What is a (Good) Promotion Rate and How To Calculate It

The promotion rate is a key metric that helps HR and business leaders understand how many employees are promoted internally within the company. Knowing how to calculate the promotion rate and benchmark your internal promotion rate against competitors allows businesses to understand how well they are promoting from within and pinpoint areas where promotion policies and practices could be improved.
In this article, we’ll explore what a promotion rate is, how to calculate it using a promotion rate formula, factors that affect it, and strategies to improve the promotion rate in your organization.
Contents
What is a promotion rate?
How promotion rate is calculated and measured
Factors that affect promotion rate
Strategies to improve promotion rate
What is a promotion rate?
A promotion rate is an HR metric that measures the rate or frequency at which employees are promoted to fill open positions within an organization over a specific period.
HR professionals need to understand the promotion rate because it helps determine how effective current promotion policies and practices are and whether any changes need to be made. It can also illuminate employee engagement, leadership development opportunities, inclusion practices, and more.
A high promotion rate suggests that employees are being promoted based on performance and that the business provides ample opportunities for development and growth. It also indicates that the company is experiencing a high level of change. However, a low promotion rate suggests a potential issue with promotion practices and a lack of development opportunities for employees.
The promotion rate can also uncover diversity and inclusion issues by comparing the overall promotion rate to that of diverse employees. Perhaps they leave the company before they reach the promotion level, or they are not being given the same opportunities others are that would put them in the line for a promotion.
Equally, it’s vital to determine whether the promotions happening in your organization are effective and contribute to the organization’s long-term goals. For example, a low retention or performance rate of promoted employees suggests that the company might be promoting the wrong people into the wrong roles, which is costly to the business.
How promotion rate is calculated and measured
To calculate the promotion rate, total the number of promotions made during a specific period, and divide this by your total number of employees. You multiply this by 100 to determine the promotion rate as a percentage.
To calculate promotion rate, use the formula:
(Total number of promotions / Total number of employees) x 100
This could be over the financial year, several months, or any other significant period to your organization. It can also be calculated for the entire organization or a specific team or department.
Let’s say your organization has 200 employees, and 10 were promoted within a year.
The calculation would be: 10 / 200 x 100 = 5%
What is a good internal promotion rate?
Promotion rates vary greatly between industries, and the size, location, and circumstances of the business also play a key factor. Therefore, the best way to determine if your organization has a good internal promotion rate is to compare it to benchmarks. SHRM’s benchmarking report states that the average promotion rate is 6%.
Factors that affect promotion rate
Many internal and external factors can have an impact on promotion rate. Let’s explore these in more detail.
1. Performance evaluation
Employee performance plays a key role in promotion decisions, with top-performing employees more likely to be chosen for promotions and remain engaged and happy at work.
HR professionals can work with managers and use regular performance evaluations to ensure all employees understand their roles, receive constructive feedback, and have all the support needed to achieve professional and personal goals. When employees understand what they need to do to perform and advance in their careers, they are much more likely to succeed.
2. Professional development and training opportunities
In a Gallup study for Amazon, upskilling was listed as the third most important benefit for employees aged 18-24. 94% of employees claim they would remain with an organization longer if it invested in their development. Meanwhile, high-potential employees are always eager to step out of their comfort zone, learn new skills, and grow.
Offering ample professional development and training opportunities to employees helps boost their confidence, makes them feel valued by their employer, and can lead to higher performance, satisfaction, productivity, and team morale.
HR professionals can support employees’ professional development by providing training sessions, workshops, job rotations, mentoring, and coaching to help employees grow and advance in their careers while meeting business objectives.
3. Workplace culture and organizational structure
The shared values, beliefs, and behaviors of an organization greatly influence the overall employee experience. A positive workplace culture can lead to higher sales, profits, productivity, engagement, and team morale, while a toxic culture can have the opposite effect and drive turnover rather than promotion. One study found that organizational structure has a clear impact on employee performance and that building a strong structure helps employees perform better in their role
To determine how the current workplace culture impacts your employees, you can measure employee performance against culture and values and see if improvements need to be made.
HR can influence workplace culture to improve promotion rate by encouraging open communication, transparency, and respect throughout the organization. Ensuring that all employees feel included and have a sense of belonging. Company values can be reinforced during the onboarding process through training and leadership programs.
4. Leadership styles
Managers and business leaders who make employee development a priority are more likely to see greater performance, lower turnover, and greater promotions because employees will have nurtured the skills and qualities needed to succeed in higher-level roles. According to McKinsey, best-in-class organizations that offer approximately 75 hours of training per employee annually also promote their employees at higher rates and enjoy higher retention.
Conversely, leaders who fail to offer development opportunities to employees can see an increase in turnover rate, with McKinsey’s research finding that 41% of employees quit their job due to a lack of career development and advancement.
5. Industry trends
During economic uncertainty or recession, organizations may be less likely to promote employees due to an unclear or limited budget. Changes in the job market can also impact promotion rates in different industries. For example, if a particular industry requires highly skilled employees and there is a small pool of them available, promotion rates may increase as organizations try to retain and nurture this talent.
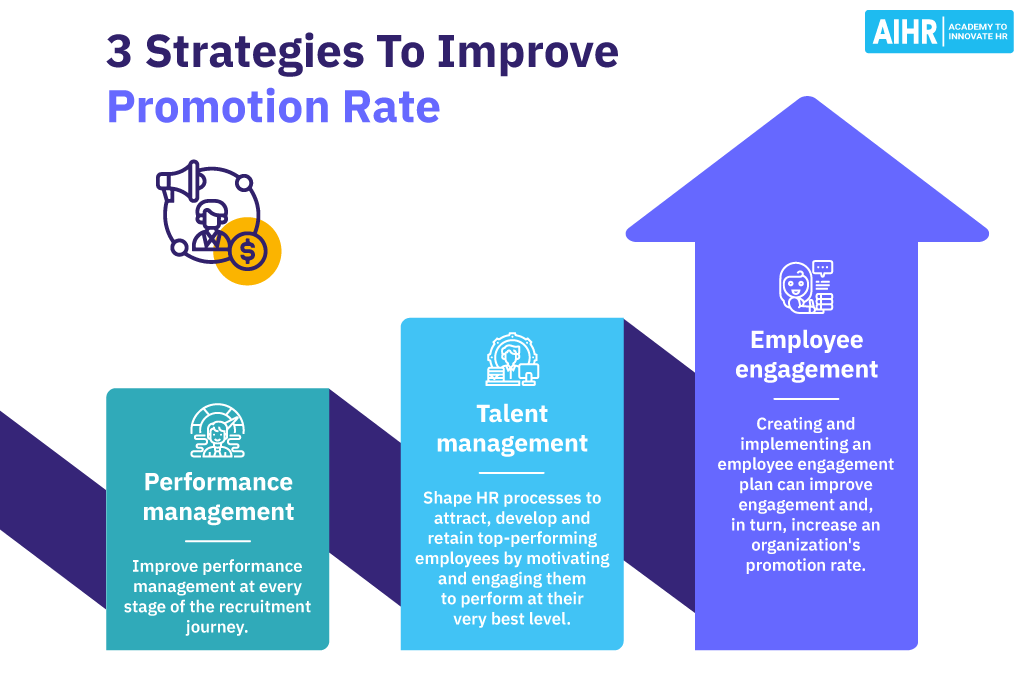
Strategies to improve promotion rate
Here are three core strategies HR can implement to improve promotion rates in an organization.
Performance management
HR can improve performance management at every stage of the recruitment journey. Sitting down with managers to discuss performance goals and expectations for each role and clearly outlining these in job descriptions can help attract aligned candidates. After hiring a candidate, these expectations should be reconfirmed, and SMART goals should be set between the employee and their manager as part of a performance management plan. Actively involve employees in this process to boost motivation and engagement.
HR and managers must continually monitor employee performance, check in with the goals set, and provide employees with constructive feedback on their progress and achievements. Doing this regularly instead of once a year is much more effective and can help highlight any issues sooner rather than later. Plus, this ensures that employees know the organization cares about their development. Be sure to celebrate and reward good performance.
Combining performance metrics with your promotion rate can help you determine the performance of your promoted employees and ensure that the right people are being promoted.
Talent management
The core aim of talent management is to boost performance. The best way to do this is to shape HR processes to attract, develop and retain top-performing employees by motivating and engaging them to perform at their best. These talent management strategies must also align with the organization’s goals, culture, and values. While it is primarily the responsibility of HR to lead talent management initiatives, it requires the support and involvement of managers, executives, and leaders to ensure its success.
By attracting and retaining the right talent, productivity and performance increase, which leads to better results and a competitive advantage. Talent management also includes investing in and deploying training and coaching to develop employees’ skills, which bridges skill gaps, encourages career growth, and helps to build and retain a skilled workforce. Identifying and developing high-potential employees early on and mentoring them to assume key roles in the future plays a large role in effective succession planning, minimizes disruption in the business, and ensures continuity. Talent management strategies also help to retain top performers by prioritizing engagement, development, and recognizing good work, which can reduce turnover.
Defining talent management goals, creating a talent management framework, and deploying a talent management process can help HR identify and develop high-potential employees. Important metrics should be selected to help pinpoint high performers, which can be tracked in a talent management dashboard.
Employee engagement
If an organization is going through a period of significant growth, a low promotion rate may point to other issues, such as a toxic work environment, job dissatisfaction, or low employee engagement. This is why tracking other metrics in addition to promotion rate helps give you a clearer picture of what’s happening in the organization.
Engaged employees are likely to be more productive, likely to stay, have lower absenteeism rates, and drive higher profits for the company. Therefore, it’s important to invest in employee engagement.
Creating and implementing an employee engagement plan can improve engagement and, in turn, increase an organization’s promotion rate. The first step is to conduct a survey to determine how engaged your employees are now. From here, you can determine any common themes and patterns and communicate your findings. Create a list of improvements you’d like to make, and prioritize them based on urgency. What will have the greatest effect on engagement? Will you focus on rewards and recognition for good work, increase learning and development opportunities, or change some of your leave policies?
Set SMART goals for your plan and ensure you are tracking specific metrics that will help you determine the success of your efforts.
Key takeaways
- Promotion rate: promotion rate is a metric that HR uses to measure the percentage of employees who received a promotion over a set period within the organization.
- How to calculate promotion rate: divide the number of promotions by the total number of employees (over a set period) and multiply this by 100.
- Factors that affect promotion rate: the primary factors that affect promotion rate are performance evaluation, professional development and training opportunities, workplace culture and organizational structure, leadership styles, and industry trends.
- Top strategies to improve promotion rate: HR can focus on performance management, talent management, and employee engagement strategies to boost promotion rates.
Weekly update
Stay up-to-date with the latest news, trends, and resources in HR
Learn more
Related articles
Are you ready for the future of HR?
Learn modern and relevant HR skills, online