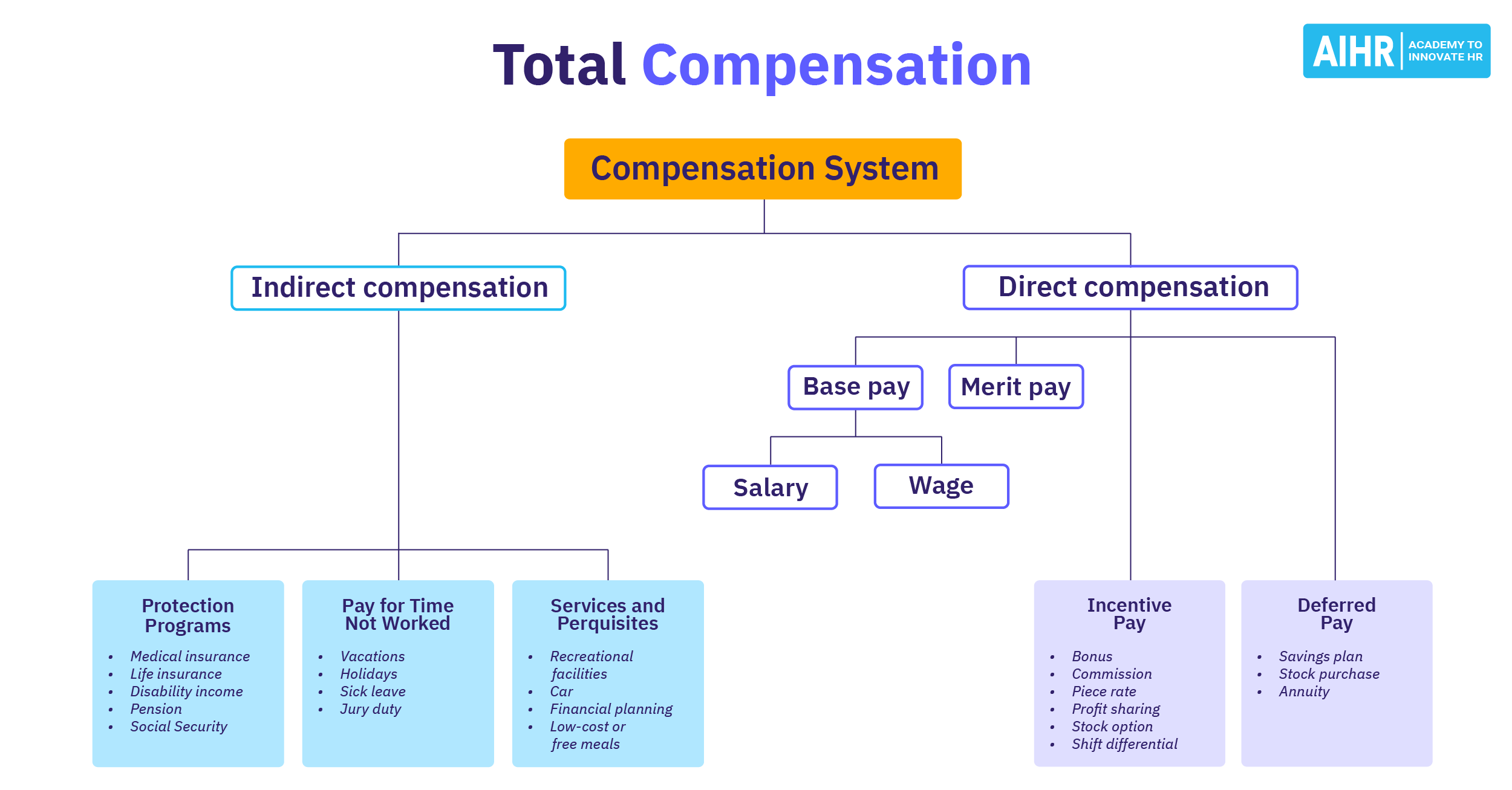
Variable Pay
What is variable pay?
Variable pay is compensation that is awarded to an employee that has gone above and beyond their regular job requirements to contribute to the organization’s success. The purpose of variable pay is to motivate behavior change. Variable pay is determined both by an employee’s performance and the organization’s performance and is typically awarded on top of the employee’s fixed pay.
Types of fixed pay vs variable pay
| Fixed pay | Variable pay |
| Basic salary | Annual/short-term incentives |
| Overtime pay | Sales bonus or commissions |
| Allowances | Profit sharing |
| Shift differentials | Gainsharing |
| 13th month (fixed) | Long-term incentives |
| Other bonuses |
What are examples of variable pay?
Performance bonus
A performance bonus is an after-the-fact discretionary reward or payment based on the performance of an individual, a group of employees operating as a unit, a division or business unit, or an entire workforce.
Sales commissions
A sales commission is a pre-determined, direct cash payment made as incentive pay for the sale of a product or service, usually calculated as a percentage of the gross sale amount or flat amount for each unit sold. A commission-only remuneration program is sometimes known as full commission or straight commission.
Profit-sharing plan
A profit-sharing plan provides employees with a share in the profits of a company. Employees receive an amount based on the company’s performance and profits based on its quarterly or annual earnings. This is awarded to employees in various forms. It can be given as a percentage of the profit in cash or in stocks. Many companies also provide profit sharing as part of their retirement plan for employees. This provides employees with a sense of ‘ownership’ in the company.
Referral bonus
An employee receives a particular amount of money for referring candidates for a job or customers for a particular program.
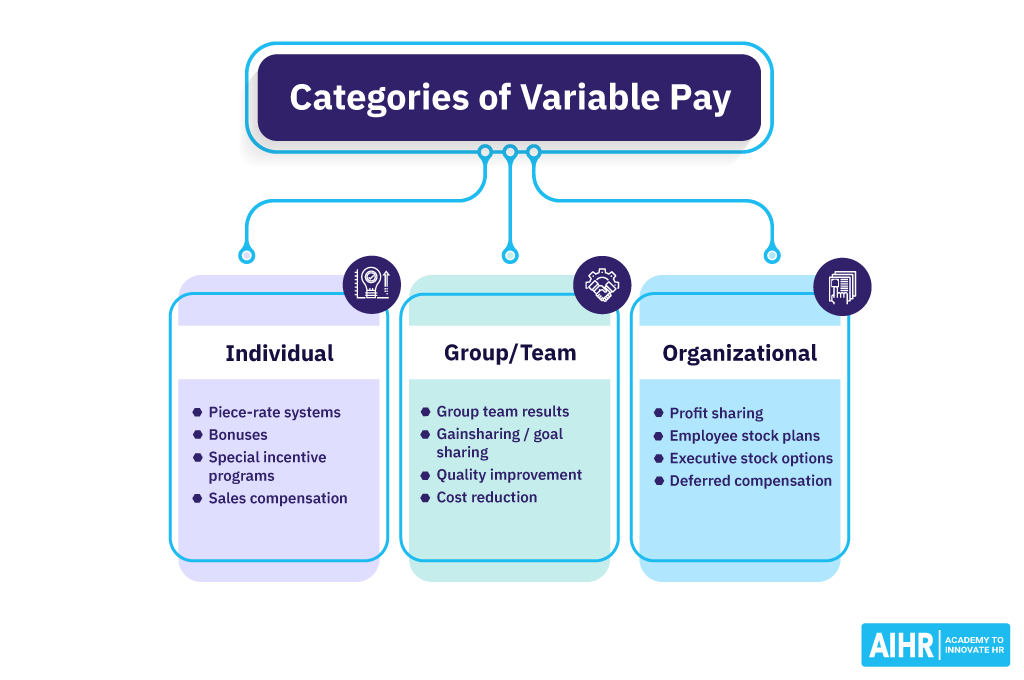
Types of variable pay
There are three categories of variable pay:
1. Individual
Variable pay is determined by the individual employee and their output. There is a clear line of sight between a person’s efforts and their variable pay, generally linked to overall performance rating.
Some of the forms of variable pay could be:
- Piece rate system: Salaries are determined by the number of pieces produced by the piece rate for one unit)
- Bonus: A one-time payment made to an employee in recognition of their performance
- Special incentive programs: Such as cash or recognition awards
- Commission: Sales commissions.
2. Group / Team
This type of variable pay either provides the same sized reward for all employees as part of the group or different sized rewards for each member, depending on the contribution. It reinforces teamwork and can change and preserve vital team behaviors. It weakens the focus on individual performance and requires measurement of team performance. This team bonus usually attracts team players.
Some unique variable pay in this category include:
- Gainsharing: This is a form of compensation where employees share an award based on their productivity and performance. As the performance increases, so does your employees’ share in the financial gain. Gainsharing is self-funded, which means that the ‘gains’ earned need to be measurable (e.g., profits made or savings, or costs reduced). It is usually paid quarterly and tied to measures of output, quality, cycle times, waste/scrap, safety, etc.
- Goalsharing: This is a program that establishes goals to support the company’s mission. For example, it might be to improve overall customer satisfaction. Goalsharing distributes compensation to employees when this goal is met. However, it is not self-funded (as in the case of gainsharing).
3. Organizational
Distributing profits among employees to increase productivity and enhance employee morale as well as organizational performance. Some of the forms of variable pay under this category include:
- Employee stock plans
- Executive stock options
- Deferred compensation.
How does variable pay work?
Variable pay is usually communicated in advance to employees as an incentive or used as a bonus after the fact. It is often paid out as a percentage of the fixed pay, depending on position and level. Some jobs usually receive more variable pay than others (for example, sales and leadership roles).
The pay mix of total variable compensation vs. total compensation cost is usually calculated as a percentage of total compensation. To calculate the pay mix of total variable pay of an employee:
Total variable pay / Total compensation cost * 100 = Variable pay %
Advantages and disadvantages of variable pay
Advantages:
- Talent management: Variable pay helps retain high-performing goal-driven staff, as employees that feel they are well compensated are less likely to leave. It also differentiates reward for those employees who contribute more.
- Economic: It aids in balancing out the salaries of employees. It is an element of remuneration that is self-funded and acts as a pressure valve. It also links pay with the fortunes of the business.
- Motivation: Variable pay related to performance increases productivity and motivation. It helps focus attention on specific areas of performance and results and reinforce and modify employee behavior.
- Talent attraction: Variable pay makes an employer competitive.
- Inclusion: This type of pay helps give a clearer identity to each department and team and enhances team membership for individuals. It also fosters more cooperation and a sense of shared identity.
- Competition: It meets competitive market norms, practices, and customs and also helps organizations avoid unduly high fixed basic salaries.
Disadvantages:
- Perception of unfairness: If the proper payment structure is not in place, it can cause the perception of unfairness and create jealousy within the organization.
- Cost: It can be costly for an organization if not implemented correctly.
- Recency bias: Variable pay can be susceptible to recency bias. As performance appraisals form part of a big part of variable payout, managers sometimes tend to rate an employee on their most recent job performance instead of how they performed the entire year. As a result, it rewards input and effort and not the result.
- Competition: Difficulty can arise in the form of unhealthy competition, making it difficult to foster collaborative teams.