Employee Grievance
What is employee grievance?
An employee grievance refers to a formal complaint that an employee raises against their employer due to dissatisfaction with some aspect of their employment. This complaint typically concerns issues that the employee feels are unfair, unjust, or deviate from company policies or employment contracts.
Types of employee grievances
Employee grievances can be categorized into several types based on their nature and the issues they address. Here are the primary types:
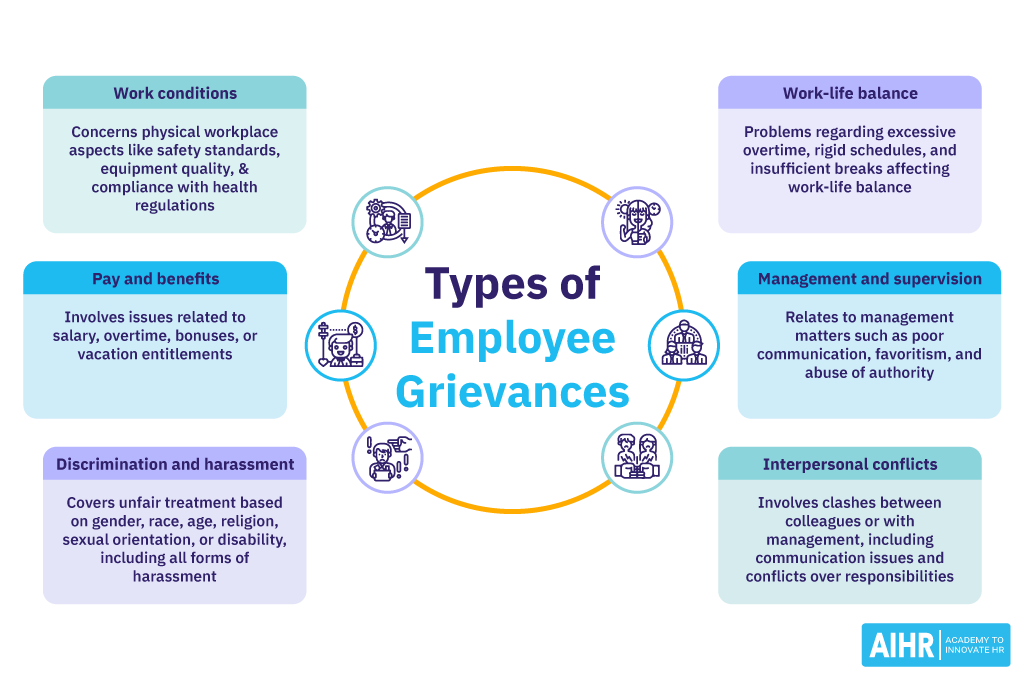
- Work conditions: These relate to the physical conditions of the workplace, including safety standards, equipment quality, workspace environment, and compliance with health and safety regulations.
- Compensation and benefits: These grievances involve disputes over earnings, salary adjustments, overtime pay, bonuses, and other compensation issues, as well as benefits like health insurance, retirement plans, and vacation entitlements.
- Discrimination and harassment: Complaints related to unfair treatment based on gender, race, age, religion, sexual orientation, disability, or any other protected characteristic fall into this category. It also includes all forms of harassment, whether sexual, verbal, or psychological.
- Work-life balance: This category involves concerns over excessive overtime, inflexible work schedules, insufficient breaks, and anything else that affects an employee’s ability to balance work with personal life.
- Management and supervision: Concerns related to management practices, including lack of communication, poor management style, favoritism, lack of support, or abuse of authority.
- Interpersonal conflicts: Problems between colleagues or employees and management that affect the working environment. This can include personality clashes, communication problems, or disputes over responsibilities.
Employee grievance examples
While grievances can vary widely depending on the employer and the issue the employee is facing, there are some common examples.
Discrimination
A grievance is raised by an employee who feels they have been consistently overlooked for promotions due to their age, despite having comparable qualifications and performance levels as other colleagues who were promoted.
Interpersonal conflicts
A grievance is filed by an employee who feels they are being unfairly treated by their supervisor, who frequently criticizes them in front of peers and assigns them less desirable tasks compared to others in the same team.
Working conditions
A grievance is filed by an employee who reports that the working conditions in the warehouse are unsafe, citing inadequate lighting and malfunctioning equipment, which they believe poses a risk to their safety and that of their colleagues.
Pay and benefits
A grievance is raised by an employee who discovers they are being paid significantly less than new hires with similar roles and qualifications.
The employee contends that this pay discrepancy is unfair and demotivating, particularly since they have been with the company for several years and have consistently received positive performance reviews.
Employee grievance policy: What to include
As you create your grievance policy, make sure it includes all the information both your HR department and your employees need to manage grievances as they arise.
- Definition of grievance: The policy should clearly define what constitutes a grievance. This could include issues like harassment, discrimination, unfair treatment, safety concerns, and violations of company policies.
- Procedures for filing a grievance: Clarify what steps employees need to take when filing a grievance, including any evidence or information they need to provide and whom to contact (typically a supervisor or HR representative).
- Confidentiality: Assurance that all grievance submissions will be handled discreetly to protect the privacy of those involved.
- Investigation process: What process will the company go through to evaluate and respond to the grievance? Who should be involved in that process? Clearly lay it out as part of your grievance policy.
- Resolution and decision-making: Provide information on how decisions will be made following the investigation and what kind of resolutions can be expected. Ensure the policy includes a commitment to treating all employees fairly and that they all have the same right to have their grievances taken seriously.
- Appeals process: If the employee is not satisfied with the outcome of the grievance, the policy should outline how they can appeal the decision and the procedures involved in the appeals process.
- Anti-retaliation policy: Note that the company prohibits retaliation against any employee who files a grievance, participates in an investigation, or supports another employee’s grievance.
How HR can handle employee grievance
Handling employee grievances effectively is crucial for maintaining a positive and productive workplace. Here are some best practices HR can follow to handle this:
- Establish a clear grievance procedure: Develop and implement a formal grievance policy that is easily accessible to all employees. This should outline the steps an employee needs to follow to raise a grievance, and the process HR will use to handle the issue. Ensure the policy complies with local labor laws and regulations.
- Encourage open communication: Promote an open-door policy where employees feel comfortable discussing concerns with their supervisors or directly with HR without fear of retaliation.
- Act promptly: When a grievance is raised, act quickly to acknowledge receipt and begin the resolution process. Delays can exacerbate the issue and lead to further dissatisfaction.
- Investigate thoroughly: Conduct a thorough investigation to gather all facts related to the grievance. This may involve interviewing the complainant, the accused, and any witnesses. It’s important to remain neutral and objective during the investigation.
- Provide a resolution: After investigating, offer a resolution based on the findings. This could involve mediation between the parties, changes to workplace practices, training, or other actions aimed at resolving the issue.
- Learn from the experience: Review each grievance for lessons that can be learned to improve the workplace. This might involve updating policies, providing additional training, or making changes to prevent similar issues in the future.
FAQ
An example of an employee grievance is a situation in which an employee files a complaint against their employer due to experiencing harassment at work and feeling that the employer has not adequately addressed the issue.
A grievance in the workplace refers to a formal complaint raised by an employee against their employer regarding an aspect of their employment that they believe is unfair or unjust or violates their rights or conditions of employment.
When an employee files a grievance, they formally submit a complaint concerning issues like unfair treatment, violations of company policy, or unsafe working conditions. This process initiates a formal investigation and resolution procedure within the organization to address and rectify the employee’s concerns.
Employers typically follow a structured process to resolve employee grievances. This procedure includes acknowledging the complaint, conducting a thorough investigation to gather facts, discussing the findings with all involved parties, and deciding on an appropriate resolution. This process seeks to address the grievance fairly and maintain a positive work environment.








