OKRs vs. KPIs: The Key Differences & Use (With Examples)
Want to make goal-setting less of a guessing game and more of a high-scoring strategy for success? OKRs lay the foundation, establishing clear objectives, while KPIs provide the reality check, measuring performance. Together, they can turn your ambitions into achievements — one measurable result at a time.

More than 80% of companies agree that Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) positively impact their organizations. OKRs set ambitious goals, while Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) provide measurable metrics to track progress, creating a powerful framework for aligning strategy with execution. Achieving synergy between the two drives organizational success.
But what is the difference between OKRs and KPIs? This article will explain the key differences, when to use each, and metrics to track when measuring each methodology.
Contents
What is an OKR?
The benefits of setting OKRs
What is a KPI?
The benefits of setting KPIs
OKRs vs. KPIs: The main differences
Why use HR OKRs
Why use HR KPIs
What is an OKR?
- Objectives serve as ambitious, qualitative descriptions of what the organization aims to achieve
- Key Results are specific, measurable milestones indicating progress towards those objectives.
This framework fosters alignment, accountability, and innovation within organizations, driving success across industries.
The benefits of setting OKRs
- Alignment: OKRs help align HR goals with the organization’s overall objectives, ensuring that HR initiatives contribute directly to the company’s success.
- Clarity: OKRs provide clarity on HR priorities and expectations, making it easier for you and your HR teams to understand what must be accomplished and how to measure success.
- Focus: By setting clear objectives and key results, OKRs help your HR teams prioritize tasks and initiatives, focusing efforts on the most impactful activities.
- Accountability: OKRs facilitate accountability within HR by establishing measurable outcomes and timelines for achieving them. This encourages you, the HR professional, to take ownership of your work and deliver results.
- Continuous improvement: OKRs promote a culture of constant improvement within HR by encouraging reflection and adjustment based on performance data. Your HR teams can use OKR results to identify areas for growth and refine their strategies over time.
- Employee engagement: When HR goals are aligned with the organization’s objectives, employees are more likely to feel engaged and motivated. OKRs provide a framework for communicating your HR priorities and creating a sense of purpose among employees.
- Transparency: OKRs promote transparency within HR and across the organization by clearly outlining goals and progress. This transparency builds trust and collaboration among team members and stakeholders.
- Adaptability: OKRs allow your HR teams to adapt quickly to changing business needs and market conditions. By regularly reviewing and adjusting objectives and key results, you can remain agile and responsive to new challenges and opportunities.
HR tip
Sears implemented the OKR framework to boost performance. Initially, the company limited this to salaried employees, overlooking sales agents. After a year, with minimal OKR impact, it realized adjustments were necessary.
Sears achieved notable improvements by refocusing efforts on outbound call centers and emphasizing add-on sales metrics. Sales increased by 8.5% and hourly sales rose from $14.44 to $15.67.
What is a KPI?
A Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a measurable value that gauges how effectively an organization is achieving its key objectives.
- Key indicates the metric’s importance in relation to organizational goals.
- Performance emphasizes its role in assessing the effectiveness and execution of strategies
- Indicators highlight the measurable nature of these metrics, which provide valuable insights into progress.
KPIs are essential tools for decision-making, helping organizations (and HR teams) to track and optimize performance toward desired outcomes.
The benefits of setting KPIs
- Performance measurement: KPIs can provide you with quantifiable metrics to measure the effectiveness and efficiency of your HR initiatives, processes, and programs.
- Goal alignment: KPIs help align your HR activities with the goals and objectives of the organization.
Data-driven decision-making: KPIs can provide you with actionable insights based on real-time data. This data will help you make informed decisions and prioritize initiatives that impact organizational performance most. - Accountability: By setting clear KPIs, HR professionals and teams are held accountable for achieving specific outcomes. This builds a culture of responsibility and ownership within the department.
- Continuous improvement: KPIs serve as benchmarks for your performance. These benchmarks help you evaluate and refine your HR strategies and processes to improve your effectiveness over time.
- Resource optimization: KPIs help you to allocate resources more effectively by identifying areas of strength and weakness. This lets you focus resources where they are most needed to drive performance and results.
- Employee development: You can use KPIs to track and evaluate employee performance, identify areas for improvement, and establish individual and team development goals. This contributes to a culture of growth and development within the organization.
- Communication and transparency: Setting KPIs promotes transparency and open communication both within HR and across the organization by clearly defining expectations and goals. This creates collaboration and alignment toward common objectives.
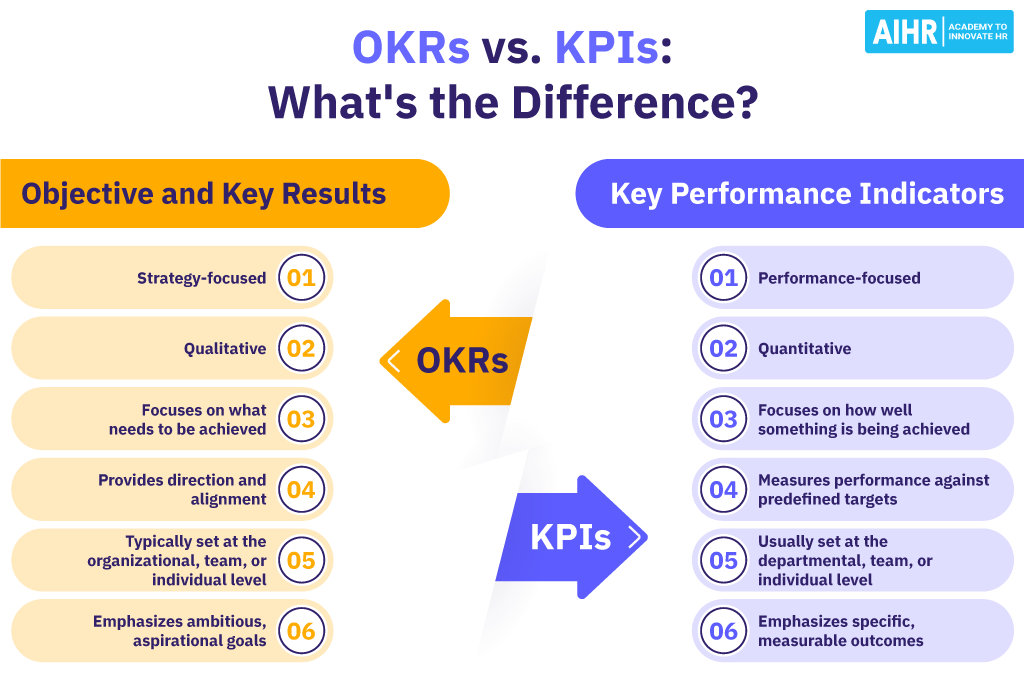
OKRs vs. KPIs: The main differences
Objectives and Key Results
Key Performance Indicators
Strategy-focused
Performance-focused
Qualitative
Quantitative
Focuses on what needs to be achieved
Focuses on how well something is being achieved
Provide direction and alignment
Measure performance against predefined targets
Typically set at the organizational, team, or individual level
Usually set at the departmental, team, or individual level
Emphasizes ambitious, aspirational goals
Emphasizes specific, measurable outcomes
Encourages innovation and risk-taking
Supports continuous improvement and optimization
Helps define priorities and focus areas
Helps track progress and performance toward goals
Results may be subjective or open to interpretation
Results are typically objective and concrete
Often set for a specific period
Can be both short-term and long-term
Supports agile and adaptable goal-setting
Provides a basis for evaluating performance and making data-driven decisions
Why use HR OKRs
Here’s why implementing HR OKRs within the HR function is beneficial:
1. Aligns with organizational goals
OKRs help you align your HR objectives and initiatives with the company’s broader strategic goals. By setting clear objectives and defining key results contributing to these goals, you can focus your HR team’s efforts on activities that drive organizational success.
2. Provides focus and prioritization
OKRs provide you with a framework for prioritizing activities and allocating resources effectively. You can better direct your efforts toward the most critical initiatives by establishing ambitious yet achievable objectives and defining key results that measure progress.
3. Maintains accountability and measurement
OKRs create accountability within HR by establishing clear expectations and metrics for success. You can achieve your HR goals and optimize your HR team’s performance by regularly tracking progress against key results and holding individuals and teams accountable.
4. Encourages continuous improvement
OKRs promote a culture of continuous improvement within HR by encouraging reflection, learning, and adaptation. Regular reviews help you identify areas for improvement, refine strategies, and iterate approaches to achieve better results over time.
HR tip
Inject creativity into OKRs by encouraging cross-functional collaboration to spark innovation and develop a culture of collective ownership of shared goals.
How HR can use OKRs
There are many objectives that OKRs can help you to achieve. Some of these include:
Improving recruitment and onboarding
Setting clear OKRs for recruitment and onboarding helps your recruiters and talent acquisition team improve their work in these key areas. For instance, the goal might be to enhance the quality of new hires with specific targets like “boost candidate survey scores by 20%”, “raise new hire retention by 15% in the first year”, and “cut down the hiring process by 10 days”.
This method focuses on attracting the best talent and making sure they settle in well, increasing their commitment and participation from the start. With OKRs, HR can use data and feedback to keep improving how they hire and welcome new employees.
Improving employee engagement and satisfaction
For instance, a goal could be “increase employee engagement and satisfaction,” with measurable outcomes like “boost employee engagement score by 25%”, “cut employee turnover by 20%”, and “start at least two workforce development programs.”
By establishing these objectives, you can work towards fostering a positive culture that appreciates and rewards employees’ efforts. OKRs promote ongoing feedback, making employees feel valued and listened to, which boosts loyalty and productivity.
Developing Diversity, Inclusion, Equity and Belonging
Use OKRs to improve Diversity and Inclusion in the workplace. For example, an objective might be to “amplify diversity and inclusion in all departmental teams” with measurable outcomes such as “increase the representation of minority groups in management positions by 15%” and “achieve a 25% increase in employee perceptions of inclusivity”.
By setting specific, actionable goals, HR can ensure that DEIB initiatives are not just token gestures but are integrated into the organization’s culture.
OKR metrics to track
Depending on your objectives, there are various metrics you can use. For example:
- Recruitment metrics (e.g., time to fill, candidate satisfaction)
- Employee engagement and satisfaction scores
- Training and development program completion rates
- Diversity and inclusion metrics (e.g., representation of underrepresented groups, diversity training participation)
- Performance management metrics (e.g., goal achievement rates, performance appraisal scores)
- HR operational efficiency metrics (e.g., HR process cycle times, HR service delivery metrics).
6 examples of HR OKRs
Example 1:
- Objective: Improve employee engagement
- Key result 1: Increase employee engagement survey scores by 10%
- Key result 2: Reduce voluntary turnover rate by 5%
- Key result 3: Implement at least three employee recognition programs.
Example 2:
- Objective: Enhance diversity and inclusion
- Key result 1: Increase representation of underrepresented groups in leadership positions by 15%
- Key result 2: Achieve 100% participation in diversity and inclusion training programs
- Key Result 3: Implement unconscious bias training for all hiring managers.
Example 3:
- Objective: Strengthen talent acquisition
- Key result 1: Reduce time to fill vacant positions by 20%
- Key result 2: Improve candidate satisfaction scores by 15%
- Key result 3: Increase employee referral hires by 25%.
Example 4:
- Objective: Optimize performance management process
- Key result 1: Increase employee and organizational goal alignment by 20%
- Key result 2: Conduct quarterly performance check-ins with all employees
- Key result 3: Raise performance appraisal completion rates to 95%.
Example 5:
- Objective: Enhance employee development
- Key result 1: Increase participation in training and development programs by 30%
- Key result 2: Achieve 90% satisfaction rate in post-training surveys
- Key result 3: Implement a mentorship program for high-potential employees
Example 6:
- Objective: Improve HR operational efficiency
- Key result 1: Implement HR automation tools to reduce time spent on administrative tasks
- Key result 2: Streamline onboarding process to reduce onboarding time by 25%
- Key result 3: Increase self-service HR portal adoption rate to 80%.
HR tip
Learn to make data-driven decisions by upskilling yourself with an AIHR People Analytics Certificate Program. The self-paced program will teach you how to analyze HR data and build interactive HR dashboards and reports so you can measure and transform data into actionable insights.
Why use HR KPs
KPIs can serve several purposes within HR:
1. Align with strategic objectives
KPIs help HR departments align initiatives and activities with the organization’s overall strategic objectives. By measuring specific metrics, such as talent acquisition, employee development, and retention, HR can ensure that its efforts contribute directly to achieving broader organizational goals.
2. Monitor key metrics
You can track critical workforce management and performance metrics with KPIs. These metrics may include employee engagement levels, turnover rates, diversity and inclusion metrics, training and development effectiveness, and HR operational efficiency. By measuring these key indicators, you can identify areas of strength and areas needing improvement. This enables you and the company to make informed decisions and take proactive measures to address issues as they arise.
3. Drive performance improvement
KPIs provide HR with insights into the performance and effectiveness of various HR programs, policies, and processes. By setting benchmarks and targets for key metrics, you can establish performance standards and identify opportunities for improvement. This enables HR to implement targeted interventions and strategies to enhance employee performance, engagement, and overall organizational effectiveness.
4. Improve decision-making
KPIs serve as valuable tools for data-driven decision-making within HR. By analyzing KPI data, you can gain insights into trends, patterns, and areas of concern within the workforce. This enables HR to make informed decisions regarding talent management, resource allocation, strategic planning, and other critical HR initiatives, ultimately leading to better outcomes for the organization.
How HR can use KPIs
Measure performance
Use KPIs to measure the performance and effectiveness of your HR programs, initiatives, and processes. For example, KPIs related to recruitment and selection can help HR assess the efficiency of talent acquisition efforts. KPIs related to training and development can help gauge the impact of employee learning programs on skill development and performance improvement.
Set and monitor goals
Establish specific KPIs aligned with HR goals and objectives and use them to set performance targets and benchmarks. By monitoring KPIs regularly, you can track progress toward achieving these goals, identify areas of success and improvement, and adjust strategies and tactics to stay on track.
Identify trends and patterns
HR can analyze KPI data to identify trends, patterns, and insights related to workforce dynamics, employee behavior, and organizational performance. For example, KPIs related to employee engagement can help you identify drivers of engagement and areas of concern, helping you develop targeted interventions to improve morale and satisfaction.
Benchmarking and comparison
KPIs can be used to benchmark performance against industry standards and best practices or compare performance across different departments, teams, or time periods. This helps you identify areas of strength and areas needing improvement relative to peers or internal benchmarks.
Drive accountability and transparency
Promote accountability and transparency by establishing clear KPIs and communicating them to stakeholders. Employees and managers can then better understand expectations and performance standards, track progress toward goals, and take ownership of their contributions to success.
Assess the effectiveness of strategies and policies
KPIs help you to evaluate the effectiveness of existing HR strategies, programs, and policies. By measuring outcomes against predefined KPIs — such as recruitment effectiveness, training program success rates, and diversity and inclusion metrics — you can determine whether its initiatives are achieving the desired results. You can then identify what’s working and what requires improvement, leading to more targeted and effective interventions.
HR KPI metrics to track
- Employee turnover rates
- Absenteeism rates
- Time to hire metric
- Training and development program effectiveness (e.g., training completion rates, skill acquisition)
- Employee engagement levels (e.g., employee satisfaction surveys, retention rates)
- Diversity and inclusion metrics (e.g., representation of underrepresented groups, inclusion index).
6 examples of HR KPIs
Example 1:
Employee turnover rate: Percentage of employees who leave the organization within a specific period, typically calculated annually.
Example 2:
Absenteeism rate: Percentage of scheduled work hours that employees are absent from work, often calculated monthly or quarterly.
Example 3:
Time to hire: Average number of days it takes to fill a vacant position from the time you post it until the organization hires a candidate.
Example 4:
Training program success rate: Percentage of employees who successfully complete training programs or courses within a given timeframe.
Example 5:
Employee engagement score: A composite measure of employee satisfaction, motivation, and commitment, often assessed through employee engagement surveys or other feedback mechanisms.
Example 6:
Diversity index: Measure of workforce diversity that considers factors such as gender, race, ethnicity, age, and other aspects of diversity, often expressed as a percentage or ratio.
To sum up
OKRs and KPIs are invaluable tools for driving organizational success. OKRs provide a structured methodology for defining clear objectives and measurable outcomes, guiding teams toward strategic goals. On the other hand, KPIs offer real-time insights into performance, enabling you to track progress and make data-driven decisions.
Weekly update
Stay up-to-date with the latest news, trends, and resources in HR
Learn more
Related articles
Are you ready for the future of HR?
Learn modern and relevant HR skills, online