management development center at Crotonville. These initiatives equip leaders with the skills to drive and manage innovation.
The HR objective: Enhancing leadership development
Objective: To develop strong leadership within the organization to ensure long-term success and stability.
To sum up
HR strategic objectives are essential for aligning HR practices with the organization’s broader goals. By setting clear, measurable goals in areas such as workforce planning, employer branding, talent management, compensation and benefits, DEIB, and employee relations, HR leaders can contribute significantly to the organization’s success.
Understanding your organization’s goals and developing HR strategies that support these goals ensures that your team plays a critical role in driving business performance and achieving long-term success.
Weekly update
Stay up-to-date with the latest news, trends, and resources in HR
Learn more
Related articles
Are you ready for the future of HR?
Learn modern and relevant HR skills, online