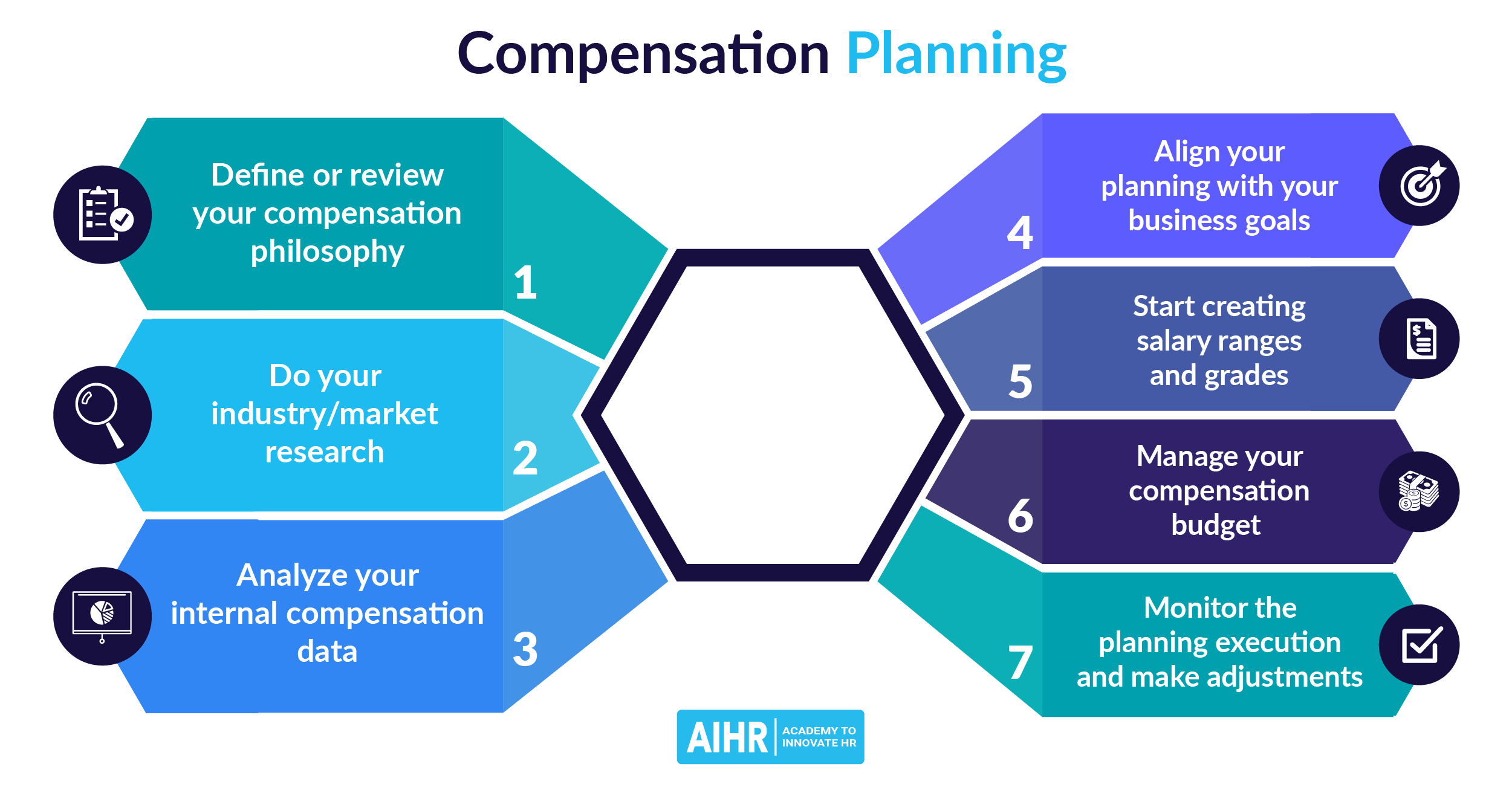
Merit Increase
What is a merit increase?
A merit increase is any salary increase awarded to an employee to reward exceptional performance and contributions toward achieving organizational goals. Some organizations give a merit increase on an annual basis, whereas others give a merit increase in direct response to great performance.
Eligibility to receive a merit salary increase is based on an organization’s internal policy, budget, and other criteria, such as the merit metrics system and the employee’s value in the job market.
Merit increase example
Kendra, an employee who successfully spearheaded a key marketing campaign resulting in a 20% increase in customer engagement, was awarded a 5% merit increase in her annual salary as recognition for her outstanding contribution to the company’s growth and success.
Merit increase vs raise
Merit increase is directly related to an employee’s performance in relation to achieving their goals. It is used to motivate and reward employees for doing great work. A pay raise is an increase in the salary of an employee based on tenure, inflation, or to keep up with the cost of living.
Merit increase vs promotion
A merit increase is not related to the promotion. It depends on the performance and not on being promoted to a new role.
Merit increase vs bonus
A bonus and a merit salary increase both represent an increase in an employee’s total compensation. The difference between them is that a bonus is a one-time payment, while a merit pay increase is a permanent change in compensation.
What is a merit increase based on?
A merit increase is based on an employee’s individual performance and achievements, evaluated against predefined criteria and goals, reflecting their contribution to the organization’s success.
This assessment typically involves a review of the employee’s accomplishments, work quality, and overall impact on team and organizational objectives. This helps ensure that the increase aligns with merit and value brought to the company.
What is the average merit increase?
Merit increases vary per country, industry, and department. An average merit increase is around 3% and can go up to over 5%.
3% may not look like a big increase, but over a long period of time, the amount compounds. For example, if someone earns $60,000 in their first year and gets a 3% merit increase annually over five years, that would amount to an annual salary of over $69,500 in the fifth year. Of course, that is not accounting for other types of pay raises.
Why do organizations give merit increases?
Businesses utilize merit increases as a strategic tool to motivate, retain, and align employee efforts with business objectives, recognizing and rewarding outstanding performance and contributions to the company’s success. Let’s break this down.
- Motivation: Organizations give merit increases to motivate employees to achieve their goals and to go the extra mile. In turn, this creates a high-performance culture and helps the organization meet its objectives.
- Retention: Merit increases build loyalty as it rewards employees for their performance. Employees will stay with an organization longer if they feel valued.
- Alignment to the business objectives: Merit increases connect employees’ efforts with the financial success of the business. As a result, it aligns employees’ goals and output with the objectives of the organization.
How to calculate merit increase
Organizations should develop a merit matrix based on merit increase budget, employees’ ranking, and employees’ compa ratio within the salary range. Below is an example:
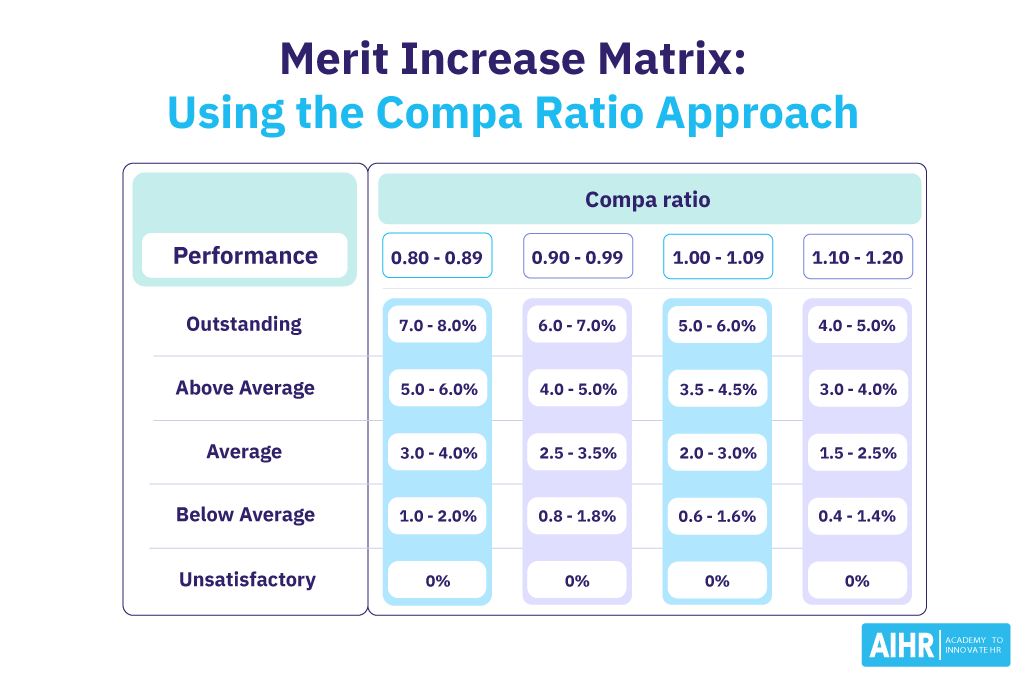
This means that an employee whose salary is at 0.9-0.99 compa ratio and whose performance is classified as above average would receive a merit increase of 4-5%.
How to effectively manage merit increases
HR and the management team need to create a fair framework that determines when and how employees should get a merit increase.
- Have a compensation philosophy in place: That will be your starting point for implementing your merit increase process.
- Develop salary ranges and determine range spread. The typical range spread is between 30 and 40 percent.
- Determine the merit increase budget. Typical compensation budgets for merit increases are around 3.5%. Factors in deciding the budget include:
- Market position and competitiveness
- Ability to pay and cost containment
- Cost of living inflation
- Company performance
- Individual employee performance
- Communicate the merit increase approach: It is important that all employees understand the criteria for a merit increase. All employees should have a clear understanding of how their performance is evaluated and awarded.
- The process should be transparent and clearly communicated to employees.
- Establish a culture of recognition: Merit increase should promote a culture of recognition, and the evaluation should be done throughout the year to drive a culture of excellence.
How to manage a merit budget
Let’s say you have a 3% normal annual merit budget.
- Explain the merit budget as a value limit to managers.
- The matrix should be a guide and not a rigid formula. There needs to be a clear link between merit and performance.
- Allow flexibility for managers, but they must stay within the 3% value limit.
- Some typical questions to ask may be:
- Was the employee recruited within the past 12 months?
- Was the employee promoted within the past 12 months?
FAQ
A merit increase is a type of raise specifically awarded for exceptional performance, distinguishing it from general raises which might be given for tenure, cost of living adjustments, or market rate alignment.
A good merit increase effectively balances the organization’s budgetary constraints with a meaningful reward for the employee, typically ranging between 3% to 5% of their salary.
Yes, a merit increase is a permanent adjustment to an employee’s salary, reflecting ongoing recognition of their exceptional performance.