Employee Information Form and Guide for 2024 (Free Template)

An employee information form is an essential tool for all organizations. It serves the dual purpose of streamlining administrative processes and ensuring employee safety.
New employee forms capture extensive personal and job-related data and act as a snapshot of an individual’s tenure and role within the company. As part of an efficient onboarding process, creating and updating this form is a non-negotiable for every HR professional’s new hire checklist.
We have created a free-to-download employee information form in PDF (editable) and as a Word doc to help you develop and customize your HR form.
Contents
What is an employee information form?
Collecting employee information: Regulatory and legal considerations
Sample employee information form
5 HR best practices: Collecting and maintaining employee personal information
What is an employee information form?
In the US, the effective management and administration of employees requires accurate and up-to-date personnel records. At the heart of this framework is the employee information form.
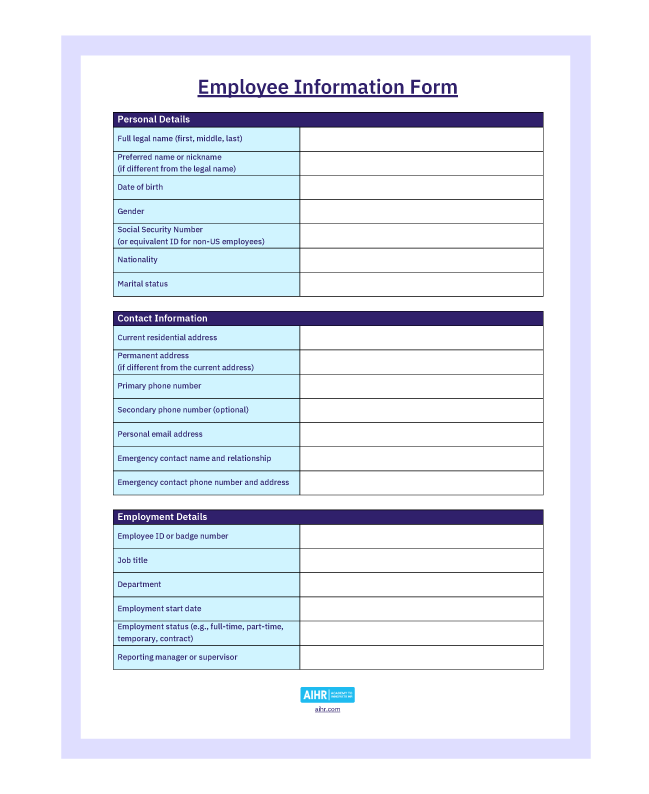
This simple document is the foundational record for each individual employee within an organization. It typically captures essential data about an employee, such as their full name, address, contact numbers, emergency contacts, social security number, and perhaps certain relevant personal details.
Not only does this form serve as a quick reference for basic employee data, but it also plays a crucial role in various organizational processes, including payroll processing, benefits administration, and maintaining contact in case of emergencies.
As an HR professional, it’s up to you to ensure:
- Employee information forms exist
- They are properly completed
- They are properly filed and easy to locate
- They are updated when required
- They are archived if an employee leaves
- All personal data captured within each form is properly protected.
It’s also important to remember that various federal regulations mandate that organizations collect and retain certain types of employee information. In addition, the collected information must be accurate.
The federal regulations include:
1. The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA)
The FLSA establishes minimum wage, overtime pay, and other employment standards affecting employees in the private sector and in federal, state, and local governments. To ensure compliance, employers must maintain accurate records of employees’ work hours, pay rates, and other related data.
While the employee information form might not record daily hours worked, it often captures the type of employment (exempt vs. non-exempt), which has implications under the FLSA.
2. Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA)
The FMLA grants eligible employees the opportunity to take up to 12 weeks of unpaid, secure job leave every year for specific family and medical-related circumstances, with continuation of group health insurance coverage.
To determine eligibility, HR must keep accurate data on the duration of an employee’s service, their work hours, and other pertinent information. While the foundational details may be recorded in the employee information form, supplementary documentation might be necessary for full FMLA compliance.
3. Other regulations
Apart from the FMLA and FLSA, other federal and state regulations mandate the collection of employee data. These can range from health and safety regulations to equal employment opportunity rights.
Collecting employee information: Regulatory and legal considerations
Your organization’s gathering and utilization of employee data should be carefully considered. The HR department plays a central role in collecting, storing, and utilizing this data, which also entails numerous regulatory and legal considerations.
Compliance is crucial not only for meeting requirements but also for safeguarding your organization’s reputation and prioritizing the trust and privacy of your workforce.
1. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
Legislations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU have set stringent standards for managing personal data, especially for businesses that span international borders.
The GDPR mandates that personal data (which includes almost all of the information that HR collects) be processed transparently, securely, and with the clear consent of the data subject (the person whom the information is about).
Key principles include:
- data minimization (collecting only what is necessary)
- ensuring accuracy
- limiting the storage duration.
Violations aren’t costly in monetary terms, and while no specific legislation like the GDPR exists in the US, it is seen as best practice.
If any data is stored in private or public cloud data centers in Europe, the GDPR would automatically apply. From a strictly reputational perspective, employees expect their personal data to be handled carefully as well.
2. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
Among the various legislations that HR in the US must be aware of, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is important. HIPAA is primarily triggered by certain medical data that forms a portion of employee information.
HIPAA mandates that any personal health data collected by employers, whether for insurance purposes, employee wellness programs, or medical leaves, must be stored and managed with the utmost care. Unauthorized disclosures can lead to severe penalties, both financial and legal. For HR departments, ensuring HIPAA compliance means rigorous data protection measures, employee training, and regular audits.
Beyond the specific mandates of GDPR and HIPAA, there is a broader crucial theme: the importance of data privacy and security.
Both these regulations underscore the need for:
- Secure storage: With the rise of cyber threats, securely storing sensitive employee information is not optional. This means employing encrypted databases, robust firewalls, and regular vulnerability assessments to ensure data remains uncompromised.
- Proper management: Secure storage is just one piece of the puzzle. Proper management includes regular data audits, ensuring data accuracy, and timely deletion of obsolete data. It also involves establishing clear protocols for data access, ensuring only authorized personnel can retrieve sensitive information.
- Employee awareness: HR must ensure that every individual involved in collecting, processing, or managing employee data is aware of these regulations and trained accordingly. A well-informed team is the first line of defense against inadvertent breaches.
Sample employee information form
To download the free employee information form as a Word document, click the button below:
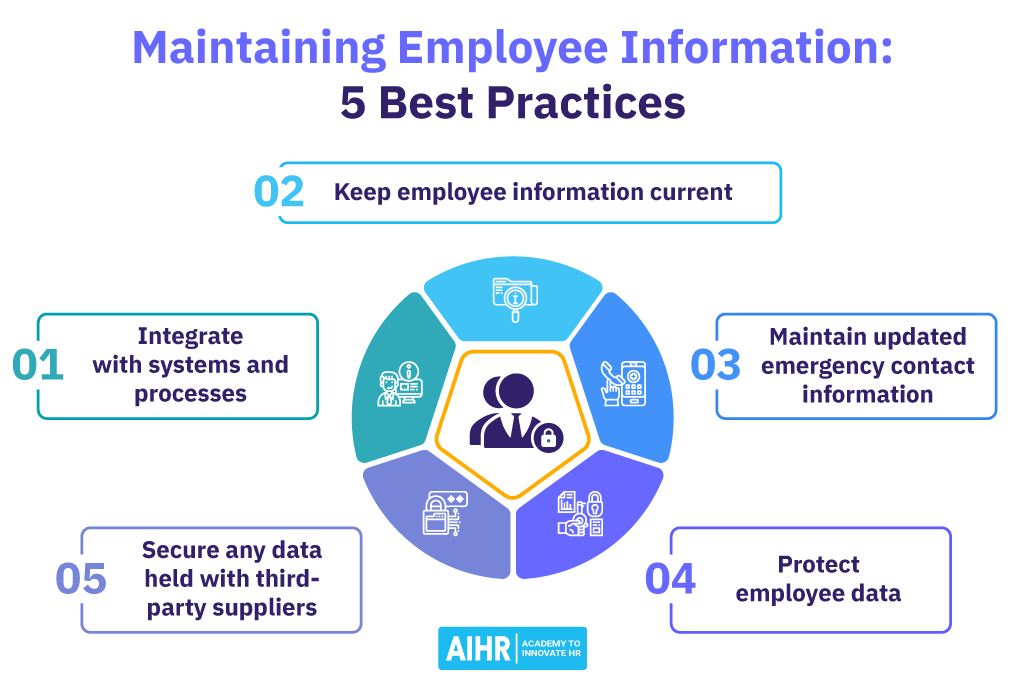
5 HR best practices: Collecting and maintaining employee personal information
Managing employees’ personal information is a critical responsibility for HR departments, particularly in a world where data privacy concerns are paramount. HR professionals must design and adopt a series of best practices to navigate this landscape effectively.
Let’s take a look at the most critical elements of HR best practices when it comes to collecting and using personal employee information.
1. Integrate with systems and processes
From collecting candidate information to employee onboarding – once an employee has been hired, the collection of personal information should be a seamless part of the entire recruitment and onboarding process.
Newly inducted employees should be introduced to standardized forms or digital portals where they can input their details, ensuring that HR captures all necessary information from day one. To streamline and secure the entire process, it may be worth considering an investment in HR information systems (HRIS) or employee self-service portals, which facilitate easy input, updates, and retrieval of data.
2. Keep employee information current
It’s important to conduct regular reviews of the stored data. This ensures that information remains relevant, especially in dynamic areas like contact numbers or addresses. It also means that you can better control the duplication of data or storing data for too long.
There are many complexities around the collection, storage, and usage of personal information, and regular reviews are a good way to keep a handle on the state of the data your organization is holding.
As an HR professional, regularly encourage employees to report any changes in their personal details through reminders or notifications via email or company communication platforms. If you are using digital systems, you could also implement features that prompt employees to annually or bi-annually review and update their details.
3. Maintain updated emergency contact information
Emergency contact details should be mandatory on all employee information forms. Stress the importance of this data for the safety and wellbeing of employees. It’s always a good idea to allow space for more than one emergency contact, ensuring that your department has alternative points of communication if the primary contact is unreachable.
The best practice is to capture the relationship of the emergency contact to the employee, which can also be crucial in emergencies.
4. Protect employee data
As mentioned above, protecting employee data is of paramount importance. Below are some tips on how to ensure employee data is adequately protected,
Some of the points below will be the responsibility of HR, while others will need to be accomplished by working with other departments, such as IT.
- Data encryption. All digital records containing personal information should be encrypted, making them unreadable to unauthorized individuals.
- Limited access. Restrict access to employee data. Only designated HR personnel and relevant management should be able to view or modify this information.
- Physical security. If storing hard copies, use secure file cabinets in access-controlled rooms.
- Regular backups. Ensure that digital data is backed up regularly, protecting against data loss due to technical glitches or cyber incidents.
- Training. Regularly train HR personnel on data protection principles, ensuring they are aware of the latest best practices and regulatory requirements.
- Data retention policy. Establish clear guidelines about how long employee data will be retained, especially after employees leave the organization. After the stipulated period, ensure the data is securely disposed of or deleted.
- Transparency with employees. Keep an open channel of communication regarding how their data is stored, processed, and protected. This builds trust and ensures compliance with global data protection regulations like GDPR.
It is also important for employees to understand the data held, its purpose, and their rights. Conduct regular workshops or training sessions to educate employees on data importance, protection measures, and recognizing phishing attempts. Develop a system for voicing concerns or reporting vulnerabilities to enhance trust and collective vigilance.
5. Secure any data held with third-party suppliers
Often, HR departments collaborate with third-party vendors to access services like payroll management, benefits administration, or HRIS solutions. It’s crucial to rigorously vet these vendors for their data protection protocols.
Establish clear contractual clauses that mandate adherence to your organization’s data protection standards and then regularly review and audit third-party practices, ensuring they meet your predefined standards. This can be facilitated through periodic reports, security audits, or direct communication to gauge any potential vulnerabilities or breaches.
Leveraging the employee information form
New employee information forms can be a checkbox or a critical tool to ensure you have all key personal information on hand for every employee in your organization. The key is to ensure that the data you collect remains safe.
As regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA continue to shape the landscape, as an HR professional, you will increasingly be entrusted with compliance and fostering a culture of data privacy within your organization.
The blueprint for achieving this lies in robust systems and processes, continuous updates, clear communication, and a firm commitment to data protection. Whether through the design of employee information sheets or rigorous vetting of third-party vendors, every step you take should reflect your department’s dedication to upholding the highest data privacy standards.
FAQs
An employee information form is a comprehensive document used by organizations to gather and record essential details about their workforce. This form is a centralized repository of personal and professional data, ranging from basic contact information to more intricate details like tax codes, benefits, and emergency contacts. Its primary function is to streamline HR processes, ensure timely communication, and facilitate informed decision-making regarding workforce management.
Every new hire within an organization should complete an employee information form as a foundational step in their onboarding process. The responsibility of filling out this form lies with the employee, ensuring that the data provided is accurate and up-to-date. However, HR departments or managers may assist in clarifying any ambiguities or questions that arise during the completion of this important document.
An employee information sheet should contain key personal and professional details. This includes the individual’s full name, contact information, date of birth, Social Security or Tax Identification number, emergency contacts, employment details such as position and date of hire, compensation, tax information, and potentially relevant medical information. It’s also important to include spaces for any changes or updates and a section for the employee’s declaration and consent regarding data storage and processing.
The employee information form should be reviewed and updated annually, at a minimum. However, employees should be encouraged to promptly notify HR and update the form whenever there’s a significant change in their personal or professional details, such as a change in address, marital status, or emergency contact. Regular updates ensure that the organization maintains current and accurate records, facilitating smooth administrative processes and effective communication.
Weekly update
Stay up-to-date with the latest news, trends, and resources in HR
Learn more
Related articles
Are you ready for the future of HR?
Learn modern and relevant HR skills, online