What Is Workforce Analytics? Your 2024 A-Z Guide
HR professionals need accurate insights to determine whether their efforts to improve the employee experience are working. That’s where workforce analytics comes in—data-driven decision-making can enhance employee retention, optimize strategies, and align your workforce with business goals.

Most organizations are under-equipped to identify problem areas and potential solutions to their recruiting challenges. With average new hire turnover rates of 14%, companies clearly need better insights into organizational requirements and strategies.
Recent research by Deloitte found that 83% of the 924 companies surveyed globally had low workforce analytics maturity. In contrast, higher-maturity organizations use consistent data definitions, embedded reporting and analytical tools, and data integration capabilities to understand employee behaviors.
Contents
What is workforce analytics?
Types of workforce analytics
The benefits of workforce analytics
Workforce analytics metrics to track
Workforce analytics examples and use cases
Workforce analytics software
Workforce planning and analytics: HR tips
Workforce analytics training for HR
What is workforce analytics?
Workforce analytics, also known as workforce planning analytics, is the systematic use of workforce data to inform and optimize HR decision-making.
It uses data-driven insights to enhance workforce efficiency, success, and strategic alignment. This helps organizations achieve their goals by ensuring the right people are in the right roles at the right time and proactively addressing workforce-related challenges.
Key elements of workforce analytics
Workforce analytics involves collecting HR data from various sources, including employee performance metrics, engagement surveys, attendance records, and demographic information. This data collection is essential for building a comprehensive understanding of the workforce.
The next step focuses on understanding the significance or implications of this data in relation to organizational goals. This entails analyzing trends, identifying patterns, and correlating workforce metrics and business outcomes. By interpreting this data, HR can gain insights into areas such as employee productivity, retention, and skills gaps.
As an HR professional, you can use this data to optimize the decision-making process. By integrating data-driven insights into HR strategies and operational plans, HR teams can make informed decisions about talent acquisition, development, and deployment. This optimized decision-making process helps create a more agile and responsive workforce, driving better business performance.
Types of workforce analytics
1. Descriptive workforce analytics
Descriptive workforce analytics involves analyzing past and current workforce data to understand the present state of the workforce.
Example metrics:
- Employee turnover rates
- Average tenure
- Absenteeism rates.
→ Use case: This type of analytics is used to identify trends and patterns in workforce data, such as increasing turnover rates or high absenteeism levels in specific departments. By understanding its workforce’s current state, HR can pinpoint and tackle areas needing improvement.
2. Diagnostic workforce analytics
Diagnostic workforce analytics goes a step further by examining the reasons behind the patterns that descriptive workforce analytics identifies.
Example metrics:
- Employee engagement scores
- Exit interview feedback
- Performance review data.
→ Use case: Diagnostic analytics might reveal that poor management practices or insufficient career development opportunities are causing high turnover in a department. This insight allows HR to address the root causes and develop targeted interventions.
3. Predictive workforce analytics
Predictive workforce analytics uses historical data to forecast future workforce trends and potential issues. It aims to predict outcomes and help organizations prepare for future scenarios.
Example metrics:
- Predictive turnover models
- Talent pipeline forecasts
- Workforce demand projections.
→ Use case: Predictive analytics can forecast an increase in retirements within the next five years, enabling HR to plan succession and talent acquisition strategies to fill anticipated gaps.
4. Prescriptive workforce analytics
Prescriptive workforce analytics builds on predictive workforce analytics by recommending specific actions to achieve desired outcomes. It uses advanced algorithms to suggest optimal solutions to workforce challenges.
Example metrics:
- Optimization models for staffing
- Scenario planning outputs
- Prescriptive talent management recommendations.
→ Use case: Predictive workforce analytics indicate a future skills shortage. Prescriptive workforce analytics can recommend training programs or hiring strategies to mitigate the risk and ensure the organization remains competitive.
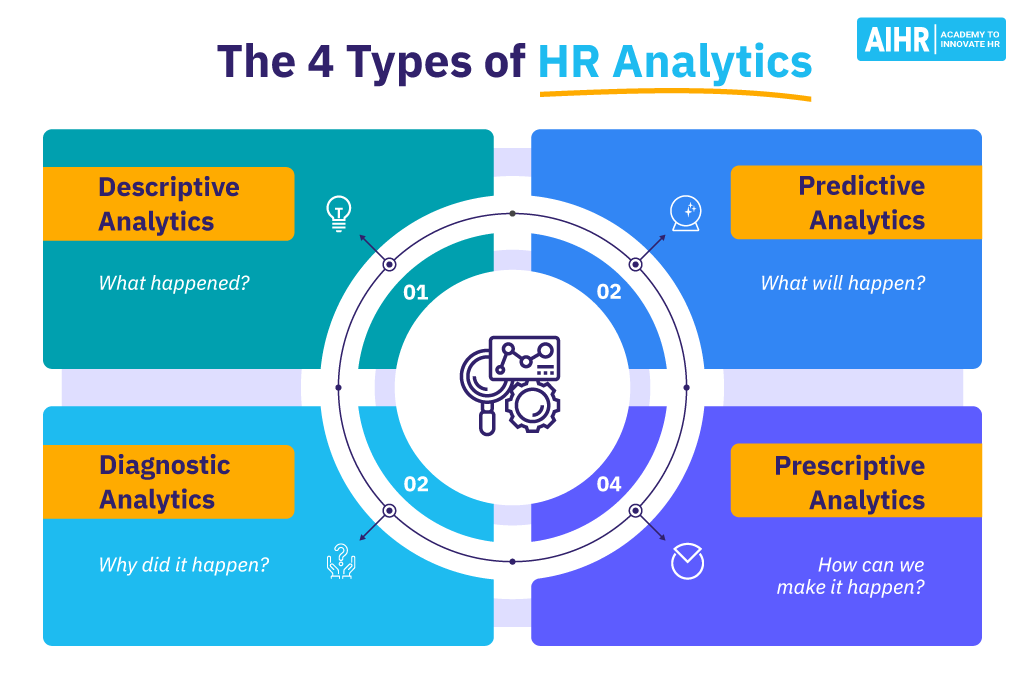
The link between different workforce analytics types
Descriptive workforce analytics provides a clear picture of current trends and happenings in the workforce, while diagnostic workforce analytics helps HR understand the reason behind them. Together, they offer a comprehensive understanding of the state of the workforce and its underlying causes.
On the other hand, predictive workforce analytics forecasts future trends based on historical data, while prescriptive workforce analytics suggests actionable steps to optimize outcomes based on these predictions. This combination helps HR proactively address future workforce challenges and opportunities.
Utilizing all four types of workforce analytics will allow you to gain a holistic view of your organization’s workforce, understand the factors driving current performance, anticipate future needs, and effectively implement strategies to achieve goals.
The benefits of workforce analytics
- Improved HR decision-making: Workforce management analytics provide HR professionals with valuable insights, leading to more informed and effective decision-making.
- Enhanced employee experience and retention: HR can identify factors influencing employee satisfaction and engagement by analyzing workforce data analytics. It can also improve onboarding processes and retention rates.
- More cost-effective business practices: Workforce analytics can highlight inefficiencies and areas for cost savings, allowing for more strategic resource allocation and reduced operational costs.
- Greater understanding of future workforce needs: Workforce planning metrics help anticipate future staffing requirements, ensuring the organization is prepared to meet its goals.
- Better alignment between HR and company goals: By leveraging workforce analytics, HR can ensure their strategies and actions align with overarching organizational goals.

Workforce analytics metrics to track
- Employee turnover rate: Measuring the rate at which employees leave an organization within a specific period (typically a month, quarter, or year) helps HR understand workforce stability and gauge its effective retention strategies. High employee turnover rates may indicate job satisfaction, compensation, or work environment issues, prompting a review of HR practices to improve employee experience and retention.
- Average tenure: Calculating your organization’s average employment length provides insight into employee loyalty and the success of HR’s retention efforts. If the average employee tenure is short, it could signal problems with onboarding, culture fit, or career development opportunities.
- Absenteeism rate: Tracking the frequency of unplanned employee absences — be it due to illness, stress, or other personal reasons — can help prompt initiatives to improve workplace wellness and support. High absenteeism rates can indicate, for instance, low employee engagement or health issues in the workplace.
- Time to hire: Measuring the period between the posting of a new open position and a candidate accepting the job offer gives HR an indication of how efficient the recruitment process is. Prolonged time to hire can harm the candidate experience and lead to talent loss, necessitating a review and optimization of the recruitment and hiring process.
- Cost per hire: Calculating the cost per hire, i.e., the average cost of hiring a new employee (including advertising, recruiter fees, and onboarding expenses), can help HR identify cost savings opportunities and optimize recruitment budgets.
- Employee engagement rating: Gauging the level of employee engagement and satisfaction through surveys and feedback gives HR a good idea of how happy employees are. Engaged employees are typically more productive and less likely to leave the organization. On the other hand, low engagement scores should prompt HR to implement initiatives to improve workplace culture, communication, and employee recognition.
- Revenue per employee: Assessing the average revenue generated per employee provides insight into overall workforce productivity and efficiency. Low revenue per employee may indicate inefficiencies or a need for better training and development programs to improve employee performance.
- Early turnover rate: Tracking the percentage of employees who leave within their first year of employment can highlight issues with the hiring process, onboarding, or early employee experience. A high early turnover rate — also known as new hire turnover — warrants a review of recruitment practices and onboarding programs to ensure new hires are well-integrated and supported.
- Employee net promoter score (eNPS): Determining eNPS through employee surveys indicates employee loyalty and their likelihood of recommending the company to others as a good place to work. A low eNPS score can signify employee dissatisfaction and potential turnover, prompting HR to investigate and address the underlying issues.
- Training effectiveness: Evaluating the impact of training programs on employee performance and development helps HR assess and improve its employee experience strategies. This includes pre-and post-training assessments and feedback. A high degree of training effectiveness can enhance employee skills and productivity, while HR can redesign or replace ineffective programs to better meet both employee and organizational needs.
HR tip
Start small and scale up. Begin your workforce analytics journey with a few key metrics that align closely with your organizational goals. As you begin to see and act on results, you can fine-tune your approach and gradually expand the range of metrics you use for more comprehensive workforce analytics.
Workforce analytics examples and use cases
Example 1: Evaluating the impact of employee engagement initiative
An HR manager at a healthcare organization wants to understand if employee engagement initiatives positively influence retention rates. The goal is to determine which engagement activities are the most effective in retaining employees.
The HR manager collects and analyzes data on various initiatives, such as wellness programs, team-building activities, and professional development opportunities. By comparing retention rates before and after implementing these initiatives and correlating them with employee feedback and engagement scores, the HR manager can identify which activities significantly impact employee retention.
Example 2: Predicting a tech company’s future workforce needs
A tech company is experiencing rapid growth and needs the right talent to meet future demands. The HR team uses predictive workforce analytics to forecast staffing needs based on historical hiring data, project timelines, and market trends.
By analyzing past hiring patterns and upcoming project requirements, the HR team predicts the number of software developers, project managers, and support staff the company needs over the next year. This allows the company to proactively recruit and train employees, ensuring they have the necessary skills and capacity to support its growth.
Example 3: Optimizing the recruitment process through data analysis
A retail company wants to reduce the time and cost associated with its recruitment process while improving the quality of its hires. The HR department uses workforce analytics to evaluate the effectiveness of different recruitment channels and methods.
The team tracks metrics such as time to hire, cost per hire, and candidate quality (based on performance reviews and retention rates) for various recruitment sources, such as job boards, social media, and employee referrals. By identifying the most cost-effective and efficient channels that yield high-quality candidates, the HR department optimizes the recruitment strategy, reducing costs and time to hire while improving overall candidate quality.
How Google is effectively using workforce analytics
Google’s People Operations team uses people analytics to derive actionable insights, such as through Project Oxygen, which identifies key behaviors of successful managers.
Similarly, Google’s Project Aristotle uses data to pinpoint the common characteristics of effective teams, focusing on elements like psychological safety and dependability. This has shaped Google’s leadership training and team-building strategies.
Workforce analytics software
There are various companies offering workforce analytics tools and software. Some of these include:
- Comprehensive HR analytics
- Predictive analytics
- Customizable dashboards
- Data visualization
- Interactive dashboards
- Integration with multiple data sources
- Predictive analytics
- Natural language processing
- Automated data preparation
- Workforce planning
- Turnover and retention analysis
- Diversity and inclusion metrics
- Global HR
- Workforce management
- Advanced analytics
- People analytics
- Benchmarking
- Predictive analytics
Workforce planning and analytics: HR tips
HR can use workforce analytics in workforce planning. Some of the areas workforce analytics can help with planning include:
- Identify skills gaps: Use analytics to assess current employee skills and identify gaps to closed through training or hiring.
- Forecast workforce needs: Use predictive analytics to forecast future staffing needs based on business growth projections, seasonal demands, and turnover rates.
- Enhance succession planning: Identify high-potential employees using performance data and engagement metrics to ensure a robust pipeline for key roles.
- Optimize talent acquisition: Analyze recruitment data to determine the most effective sources and methods for attracting top talent.
- Improve employee retention: Use retention analytics to identify factors contributing to employee turnover, and develop strategies to improve job satisfaction and retention.
- Align workforce with business goals: Ensure that workforce planning and analytics are aligned with overall business strategies and goals to drive organizational success.
- Monitor and manage performance: Utilize performance analytics to track employee productivity and effectiveness. This helps HR identify areas for improvement, as well as recognize top performers.
- Budget effectively: Use workforce analytics to inform budgeting decisions, ensuring financial resources are allocated as efficiently as possible to meet workforce needs.
- Enhance employee engagement: Leverage engagement analytics to understand employee sentiment and develop initiatives that enhance employee engagement and morale.
- Support diversity, equity, inclusion and belonging (DEIB): Use analytics to monitor diversity and inclusion metrics to ensure the organization progresses toward its DEIB goals.
Workforce analytics training for HR
As an HR professional, upskilling yourself in workforce analytics can help you make better data-driven decisions. This is where workforce analytics training comes in. Engaging in specialized training programs will improve your ability to analyze and interpret workforce data, leading to more strategic and effective HR practices.
AIHR analytics courses
AIHR offers various analytics certificate programs to help you develop your data analytics skills:
- People Analytics Certificate Program: This comprehensive program covers essential topics in people analytics, including data collection, analysis, and interpretation. It equips HR professionals with the skills they need to implement and leverage analytics effectively in their organizations.
- People Analytics Foundations online course: This course provides a solid foundation in people analytics, focusing on key concepts and practical applications. It’s ideal for HR professionals looking to build a strong understanding of using analytics to drive business decisions.
- HR Data Analyst online course: This course is designed to develop the skills necessary for analyzing HR data. It covers various analytical techniques and tools, helping HR professionals become proficient in data-driven decision-making.
To sum up
Incorporating workforce analytics into your HR practices provides a strategic advantage, enabling data-driven decision-making that aligns with organizational goals. By systematically collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data, you can address challenges proactively, optimize talent management, and improve overall business performance. This approach ensures the right people are in the right roles, enhancing organizational efficiency and effectiveness.
The distinct types of workforce analytics (descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive) offer valuable insights at various stages of the HR process. From understanding current workforce trends to predicting future needs, these analytics tools empower HR teams to make informed decisions that drive success. As the business environment continues to evolve, workforce analytics will remain crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and achieving long-term organizational success.
Weekly update
Stay up-to-date with the latest news, trends, and resources in HR
Learn more
Related articles
Are you ready for the future of HR?
Learn modern and relevant HR skills, online