The Supreme Guide to Sales Compensation in 2024 (+ Plan Examples)

Are you looking to create a sales compensation plan for your company? U.S. organizations spend more than $800 billion each year to manage their sales force, with $200 billion devoted solely to compensation. Almost 80% of U.S. firms revise their compensation structure every two years or less, to better motivate salespeople and to tailor their behavior to the constantly evolving sales environment.
Because sales compensation plans play a vital role in attracting and retaining top sales talent, HR needs to know how to design a competitive and appealing compensation structure that offers attractive incentives and rewards to drive performance and sales results. Compensation structures establish clear goals, determine the right mix of fixed and variable pay, and create benchmarks that motivate salespeople to achieve targets and contribute to business growth.
Contents
What is sales compensation?
Sales compensation models
7 Steps for developing a sales compensation strategy
Sales compensation plan examples
Sales compensation planning: Tips for HR
What is sales compensation?
Sales compensation is a critical aspect of B2B organizations. Structuring the compensation strategy correctly is crucial in motivating and helping the sales team achieve its goals.
A successful sales compensation plan is designed to incentivize salespeople, align their interests with the company’s objectives, and drive business growth. It typically includes a combination of base salary, commissions, bonuses, and performance-based incentives, tailored to the company, industry, and individual roles.
The variable component, such as commissions and bonuses, plays a significant role in a salesperson’s total compensation, reflecting the direct link between sales performance and financial outcomes. In addition, sales compensation plans may incorporate other incentives like profit sharing, stock options, or sales contests. The overarching goal is to motivate salespeople to maximize their performance and contribute to the company’s success.
Determining suitable compensation can be complex due to market conditions, product complexity, customer preferences, and sales cycles. Establishing clear performance metrics, assessing individual contributions, and accurately measuring sales effectiveness are all crucial for determining suitable compensation levels. It’s about balancing motivating salespeople and ensuring the company’s profitability.
Sales compensation models
There are various sales compensation models, which can be can be customized by each company to align with their business goals and sales strategies. Some of these models include:
Sales compensation model Description Salary Sales representatives receive a fixed salary as their primary form of compensation. Commission In a commission-based plan, salespeople earn a percentage of their sales revenue. The commission rate may vary based on factors like sales volume, product category, or customer segment. For instance, a salesperson may earn a 5% commission on each sale. The more they sell, the higher their earnings. Salary + Commission Sales representatives receive a base salary along with a commission based on their sales performance. Tiered commission Sets commission rates based on predefined sales thresholds or tiers. As salespeople surpass each tier, their commission rate increases. This plan provides additional motivation for salespeople to reach higher sales levels. Draw against commission Sales representatives receive a draw or advance on future commissions, which is later reconciled. Profit sharing Rewards salespeople based on the company’s overall profitability. Salespeople receive a percentage of the company’s profits, which may be distributed annually or periodically. This plan aligns the sales team’s efforts with the company’s financial success. Performance-based bonus Rewards salespeople for achieving specific targets or milestones beyond their regular commissions. These targets could include surpassing sales quotas, acquiring new customers, or achieving revenue growth. The bonus amount is typically a fixed sum or a percentage of the achieved target. Sales incentive plan Rewards for meeting or exceeding predetermined objectives or metrics. These incentives can take various forms, such as cash bonuses, gifts, trips, or recognition. Salespeople are motivated to reach specific goals and are rewarded accordingly. Residual income Sales representatives earn recurring commissions or residuals from ongoing customer relationships. Team-based compensation Sales compensation is based on team performance, such as achieving team sales targets. Territory-based Sales representatives are compensated based on the size and profitability of their assigned territory.
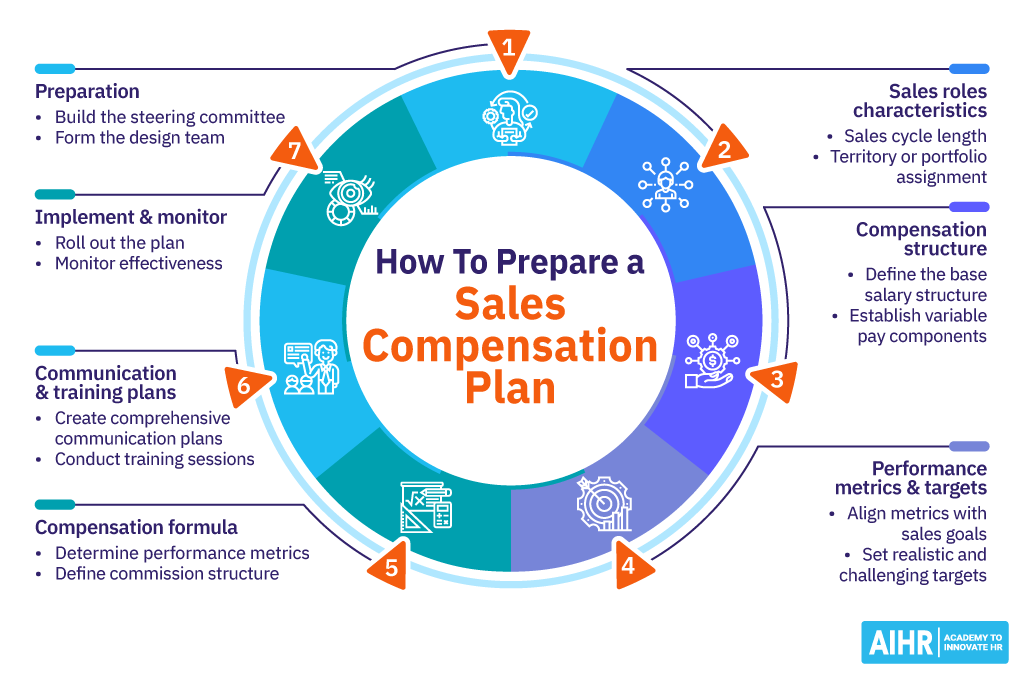
7 Steps for developing a sales compensation strategy
Step 1: Preparing to design a sales compensation plan
- Build the steering committee: The steering committee comprises senior business leaders who will sponsor the project. They are responsible for approving the recommendations developed by the design team and providing guidance throughout the process.
- Form the design team: The design team comprises sales leaders, along with representatives from HR/compensation, finance, sales operations, and compensation administration. This team is responsible for defining the plans’ structure, components, and metrics. Additionally, they ensure effective communication of the plans to the sales force.
- Establish the implementation team: The implementation team is tasked with turning the designed plans into reality. Typically consisting of HR or compensation professionals, sales operations personnel, and compensation administration staff, this team prepares the systems and processes for tracking and reporting of the plan’s measures. They ensure that the incentive plan is effectively implemented and operationalized.
- Establish the overall goals with the business leaders: Collaborate with sales and management teams. Engage in discussions and meetings to better understand their sales strategy, objectives, and priorities. A compensation plan aligned with the broader business goals will support the sales team in achieving desired outcomes.
- Identify specific sales objectives. These can include revenue targets, market penetration goals, customer acquisition metrics, or other key performance indicators relevant to the sales strategy. Defining these objectives will enable you to align the compensation plan to incentivize and reward behaviors that contribute to achieving these goals.
- Understand the sales team: Understanding the sales team allows you to tailor your approach, initiatives, and sales compensation plans to meet their needs. Conducting interviews and surveys to better understand their needs will enhance engagement, optimize performance, and retain talented sales professionals. By viewing the sales team as the ultimate “customer,” you can ensure that you effectively support and enable their success.
Step 2. Determine key characteristics of sales roles
Review and analyze sales roles and responsibilities and list them in a sales role profile. Characteristics include the following:
- Sales cycle length: Some roles may focus on short sales cycles, where deals are closed quickly, while others may handle longer, more complex sales cycles that require sustained relationship-building and multiple touchpoints.
- Territory or portfolio assignment: Sales roles often have specific territories or portfolios assigned to them – a geographic or market area that sales professionals are responsible for, allowing them to focus their efforts and build relationships within their designated area.
- Key accountabilities: Key accountabilities outline the core responsibilities and objectives of the position. These may include prospecting, lead generation, client acquisition, relationship management, achieving sales targets, and customer retention.
- Interdependencies: Understanding the interdependencies between sales and other departments, such as marketing, customer support, or product development, is crucial for effective coordination and alignment.
- Prominence: Some sales roles have a higher profile, dealing with strategic accounts or high-value clients, while others focus on broader market penetration and volume-based sales.
- Incentive measures: These can include commission structures, bonuses, sales targets, or other performance-based rewards. These are designed to align salespeople’s efforts with organizational goals and provide tangible rewards for achieving or exceeding targets.
- Determine eligibility: Once you have your role profiles, it’s important to confirm eligibility, taking into account the qualifications, skills, and experience needed for the role. The key competencies critical for success in the role include communication, negotiation, relationship-building, resilience, and goal orientation.
Evaluate the candidate’s past sales performance to gauge their ability to meet targets and achieve results and look for indicators of success in similar sales roles. Engage candidates in interviews or skills assessments that allow you to assess their knowledge, skills, and suitability for the specific sales role.
Step 3. Develop the compensation structure
Developing a compensation structure for sales roles involves careful consideration of three factors to ensure it aligns with business objectives and motivates sales performance:
- Define the base salary structure: The base salary range for each sales role is based on job responsibilities, experience level, market rates, and internal equity considerations.
- Establish variable pay components: Identify the variable pay components that will incentivize and reward sales performance. Variable pay elements include commissions, bonuses, and incentives tied to individual or team sales targets, revenue generation, customer acquisition, or other relevant metrics.
- Determine the ratio between fixed and variable pay: Decide on the appropriate ratio between fixed and variable pay for each sales role. The ratio will depend on the level of risk and uncertainty in the role, desired performance outcomes, industry norms, and financial considerations.
HR tip
To delve deeper into designing sales compensation plans and enhance your knowledge in compensation and benefits management, explore AIHR’s Compensation & Benefits Certificate Program. It offers valuable insights, practical tools, and best practices to design and implement successful plans.
Step 4. Set performance metrics and targets
Setting performance metrics and targets is crucial in aligning sales efforts with organizational goals and driving motivation among sales professionals. Here’s how to establish effective performance metrics and targets:
- Align metrics with sales goals: Identify key performance metrics that directly contribute to the sales goals. Common sales metrics include sales revenue, new customer acquisition, customer retention rates, average deal size, conversion rates, and sales cycle length.
- Set realistic and challenging targets: Determine performance targets that are both attainable and challenging. Targets should stretch sales professionals but also be realistic based on historical data, market conditions, and other relevant factors. Overly aggressive targets may lead to demotivation or burnout, while easily achievable ones may not drive optimal performance.
- Consider individual, team, and company-wide metrics: Including all metrics will reflect the overall sales performance and its alignment with organizational objectives.
Step 5. Establish compensation formula
A fair and transparent compensation formula is essential to motivate and incentivize sales professionals:
- Determine performance metrics: Identify the performance metrics and targets that will form the basis for variable pay calculations. These metrics should directly align with the sales goals, such as sales revenue, new customer acquisition, or product-specific targets.
- Define commission structure: Choose a commission structure that suits your organization’s needs. Flat rate commissions provide a fixed amount per sale, while tiered rates offer increasing commission based on predefined sales thresholds. Percentage-based models calculate commission as a percentage of the sales value.
- Ensure transparency and clarity: Sales professionals should understand how their variable pay is calculated and the factors that contribute to it. Clear communication and documentation of the formula will help build trust and maintain motivation.
Step 6. Develop communication and training plans
Developing effective communication and training plans is crucial to ensure sales professionals understand and embrace the new compensation plan. Here’s how you can approach it:
- Create comprehensive communication plans: Develop a concise communication strategy outlining key messages, target audiences, and communication channels. Make sure your communication is compelling and easy to understand. Schedule regular communication updates to keep the sales team informed about any changes or updates related to the plan.
- Conduct training sessions: Organize training sessions to provide in-depth explanations of the compensation plan, including how metrics are measured, targets set, and earnings are calculated.
- Address questions and concerns: Create channels for open communication, such as Q&A sessions, surveys, or dedicated email addresses, to allow salespeople to ask questions or express concerns. Develop a comprehensive FAQ document and make it easily accessible. Encourage sales professionals to provide feedback.
Step 7. Implement and monitor the plan
Implementing and monitoring the sales compensation plan is essential to ensure its successful execution and alignment with business objectives.
- Roll out the plan: Ensure a seamless integration of the plan with payroll and HR systems, verifying that accurate calculations and payouts are made on time
- Monitor effectiveness: Track and analyze key performance indicators (KPIs) tied to the sales compensation plan to assess its effectiveness, and gauge whether the plan motivates and incentivizes salespeople appropriately.
- Collect feedback: Gather input from sales professionals and management regarding their experience with the compensation plan through surveys, interviews, or focus groups. Encourage open and honest communication to identify any challenges, concerns, or suggestions for improvement.
Sales compensation plans examples
| Sales compensation plan | Example |
|---|---|
| Commission-based plan | Sarah is a sales representative at a software company. She earns a 10% commission on all software licenses she sells. If she closes a deal worth $50,000, her commission would be $5,000. |
| Tiered commission | John has a tiered commission structure. For sales up to $100,000, they earn a 5% commission; for sales between $100,001 and $200,000, they earn a 7% commission; and for sales over $200,000, they earn a 10% commission. If they generate $250,000 in sales, they would earn $22,500 in commission. |
| Draw against commission | A sales representative receives a monthly draw of $2,000 against future commissions. If they earn $1,500 in commissions for the month, they would still receive the $2,000 draw, creating a deficit of $500 that would be deducted from their commissions in the following month. |
| Profit sharing | In a profit-sharing plan, David’s company distributes 10% of its annual profits among the sales team. If the company’s profit for the year is $1,000,000 and David contributed 20% of the total sales, he would receive $20,000 as his share. |
| Performance-based bonuses | James works for a telecommunications company. If he exceeds his quarterly sales target by 20%, he receives a bonus equal to 5% of the extra revenue he generated beyond the target. |
| Sales incentive plan | Amy’s company implements a sales incentive plan. If she achieves 120% of her monthly sales target, she receives an all-expenses-paid trip to a tropical destination as a reward. |
| Residual income | Clive earns a 10% commission on a subscription-based product. As long as the customer remains subscribed, the sales representative continues to receive 10% of the monthly payment as residual income. |
| Team-based compensation | A sales team is assigned a collective sales target. If the team achieves the target, a bonus is distributed among team members based on their individual contributions. |
| Territory-based compensation | Ryleigh is assigned a specific territory and is compensated based on the sales revenue generated within that territory. For example, if their territory generates $1,000,000 in sales and they have a 2% commission rate, they would earn $20,000 in commission. |
Sales compensation planning: Tips for HR
HR plays a crucial role in designing and implementing sales compensation plans. Here are HR’s key responsibilities:
- Understanding business objectives: By collaborating with the sales and leadership teams, you’ll understand the company’s sales strategy, business goals, and sales force requirements. This involves analyzing market conditions, sales targets, competitive landscape, and the organization’s financial objectives.
- Designing compensation structure: Working closely with sales and finance, you can design a sales compensation structure that aligns with the company’s objectives. This includes determining the appropriate mix of base salary, commissions, bonuses, and other incentives. It’s your responsibility to ensure that the compensation plan is competitive, motivating, and supports retention and recruitment efforts.
- Market research and benchmarking: Conducting market research and benchmarking studies will allow you to gather data on industry standards, competitor practices, and compensation trends in sales roles. This will help you to develop a fair and attractive compensation package.
- Establishing performance metrics: Collaborating with sales leadership will help you define performance metrics and targets that reflect sales objectives. Metrics include revenue targets, sales volume, customer acquisition, customer retention, or other key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to the sales function.
- Ensuring compliance and fairness: Consider minimum wage, overtime, discrimination, and other employment regulations. It’s your responsibility to ensure fairness and equity within the sales compensation structure.
- Communication and training: Document plan details, performance metrics, and payout calculations clearly. Conducting training sessions and giving resources to sales professionals will help them understand how the compensation plan works and how they can maximize their earnings.
- Performance evaluation and review: Review the compensation plan’s effectiveness, identify improvement areas, and propose modifications as needed. Performance reviews can provide guidance on promotions, bonuses, or adjustments to compensation.
- Administration and payroll processing: By overseeing the administrative aspects of sales compensation, such as maintaining records, calculating payouts, and coordinating with the payroll department, you can ensure accurate and timely payment of commissions and bonuses.
To sum up
Sales compensation plays a crucial role in driving sales performance and motivating sales professionals. HR professionals are vital in developing effective sales comp plans that align with business objectives and engage the sales team. You can create impactful sales compensation strategies by understanding the intricacies of sales roles, setting performance metrics, establishing a fair compensation structure, and implementing clear communication and training plans.
Weekly update
Stay up-to-date with the latest news, trends, and resources in HR
Learn more
Related articles
Are you ready for the future of HR?
Learn modern and relevant HR skills, online