How to Create an Effective Compensation Philosophy

A compensation philosophy guides your organization in creating fair, transparent compensation programs and helps you attract and retain employees. Learn about the different types of compensation philosophies, components of a compensation philosophy, how to create your own, and how to measure its effectiveness.
Contents
What is a compensation philosophy?
Why does your organization need a compensation philosophy?
What are the different types of compensation philosophies?
Components of a compensation philosophy
How to create a compensation philosophy
What is a compensation philosophy?
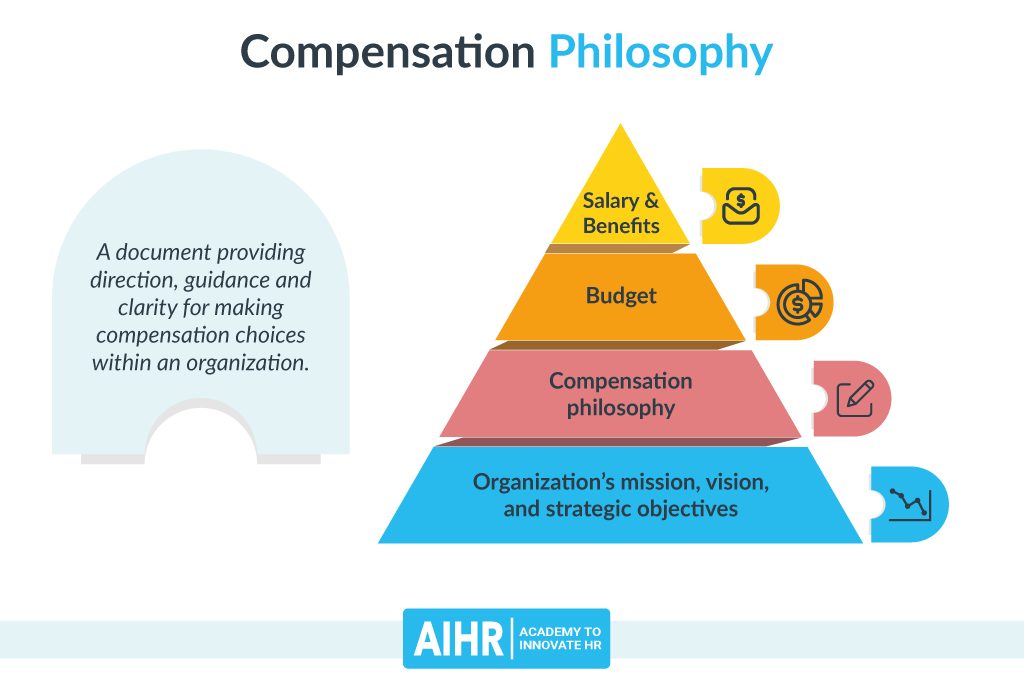
A compensation philosophy, or pay philosophy, is a document providing direction, guidance, and clarity for making compensation choices within an organization. In other words, it is the foundation of your approach to employee compensation based on your organization’s vision, mission, values, and strategic objectives.
The culture of the organization, size of the organization, and its resources influence the compensation philosophy. Board of directors, executive leadership, Human Resources, and Compensation & Benefits subject matter experts (the Comp Team) are usually involved in developing the compensation philosophy and designing the compensation structure.
A documented compensation philosophy is typically one to several pages long.
Why does your organization need a compensation philosophy?
A compensation philosophy guides designing compensation structures, managing compensation & benefits programs, determining compensation packages for new hires, and providing guidance on how to incentivize and retain your most valuable employees. The benefits of a compensation philosophy are, therefore:
- Attracting talent – It allows you to present yourself as an attractive employer and differentiate your organization from the competition. As the war for talent continues, compensation is one slice of the pie that attracts new skilled employees to organizations.
- Retaining employees – A fair and transparent pay philosophy helps you promote employee satisfaction, motivate employees to produce quality products or provide exceptional service, and incentivizes employees to stay and advance within the organization.
- Pay equity – It ensures equal pay for equal work and compliance with the law. The Lilly Ledbetter Fair Pay Act of 2009 is a law enacted by Congress that strengthened worker protections against discrimination in pay.
- A positive employee experience – A transparent compensation philosophy demonstrates an organization’s commitment to equity, inclusion, and fairly rewarding its employees.
What are the different types of compensation philosophies?
There are four main types of compensation philosophies:
Market pay
Market pay philosophy is based on factors within the organization’s industry, where they want to be competitively positioned (pay percentile) within the market and is also influenced by the specific geographic locations within which the employee may be working.
Jobs are broken down into different components and then graded to determine their value. Some of the elements which determine value are:
- The complexity of the job
- The qualifications needed to function effectively in the job
- The inherent risk that may come with the job
- Scarcity of talent to perform the job.
Compensation within a market pay is therefore based on merit and is constructed to be a fair, objective, and competitive approach to pay. However, if you are a small or family-owned business, a market pay philosophy may be challenging as you may have limited resources to provide competitive pay.
Equal pay
This philosophy means that everyone receives the same pay regardless of the complexity of the job or geographic location. It is more common in family-owned businesses. The benefit of this philosophy is that it potentially eliminates the pressure to be competitive in the market, and there is no internal competition.
However, the obvious challenge that comes with this is employee and job dissatisfaction. Since not all jobs are created equal – there are more complex or demanding roles even in a family business. However, when there is no compensation differentiation that recognizes that, employees may become dissatisfied, may leave, and the quality of service provided may suffer.
Flexible pay
This philosophy allows the board of directors and leadership to utilize market pay (objective) with organizational cultural measures (subjective) to compensate employees. The benefit of this is the ability to customize compensation to unique scenarios and needs. Unfortunately, a flexible pay philosophy can also lead to perceptions of bias, inequity, unfairness, and even discrimination.
Tailored pay
In this case, compensation is determined by market conditions, the performance of the employees, and the organization’s performance. This type of compensation philosophy motivates employees to achieve specific goals or teams to hit pre-determined targets that can potentially improve their earning capacity.
This may take the form of merit increases, promotions, or bonus payments. In turn, the organization remains competitive within the market and can continue to competitively compensate its employees.
Components of a compensation philosophy
According to James Reda, an expert in executive compensation, a compensation philosophy consists of the following five components:
1. Compensation program objectives
These are the guiding principles of the compensation philosophy. For example, “Our executive compensation program is designed with the flexibility to be competitive and motivational within the various marketplaces in which we compete for executive talent, while being subject to centralized design, approval, and control.”
2. Internal vs. external pay equity
The compensation team must determine what type of philosophy suits their culture. Internal equity is essential from a compliance perspective, but also to achieve inclusion, belonging, and strong engagement. External equity is also critical to remain competitive in the industry and to attract and retain employees. Finding the right balance can be challenging, so many organizations participate in and/or purchase compensation benchmark surveys for their specific industry.
3. Peer group comparisons
Organizations can use broad-based peer group comparisons as one of the factors when deciding the base salary, annual bonus, and benefits. James Reda recommends a compensation peer group to consist of at least 15 companies.
4. Pay positioning strategy
Many organizations set their pay positioning strategy at the beginning of each year. It typically consists of the following:
- “Percentile ranking of components of pay vs. market: For salary, bonus, long-term incentives, pension, health and wellness benefits, perquisites, and severance practices, a compensation philosophy should specify how each element of compensation is set. Most companies target the median (50th percentile) for setting total compensation, with variations for each element.
- Pay mix: This consists of salary, short-term incentive (“STI”) compensation and long-term incentive (“LTI”) compensation.
- Pay for performance curve: This consists of threshold, target, and maximum payout. The threshold varies by relative or absolute, the target pays out at 100%, and the maximum is for 75th percentile performance.”
5. Performance alignment with business plan
There are several factors that lead to the success of a business plan. One of those factors is alignment of compensation programs to strategic business objectives and goals. A misaligned compensation program can foster demotivated employees who are expected to produce a lot with little reward. Or employees can be overpaid in an economy or market that cannot sustain high wages. Therefore, after the pandemic hit in 2020, some organizations reduced wages, discontinued variable pay, and laid off staff.
How to create a compensation philosophy
1. Lay the foundation
Where do you begin when creating your compensation philosophy?
- Review the organization’s strategic objectives – Any decision made, and especially those around compensation, should reflect the organization’s vision and mission and support its strategic objectives.
- Assess the financial resources – A realistic and professional assessment of your resources is key to providing compensation packages that lead to productive employees, motivated staff, and strong profit margins. Leadership should consider their assets, equity, and liabilities before deciding and designing the organization’s compensation philosophy.
- Consider the strengths and opportunities – An analysis of the organization’s internal strengths (products, services, unique skills) and external opportunities (consumer demand, niche market presence, strong investors) assists organizations in envisioning the philosophy that is best for them.
- Strategize against weaknesses and threats – There are weaknesses in all organizations. It is important to acknowledge this and also identify what those weaknesses are. Weaknesses can be outdated technology, low employee engagement, or an uptick in employee grievances that need to be investigated. There are also threats external to the organization in the form of new competitors entering the market, waning customer interest, a pandemic, or a sluggish economy. A strategy to mitigate the negative impact of weaknesses and threats is critical to building a successful pay philosophy.
- You don’t have to start from scratch – Review everything you already have on compensation and see how you can repurpose it when building your compensation policy.
Once the comp team assesses and analyzes these factors, they can determine how the organization can allocate its resources to compensate its employees. They can start taking the necessary steps to create an effective compensation philosophy to achieve the organizational strategic objectives.
2. Tailor your compensation philosophy to your business goals, industry, and market
Your compensation philosophy will be unique to your company’s needs and objectives. Understand who you are competing with by making a peer group comparison and reviewing industry and market benchmarks.
An interesting example of a pay philosophy is Gravity Payments. The CEO gave his employees a minimum wage of $70,000, which he considered the living wage. Many businesspeople advised him against it and expected him and his business to fail. However, quite the opposite has reportedly happened; revenue tripled, his employees became more engaged and were able to purchase homes.
3. Structure your compensation philosophy document well
There are several elements you should include in your compensation philosophy document. Some of them are:
- A statement that sums up the philosophy
- Commitment to pay equity
- Pay position strategy
- Focus on base pay
- Variable pay options if applicable
- Salary structure for the whole organization
When structuring your document, you can get inspiration from publicly available compensation philosophy documents. Universities such as DePaul University or The University of Iowa feature their compensation philosophies on their websites. A non-profit organization Community Action Partnership of Ramsey and Washington Counties has their compensation philosophy one-pager accessible to the public too.
4. Consider compliance
Make sure that your philosophy document content is compliant with local laws and regulations. In the US, these would be, for instance, FLSA, Equal Pay Act, etc., but it will differ per country/region.
5. Be consistent
Your compensation philosophy document will be guiding a variety of decisions – when hiring, promoting, and generally rewarding people. Make sure you apply your philosophy consistently across the employee life cycle. That will help you promote transparency regarding compensation decisions within your organization.
6. Communicate your compensation philosophy
Communicating your compensation philosophy internally provides your employees with an insight into how and why you make compensation decisions the way you do. It also helps you manage employee expectations regarding salary raises, bonuses, and everything compensation-related.
As we’ve already mentioned, some organizations choose to make their compensation philosophy document accessible to the public, too. You can create a condensed, less detailed version of your philosophy to publish on your website as part of your employer branding strategy. That way, your (potential) job candidates can learn more about your approach to compensation.
Buffer shares the guiding principles of their compensation philosophy on their website:
- “Transparency: We openly share our approach and all salaries to create trust, hold ourselves accountable, and serve as a resource for the industry.
- Simplicity: We aim to maintain an easy-to-understand formula that allows anyone to easily see how we arrive at any individual salary.
- Fairness: We ensure that those with the same role and responsibilities who are at the same experience level are paid equitably.
- Generosity: We pay above market to attract the team we need, thrive as individuals, and avoid exceptions and inequity resulting from negotiation.”
7. Check if your compensation philosophy is effective
According to the Society for Human Resources Management, “an effective compensation philosophy should pass the following quality tests:
- Is the overall program equitable?
- Is the overall program defensible and perceived by employees as fair?
- Is the overall program fiscally sensitive?
- Are the programs included in the compensation philosophy and policy legally compliant?
- Can the organization effectively communicate the philosophy, policy and overall programs to employees at all levels?
- Are the programs the organization offers fair, competitive and in line with the compensation philosophy and policies?”
Ask yourself these questions when drafting your document.
8. Let your compensation philosophy evolve
Your compensation philosophy is not set in stone. It is natural that as your organization develops, economies change, and technology advances, so will the way you compensate your employees. Make sure to communicate changes to your employees and candidates to maintain transparency.
A final word
Having a compensation philosophy promotes transparency and equity in rewarding your employees. Take into account that rather than a full compensation program, compensation philosophy should be about your compensation objectives and guiding principles for approaching compensation. It should always be compliant and aim to be equitable.
Weekly update
Stay up-to-date with the latest news, trends, and resources in HR
Learn more
Related articles
Are you ready for the future of HR?
Learn modern and relevant HR skills, online