What Is Performance Management? The Complete Guide
Not only do organizations with effective performance management practices outperform their competitors, but they also see higher employee engagement and retention and improved corporate culture. That’s why your business shouldn’t compromise on performance management.

Effective performance management helps organizations ensure that employees understand their roles, receive constructive feedback, and have the support they need to achieve their goals and business objectives. Let’s look at what performance management is, what the performance management process looks like, and some examples.
Contents
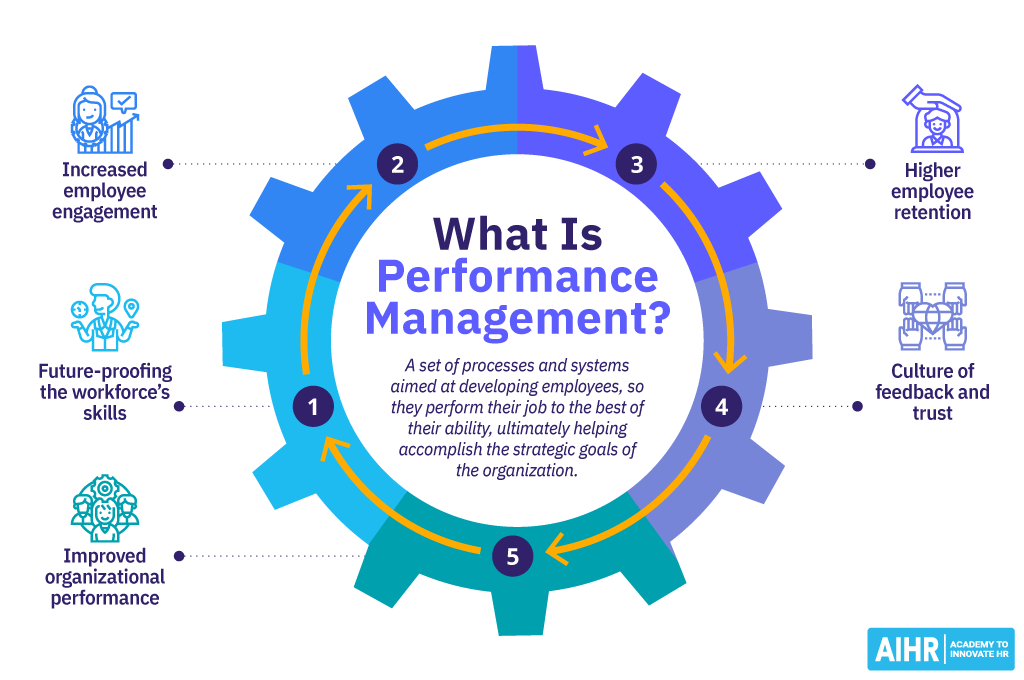
What is performance management?
Performance management goals
Why is performance management important?
What are the stages of performance management?
Performance management process: Best practices
Performance management examples
What is performance management?
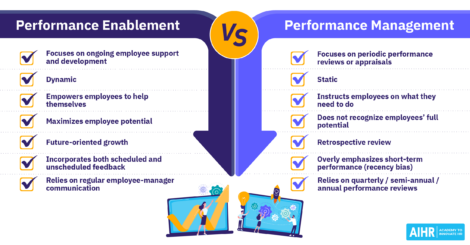
Performance management is an ongoing process in which managers and employees regularly communicate to assess and review job responsibilities, expectations, performance, and development strategies. The goal is to empower employees to perform at their best, align their efforts with the organization’s strategic objectives, and create a positive and fulfilling work environment for everyone.
An effective performance management process is strategic and systematic, establishing a continuous conversation between employees, managers, and HR to drive individual and organizational success. It combines verbal and written components, which take place throughout the year, culminating in an annual performance appraisal. The process involves the following:
- Establishing clear expectations,
- Setting individual objectives and goals that align with team and organizational goals,
- Providing ongoing feedback, and
- Evaluating results.
Career decisions, including promotions, bonuses, and dismissals, are linked to the performance management process.
Performance management goals
Performance management aims to develop the skills and competencies employees need to improve performance and success in their job. In turn, these skills help the organization meet its goals.
However, a Betterworks study reported that 21% of employees say their goals are set annually and never looked at again. A further 16% say they do not set any goals. A third of employees report that they don’t have one-to-ones with managers or receive feedback to help them work towards goals more than twice a year. 1 in 10 employees claim they rarely or never receive this type of feedback.
Performance management goals include setting performance expectations. It’s important that employees have clarity on what is expected of them and what they can gain by meeting these expectations, including compensation, rewards, or even a promotion.
Continuous, real-time feedback helps employees understand where they are, learn, self-correct, and grow. They can constantly improve their performance at work, providing them with a greater sense of accomplishment. This equips the organization with a skilled, engaged, and qualified workforce.
A Willis Tower Watson study found that companies using performance management programs effectively are 1.5x as likely to outperform their competitors financially and 1.25x as likely to see an increase in employee productivity.
Performance management improves individual and team performance which helps businesses achieve their goals and objectives. For example, if a business objective is to grow revenue, effectively managing the performance of your sales employees can help you achieve this.
Performance management also allows employees to see how their individual goals align with the company goals and understand how they contribute to achieving those, encouraging engagement.
Why is performance management important?
If the above performance management goals are achieved, there are several benefits for both your employees and the wider organization.
Future-proofing your workforce’s skills
Establishing a continuous line of communication with employees and monitoring their skills, learning, and training developments helps uncover potential skills and performance gaps in the organization. You can then work to close these, providing the business with a strong competitive advantage.
Increased employee engagement
When carried out effectively, performance management sets expectations for your employees in a transparent way.
It provides them with learning and development opportunities, a clear career path in the organization, and an understanding of their role’s impact on meeting organizational goals. Plus, continuous performance management helps employees feel valued and cared for. That makes them more open to receiving constructive feedback and working to improve.
Higher employee retention
When an employee can see their progression at work and clearly understands their career path and what they need to do to earn a promotion, it leads to more engaged employees who are likely to stay with your organization.
Culture of feedback and trust
Establishing a culture of communication, transparency, and trust begins with leadership and HR initiatives that will trickle down to the rest of the organization. That includes the nature of your performance management process and a transparent performance management policy.
When managers are open and give honest, constructive feedback to employees, this encourages employees also to be open and honest, building mutual trust. It also fosters a healthy overall company culture.
Improved organizational performance
Managing employee performance ultimately leads to significant improvements in organizational performance, including revenue growth and customer satisfaction. Helping your employees learn, develop and perform better in their roles has a positive knock-on effect on the wider business.
According to Bryan Adelson, a consultant at Red Clover HR, organizations need to understand the “why” behind their performance management strategy.
“Why are they conducting these conversations in the first place, what is their value, and what takeaways do they want from them? Understanding these questions will ultimately help structure and provide the most effective outcomes to the employee and organization,” Adelson points out.
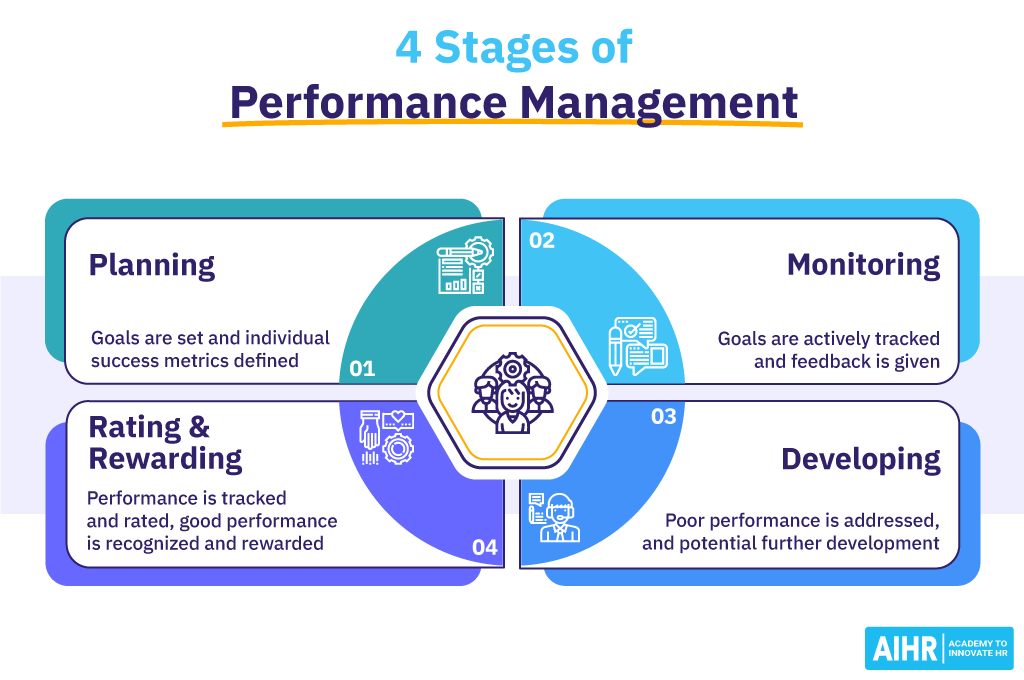
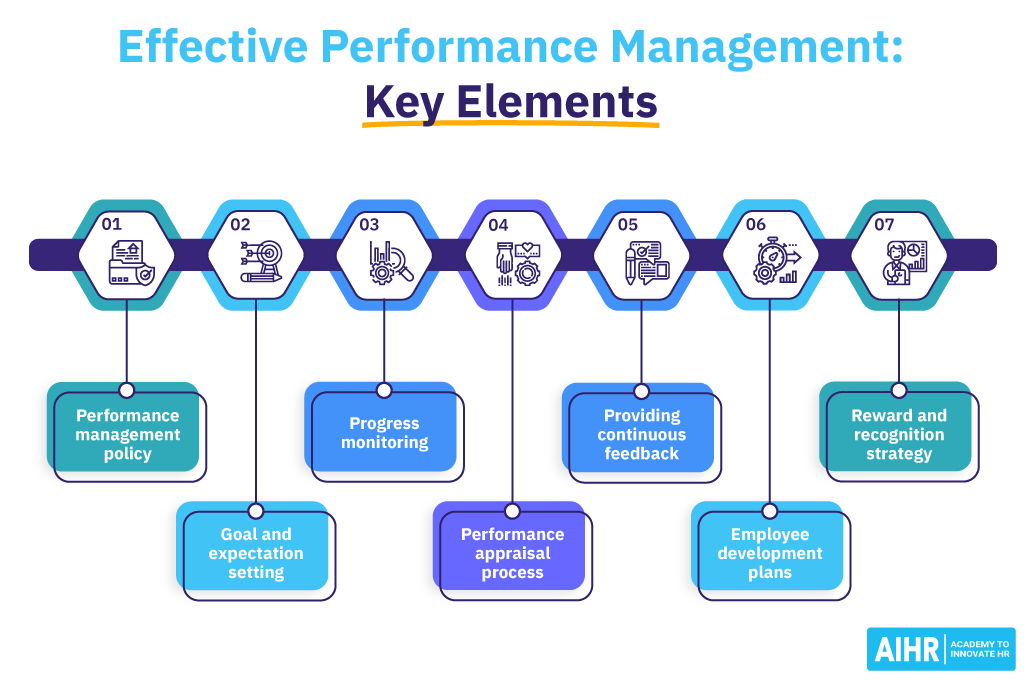
What are the stages of performance management?
A typical performance management cycle has four key stages. Let’s explore them in more detail.
1. Planning
The planning stage is dedicated to establishing performance expectations with employees. Job descriptions should clearly outline these goals to attract the right candidates. After hiring the candidate, you need to reconfirm these expectations and set SMART goals and employee performance metrics together.
Performance management plans must also be flexible so they can be adjusted as organizational objectives change along the way.
The employee should be actively involved in the planning process because this increases satisfaction and motivation to improve.
HR plays a key role in performance management. According to Jonathan Westover, OD/HR/Leadership consultant from Human Capital Innovations, HR can enable managers to effectively manage performance by providing them with the necessary tools, resources, and training.
“This includes performance management software, performance metrics, goal setting templates, and training on effective communication and feedback. HR can also support managers by conducting regular check-ins with them to ensure they are following best practices and addressing any performance issues in a timely and constructive manner,” says Westover.
2. Monitoring
The second stage is monitoring. During this stage, HR and managers must regularly monitor employee performance concerning the goals set and provide feedback to employees on their progress. Doing this regularly rather than annually allows issues to be highlighted and corrected sooner rather than later.
Performance management software can assist in tracking employee performance in real time. Still, data and reports should not be a substitute for face-to-face discussions.
3. Developing
During the developing stage, the data collected during the monitoring stage is analyzed and used to boost employee performance.
Underperformance may be corrected by suggesting refresher courses, further training, performance coaching, and other L&D methods. Managers and HR could further facilitate superior performance by assigning an extra project to help improve knowledge and performance, allowing the employee to excel further.
4. Rating & rewarding
The final stage is rating and rewarding. Employee performance needs to be rated regularly throughout the year and during a performance review or appraisal. This helps quantify employee performance, determine the value added by each employee to the organization, and make any changes as needed. Both employees and managers should give their evaluations for 360-degree feedback.
Continual sub-par performance could lead to a cross-function move or dismissal. Your organization should also recognize and reward superior performance. You can do this through praise and recognition, a raise in salary, or a promotion.
Performance management methods
Choosing the right performance management method will help you encourage continuous improvement, foster professional growth and development of your employees, and, ultimately, maximize their contribution to your organizational performance. Here are some different methods of performance management explained.
Goal setting
Setting SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) goals is a popular method of performance management because it gives employees clarity, purpose, and motivation. It also helps them understand how their work and performance help the company achieve its goals. With clear and specific goals, employees know how to prioritize day-to-day tasks and are more motivated to achieve them.
There are different SMART goals that managers can set together with employees depending on their needs and the objectives of the business:
- Performance goals: Goals that are usually aligned with specific job requirements
- Development goals: Goals that help employees develop skills and competencies that prepare them for progression to other roles in the company
- Stretch goals: Goals that challenge employees by getting them out of their comfort zone and stretching their current capabilities.
Continuous performance management
Continuous performance management is a holistic approach to performance management where managers and employees discuss the employee’s work performance and goals on a continual basis throughout the year. The managers provide constructive, real-time performance feedback to their team members, which is combined with goal-setting and check-ins.
With feedback occurring more frequently, employees and managers are able to build a stronger foundation of trust and authenticity, promoting healthier working relationships. In-the-moment feedback also helps address problems quickly before they escalate, improve communication between employees, managers, and mentors, and foster a culture of growth and development where everyone can fulfill their potential.
Management by Objectives (MBO)
Management by objectives (MBO) is a great performance management method that helps analyze the overall performance of an employee in their role. It allows managers to assess the job requirements of a role and see how they align with organizational objectives, then set realistic goals for employees to achieve.
The next step is to collect and analyze employee performance data to see how well they are meeting these goals and provide employees with feedback. This enables them to gain an understanding of what they’re doing well and where they can improve. Then, they can seek help and support in any areas of their job that they are struggling with.
This method can also help HR identify emerging skills gaps, as well as areas for further training. It can also offer a good indication of workload and whether employees are able to manage their current workload or if certain tasks need to be delegated.
360-degree feedback
360-degree feedback (also known as 360 review) is a performance management method where an employee receives feedback from their manager, peers, and self-evaluation. Not only does this provide employees with a broad overview of their performance, rather than a single view from their manager, but the act of creating this feedback for peers encourages them to constantly consider their own performance and development needs.
While team members take on a large percentage of this task, managers are involved in overseeing all reports to note and address key concerns and comments of praise. Feedback can also be used to inform employee training and development plans. This demonstrates to all employees that their feedback is being taken seriously, which is likely to boost engagement in the process.
Performance appraisals
One of the more traditional performance management systems is the performance appraisal. This will typically take place annually, bi-annually, or quarterly, and involve a one-to-one meeting between the employee and their manager. Managers will often prepare thoughtful feedback relating to all areas of the employee’s performance, identifying their strengths, weaknesses, and key areas for improvement.
Performance appraisals are a helpful tool for providing employees with a clear picture of their career path within the company, and the steps they need to take to get promoted. This can also help increase engagement, boost morale and performance, and, in time, improve retention rates.
Coaching
Coaching is a performance management process aimed at mentoring and developing an employee’s skills, knowledge, and performance primarily through one-to-one conversations. Typically focusing on specific skills or goals, coaching sessions are non-directive. That means that employees are not given specific solutions but encouraged to find solutions for themselves, which fosters autonomy and initiative.
Coaching is a skilled activity which means that managers must have the required training to be able to effectively coach employees.
It’s important to note that most organizations will use a combination of several of these performance management methods to manage employee performance.
Performance management process: Best practices
Evaluate what currently is and isn’t working
Before you make any changes to your current performance management process or tools, you must understand what is currently working, what’s not, and why. HR should survey both employees and managers and collect opinions on the current process and suggestions on what could be done better.
You can then convey these internal findings, coupled with studies and evidence-based research, to business leaders and decision-makers who can sponsor and drive change in the business. Show them the impact of an improved performance management process on business results.
Choose the right approach
There are two common approaches to performance management: a behavioral approach and a results-oriented approach.
Behavioral approach: Behaviors are identified and evaluated, and employees are evaluated based on their behaviors and effort. This approach is suitable for giving detailed feedback on behaviors by mapping desirable future behaviors and when individual results are hard to measure. Examples include individual players in a team, support staff, and HR professionals.
Result-oriented approach: Employees are evaluated based on objective criteria. The focus is not on input but on output in terms of quality and quantity. This approach is suitable when there are multiple ways to do the job. The end result matters rather than how it has been achieved. Examples include contact center employees who have specific success metrics, as well as sales professionals. The evaluation of lawyers and accountants is also highly result-oriented, as they keep track of their billable hours.
Consider what the role is when choosing the approach to ensure the effectiveness of your performance management process.
It’s also important to reevaluate the process with changes in your work model, for example, remote or hybrid working methods. A Willis Tower Watson study reported that only about one in six employers (16%) had altered their performance management process to align with remote and hybrid work models.
Meet & train managers
Managers are integral to the success of your performance management program. They play a vital role in engaging, motivating, and developing employees. Therefore, it’s essential that HR has a clear plan in place for training managers to give and receive constructive feedback.
Managers should also get coaching on how to maintain a continual, open feedback dialogue with their staff.
Help set SMART goals
Managers and employees should set SMART goals for employee performance, and involve HR when setting goals for employee development.
Every employee should have their own clear, personalized set of key performance indicators (KPIs) so that they understand their manager’s expectations and so that their manager can keep track of their scores and achievements. Personalization is important based on the job and function and the employee’s personal and professional ambitions.
With these goals, you can effectively measure performance and spot opportunities for improvement. Shaun Wilde, CEO and HR Director at the learning platform Think Learning, highlights the importance of monitoring progress.
“Investing in a talent management system can allow managers and employees to continuously monitor their progress, and also make quick changes, evaluate, or put on hold what’s needed. As employees progress, their goals will likely fluctuate with them, which means you need to allow for a certain amount of fluidity,” explains Wilde.
“Having regular developmental conversations and effectively tracking the goals means targets stay up to date, and there’s no doubt around what needs to be achieved to progress.”
Apply continuous performance management
The Willis Tower Watson study also found that while most (93%) organizations cited driving organization performance as a key objective for performance management, fewer than half (44%) claimed their performance management program met that objective.
One of the primary reasons for this is relying on an annual performance appraisal or review and failing to follow up on this regularly throughout the year or conduct one-to-one check-in meetings where constructive feedback and coaching are provided.
HR can educate managers on providing employees with this type of ongoing constructive feedback. This drives motivation, catches issues early on, and helps you manage underperforming employees correctly and offer them tools to improve.
“Performance management should be an ongoing dialogue that happens throughout the year, not just during an annual review. This approach allows for timely feedback, effective goal-setting, and more accurate assessments of employee performance,” notes Tara Furiani, “Not the HR Lady” keynote speaker and consultant.
Innovative organizations are turning to agile performance management, which focuses on continuous learning, frequent check-ins, and building trust and a sense of connection to the team.
Set up a formal system
Continual performance management boosts employee engagement, motivation, and performance. However, a formal performance review or appraisal system where top-performing employees can get a raise, a bonus, or a promotion for meeting certain goals and objectives is just as important. This communicates to all your staff that great work will be recognized and rewarded.
Help workers create employee development plans
When employees have a solid plan for their career progression with the organization, it empowers them at work and helps them take charge of their professional development while reducing turnover rates.
Human Resources professionals can work closely with managers to understand their employees’ needs, schedule meetings to discuss their career development, and help provide employees with required training.
Employee development plans are notoriously hard to implement simply because managers and employees are too busy. This is where HR can help by creating plan templates for managers which they can use to create development plans with their team members.
Employ technology
Leveraging HR technology and software helps improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the performance management process. Performance management data can offer detailed insights and patterns that manual tracking and surveys cannot compete with.
The right technology can also save a manager’s time, but only if a clear performance management strategy is in place. They also need to be able to view real-time data at any time to determine the right goals for success.
However, it’s important to be mindful that performance management is a people-centered process. Technology cannot (and shouldn’t) replace the need for direct communication and difficult conversations with managers. Managers need to take and remain in ownership of this. But the right data in a dedicated performance management system can eliminate implicit bias, affirm to employees that they are being objectively assessed, and facilitate honest discussions.
Performance management examples
HSBC
HSBC now has an HR mobile app where employees and managers can easily capture achievements and share feedback.
Employees can access an HR-to-do list, their performance and development plans, online learning resources, and manage their personal employment information. Managers can handle approvals on the go, set goals, and regular check-ins to maintain productivity and facilitate continual growth.
The app lends itself well to flexible and remote working models without compromising results. It has created a stronger relationship between managers and employees, where employees feel more supported, and end-of-year appraisals feel more meaningful.
Deloitte
Deloitte rolled out a pilot performance management program that encouraged team managers to have frequent check-ins with team members about their performance, priorities, and strengths. Surveys completed by employees helped team leaders understand the process from their perspective and make improvements.
Custom career development plans were created for all employees. What’s more, everyone was provided with a career coach to help them develop.
Data has been beneficial, particularly in helping underperforming employees see where they sit in relation to their colleagues, listen to constructive feedback, and take action. It has also helped Deloitte understand people, team, and leadership trends they haven’t been able to see before this. One example is the connection between feedback conversation frequency and employee performance.
IKEA
IKEA set out to drive business performance by strengthening management and leadership skills.
An accredited “train-the-trainer performance management coaching program” was created for them and rolled out to 750 managers and supervisors across the UK. This included an interactive seminar, developing coaching skills (aligned with the International Coaching Federation), certification, and the identification of internal coaching champions.
Departments with managers who attended performance management coaching training saw a 5% KPI increase and went from 60% scores in management ability to 90% scores across the board.
A final word
Performance management is a crucial aspect of any organization’s success. By focusing on goal- and expectation-setting and creating a continuous performance management process, you’re empowering your employees to develop and improve every day and ultimately setting your organization up for success.
FAQ
Performance management aims to enhance an employee’s job performance through a range of processes like goal setting, progress monitoring, skills development, and rewards.
Performance management contributes to individual and team performance, which helps businesses achieve their goals and objectives. By effectively managing employee performance, organizations can build an engaged, skilled, and future-ready workforce, leading to business success.
Performance appraisal is the individual session between the employee and the manager. This often happens (bi-)annually. Performance management is a periodic, systematic, and objective process of developing an employee to perform their job to the best of their ability. The performance appraisal is thus part of performance management.
The four major processes of performance management are:
Planning: Managers and employees establish performance expectations and set SMART goals together.
Monitoring: HR and managers monitor employee performance in relation to the goals set, and provide regular feedback to employees.
Developing: The data obtained during the monitoring stage is analyzed, and the results are used to improve employee performance through further training, assigning extra projects, etc.
Rating & rewarding: Finally, employee performance is rated, which helps quantify it and determine the value every employee adds to the company. Poor performance can then be addressed, while excellent performance can be recognized and rewarded.
An example of performance management is HSBC’s HR mobile app which enables employees and managers to easily capture and share feedback and achievements. It combines performance management methods of goal setting, continuous performance management, and traditional performance appraisals.
The app enables employees to manage their performance, track their development, set up regular check-ins with their manager, and access online learning resources, which cultivates a culture of continual growth and strengthens the employee-manager relationship.
Weekly update
Stay up-to-date with the latest news, trends, and resources in HR
Learn more
Related articles
Are you ready for the future of HR?
Learn modern and relevant HR skills, online