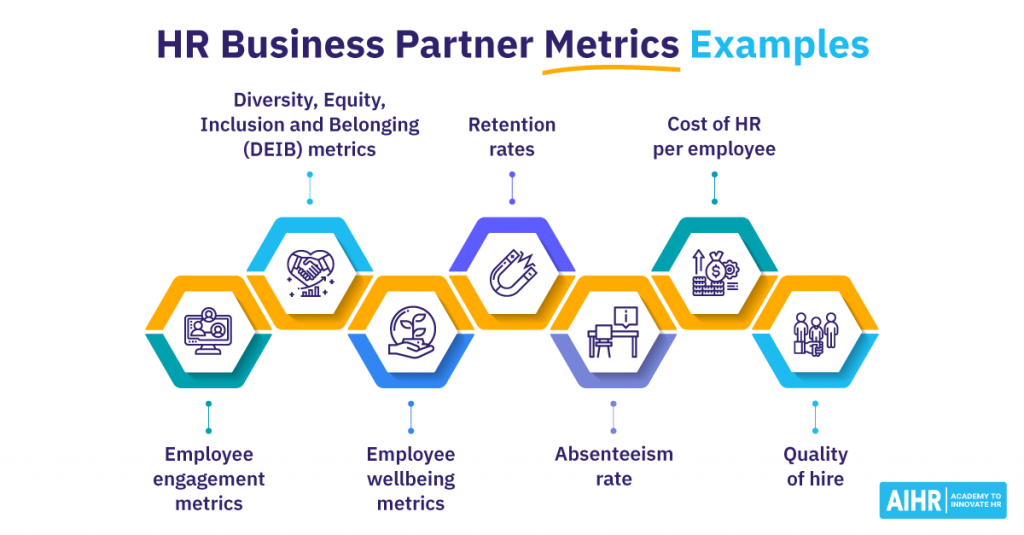
7 HR Business Partner Metrics Examples

Organizations with efficient HR business partners have enhanced employee performance, revenue, and profits by 22%, 7%, and 9%, respectively. HRBPs can greatly impact organizational performance and achieving overall business objectives. Thus, it is essential to track HR business partner metrics to ensure that your company’s HRBPs are effective. These will also allow you to uncover areas of improvement to help employees and the organization perform better. Let’s dive into the HR Business Partner metrics!
Contents
What are HR Business Partner metrics?
Why track HR Business Partner metrics
HR Business Partner metrics examples
What are HR Business Partner metrics?
HR Business Partner metrics are used for assessing, comparing, and recording the performance or productivity of HR Business Partners within an organization. In other words, these metrics help organizations and HRBPs themselves evaluate the HRBP’s performance, compare with the goals, and suggest improvements when required.
The role of a Human Resources Business Partner is to ensure the smooth operation of the business from an HR perspective. They support senior business leaders by aligning people goals with organizational goals while helping shape the overall strategy. They serve as a coach and consultant, use a data-driven approach and evidence-based HR to enable decisions, and play a key role in enhancing the company culture and the employee experience.
HRBP metrics allow employers and HR Business Partners to quantify the above work and its impact to determine the performance of HRBPs.
Why track HR Business Partner metrics
HRBPs are responsible for various HR activities, as mentioned above. HRBP metrics help track the impact of their work, allowing them and their companies to understand their areas of improvement. This data-driven approach saves time, helps make sound decisions, and reduces cost and effort. The overall purpose of tracking the HRBP metrics can be summed up in the following:
- How much has been achieved
- How well it was done
- What needs to be changed
HR Business Partner metrics examples
With all of the above being said, an HR Business Partner role is not easy to quantify. HR Business Partner works in collaboration with multiple stakeholders, and it’s difficult to pinpoint exactly what their impact was and attach a quantifiable metric to it.
What’s more, while some HR metrics associated with the work of HRBPs may be easy to track, such as the cost of hiring, many subjective factors like employee wellbeing and happiness may be more challenging to measure.
To assess and analyze performance efficiently, it is useful to set individual goals that align with an HRBP’s responsibilities. You can combine input and output metrics. Input metrics refer to the behaviors and activities carried out, like updating two work policies every quarter. Output metrics measure the results of those activities, for example, reducing absenteeism by 1% by Q3.
In this section, let’s have a look at some examples of HR business partner metrics and how you can set goals for yourself as an HRBP, or for HR Business Partners on your team.
1. Employee engagement
Employee engagement refers to the employees’ connection with the company culture, work, colleagues, and organizational goals. Strong employee engagement positively impacts the operation of an organization, whereas poor engagement may result in lower productivity and a toxic work environment.
This metric allows employers to understand the relationship between an employee and their workplace, which significantly influences the organization’s overall performance. Since HRBPs play a key role in HR strategy formulation that directly impacts employees, this is a valuable metric to track.
One of the ways to measure employee engagement is by calculating the employee Net Promoter Score (eNPS), a well-known metric in the HR world. This involves answering questions on a scale of 1 to 10 in a survey. The questions are mainly aimed at understanding if an employee would recommend their company and job to someone else. Based on the score, employees could be classified as:
- Promoters (mostly scoring 9 & 10 on all questions)
- Passives (mostly scoring 7 & 8 on all questions)
- Detractors (scoring between 0 to 6 on all questions)
Promoters are the most satisfied employees, Passives are happy enough but not enthusiastic about their work, and Detractors are dissatisfied employees who wouldn’t recommend the company.
You can calculate eNPS as shown below:
A score of 10 to 30 is usually considered good, while an above 30 score is excellent.
You can also track other employee engagement metrics like ROI on employee engagement and Glassdoor.com rating.
An example of an employee engagement goal
Boost employee engagement by 8% by the end of next year.
- Conduct three surveys to identify employee requirements for improving inter-departmental collaboration
- Implement one new initiative based on the survey results
- Introduce 1 day of paid leave every quarter to volunteer at a local charity
2. Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Belonging metrics
Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Belonging (DEIB) metrics are another way to measure HRBP effectiveness in your organization. It gives you an understanding of fairness and equity in the workplace. These metrics help employers commit to better diversity and inclusion initiatives by identifying the gaps and blind spots.
In most cases, HRBPs are directly involved in the strategic planning of the DEIB initiatives. Effective planning can positively impact the employer brand and create more sense of belonging among the employees.
When quantifying the state of DEIB in a company, some factors to consider are demographics and pay equity. For demographics, you should consider the ratio of females, BIPOC, LGBTQ+, and employees with disabilities working in the organization. To find the percentage, you can use the following formula:
(Category of employees (e.g. women professionals) / Total number of employees) x 100
To calculate the pay gap between men and women, you can use the following:
((Average hourly rate for men – Average hourly rate for women) / Average hourly rate for men) X 100
Diverse demographics and a low pay gap are positive indicators, demonstrating that the DEIB measures of the company are significant and capable of adding value.
An example of a DEIB goal
Increase the share of women in the organization by 10% in the next three years.
- Post 100% of job listings to women-focused job boards like Fairygodboss and The Mom Project
- Reduce the gender pay gap by 15%
3. Wellbeing metrics
Employee wellbeing is a concept that can be difficult to measure. It’s based on the notion that employees are doing well physically, mentally, financially, and in other aspects. They are content, satisfied, and fulfilled at work.
Since employee wellbeing directly impacts performance and productivity, HRBPs are often involved in ensuring the right wellbeing programs are implemented efficiently. This makes it another key metric to assess their performance.
While there are many ways to measure employee wellness, one of the most common ones is through a survey. A comprehensive survey including questions about personal wellbeing, satisfaction at work, and teamwork can be a great way to get feedback and gather data on their point of view.
Other efficient ways to measure wellbeing could include keeping a check on sick leave days, absenteeism, and healthcare expenses dedicated to employees.
An example of an employee wellbeing goal
Start a wellness program covering all full-time, part-time, and contractual employees in Q1.
- Introduce an initiative to help 3% of smoker-employees reduce/ quit smoking each quarter
- Conduct workshops on mindfulness and wellbeing every 2 months
4. Retention rates
The employee retention rate refers to the percentage of employees who stayed with the business during a given period. Organizations typically measure this over a longer period, for instance, annually. This is a valuable metric allowing companies to understand how long an employee stays with them and at what points in their careers they leave.
As HRBPs take part in activities that impact employees actively throughout the employee lifecycle, their work directly impacts the retention rates in a company. If the retention rates are high, it means their efforts have a positive effect on the company. However, if these are low, there is a need to revamp the strategy. Thus, retention rates can be a great way to assess HR Business Partners’ work.
You can calculate the retention rate in the following manner:
A retention rate of about 90% is considered a good number. While 100% may sound optimal, it doesn’t allow you to hire more employees depending on the business needs. Hence, anything around 90% may be ideal for your company. However, this will depend on your industry, so you might want to check the industry employee retention benchmarks.
An example of a retention rate goal
Increase the retention rate by 6% annually.
- Ensure that managers have a salary dialogue with a personalized development path with 75% of employees in the next year
- Conduct exit interviews for 100% of leaving employees to understand common reasons for leaving
5. Absenteeism rate
As the term suggests, the absenteeism rate defines the percentage of employees taking unplanned leave, like sick leave or even unexcused absences. Holidays or any other planned leaves are not included in absenteeism. A higher absenteeism rate reflects a lack of wellbeing and wellness measures in a company or a general notion that employees aren’t doing well mentally or physically.
If the rate of absenteeism is high, HRBPs need to take measures to make work more fulfilling and engaging. A higher rate can negatively affect the company’s overall performance, impacting profits and revenue. Hence, the absenteeism rate is another way to keep a check on an HRBP’s efforts.
Here is how you can calculate the absenteeism rate:
An example of an absenteeism goal
Decrease absenteeism from 5% to 3% year-over-year.
- Introduce the option to work from home 2-3 days a week for all roles where this is possible
- Conduct a survey on understanding the quality of management
6. Cost of HR per employee
The cost of HR refers to the total cost that a company spends on the HR function. This includes the cost of developing and maintaining the workforce, recruiting, mentoring, and coaching employees, and managing employee communications, among other things.
This metric helps companies understand the cost expenditure, where they are spending more, and where they have a possibility of reducing the costs. HRBPs are directly responsible for keeping HR per employee costs optimal as they work across different functions. Lower HR costs may signify the efficiency and success of the roles performed by HRBPs.
Generally, smaller companies have a higher cost of HR per employee due to a lower number of staff. Hence, medium and large companies have lower costs of HR. Furthermore, this metric is also a good indicator of return on investment. The cost of HR can be calculated in the following way:
(Total HR cost per year / Total number of FTEs) x 100
An example of a cost of HR per employee goal
Reduce the cost of HR per employee by 5% per quarter.
- Conduct an HR tech stack audit and pause/cancel unnecessary subscriptions for HR tools
- Reduce time spent on administrative tasks by 55% in one year
7. Quality of hire
If an HRBP is directly involved in the recruitment function of the company, quality of hire is another major metric to determine the performance. Quality of hire refers to the value a new hire adds to the company. These usually include performance metrics such as meeting sales targets, achieving customer satisfaction in the form of ratings, or delivering high-quality products or services within the deadline.
Some common indicators of quality of hire in a company include performance appraisal score of the new employees, retention rate, 360-degree feedback score, bonuses, number of awards, profit contribution, and customer satisfaction score, among others. Once you’ve decided on the indicators, you can calculate QoH in the following way:
(Indicator 1 percentage + Indicator 2 percentage + …Indicator n percentage / Total number of indicators) x 100
Calculating the quality of hire is essential to business as it gives a better understanding of how successful the hiring process was. Recruitment is a long process with a considerable amount of costs. Hence, it is essential to know its efficiency and see what changes you can make for better results.
An example of a quality of hire goal
Improve the quality of hire by 4% per quarter.
- Conduct quarterly surveys to evaluate the hiring managers’ satisfaction with every hiring manager
- Increase the investment into the sourcing channel yielding the highest quality of hire by 15%
Over to you
Due to the nature of work, HR Business Partner metrics are challenging to implement. However, in practice, they can greatly impact the functioning of the HR department and the organization. One of the best ways to track how an HR Business Partner is performing is by setting goals for their work related to the HR and organizational objectives and tracking progress. This can help you better understand how the HR Business Partner is doing and where they need the necessary support to achieve the goals.
Weekly update
Stay up-to-date with the latest news, trends, and resources in HR
Learn more
Related articles
Are you ready for the future of HR?
Learn modern and relevant HR skills, online