How To Develop a Generative AI (ChatGPT) Policy + Free Template

Given the rapid and often ad hoc adoption of ChatGPT and other generative AI platforms, it’s time for organizations to establish a generative AI policy.
While OpenAI’s ChatGPT and similar large language models are quickly finding their way into enterprise workflows, organizations have concerns about generative AI presenting incorrect conclusions, as well as data privacy and security. That’s why whether, when, and how to adopt generative AI should not be left to individual employees’ judgment.
In this article, we’ll dive into all you need to know about creating a generative AI policy for your business, as well as provide a free-to-download AI usage policy template.
Contents
What is generative AI (ChatGPT)?
Why do organizations need a generative AI policy?
Examples of companies implementing generative AI policies
How to develop a generative AI policy
AI usage policy template
What is generative AI (ChatGPT)?
ChatGPT, OpenAI’s text-generating AI chatbot, has taken the world by storm. On its release, it became the fastest-growing app in history, prompting Big Tech to launch other AI chatbots in response.
The language model can answer questions and assist people with various work tasks, such as brainstorming ideas, composing emails and content, writing code, and analyzing data based on short text prompts. By augmenting individuals’ existing skills and abilities, it’s enabling organizations to work smarter and boost productivity.
But it also has a dark side. Generative AI can also make stuff up, a phenomenon known as AI hallucinations. It can generate inaccurate or false data and make incorrect inferences from existing data.
The challenges with ChatGPT, therefore, lie in ensuring content quality, navigating ethical concerns, and minimizing the risk of producing misleading, fake, or downright nefarious content.
How are employees using ChatGPT (and other generative AI) at work?
Employees are increasingly integrating ChatGPT and other generative AI tools into their daily workflows. In content creation, these AI models assist in drafting articles and ad copy and enhancing written content.
They’re also prominent in customer support, acting as frontline chatbot solutions to answer FAQs, guide troubleshooting, and improve the overall customer experience. In research and data analysis, generative AI helps predict patterns, simulate scenarios, and offer insights from massive datasets.
In creative departments, generative AI aids in brainstorming and generating innovative design concepts. Developers use AI tools for coding assistance, bug detection, and software optimization. HR professionals deploy them for a variety of tasks, such as recruiting, onboarding, and people analytics.
The potential applications are vast. As generative AI technology advances, its incorporation into various job functions is set to expand, refining and reinventing traditional work processes and enhancing existing workflows.
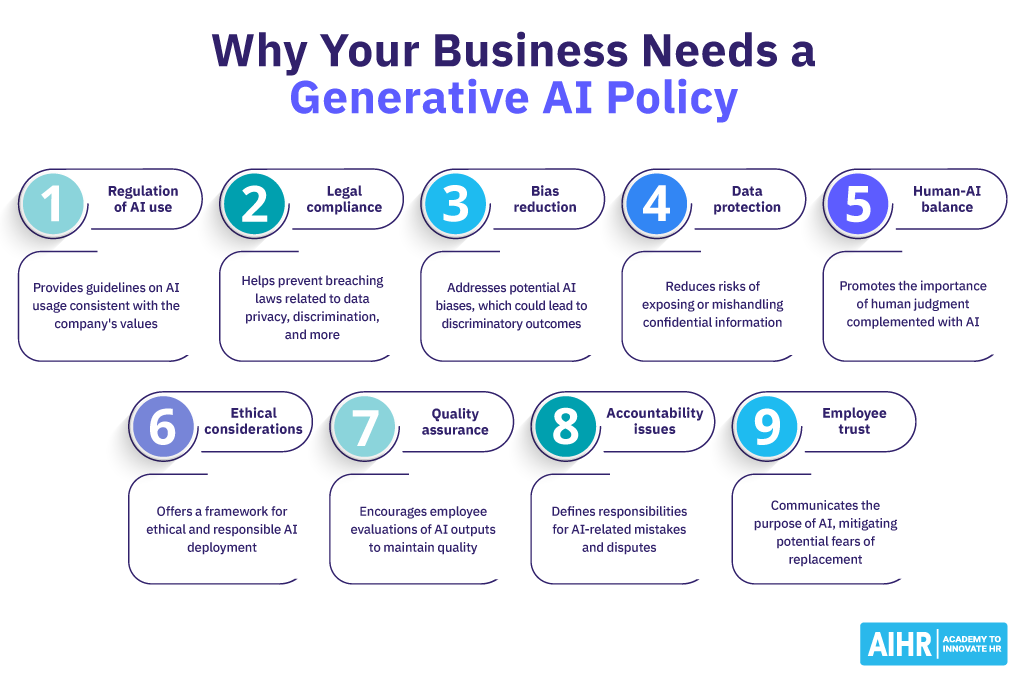
Why do organizations need a generative AI policy?
Without providing guidance to their employees on how to use generative AI in the workplace, organizations are risking misuse, ethical dilemmas, decreased productivity, and potential harm to their reputation.
Let’s take a closer look at the benefits of having a generative AI policy:
- Regulating how employees use AI at work: A generative AI policy lays out guidelines for how workers can utilize AI in a way that’s consistent with the company’s values and ethical standards.
- Preventing legal violations: Without proper oversight, organizations might unknowingly breach laws related to data privacy, discrimination, or other areas. For example, New York City’s Automated Employment Decision Tool law mandates employers to regularly conduct third-party audits of their AI recruitment technology.
- Reducing bias and discrimination: AI models might replicate or even amplify biases present in their training data. This can result in biased or even discriminatory outcomes, for example, if AI is used for hiring. A generative AI policy can address how to use AI in decision-making.
- Protecting sensitive data: A robust generative AI policy minimizes the risk of unintentionally exposing, misusing or mishandling confidential employee or company information, which could lead to breaches of trust and potential legal consequences.
- Balancing human and AI input: The policy underscores the irreplaceable value of human expertise, promoting a balanced approach where AI complements, rather than replaces, human judgment, especially in nuanced scenarios.
- Addressing ethical concerns: With clear ethical guidelines in place, a generative AI policy provides a framework for responsible AI deployment, striking a balance between efficiency, transparency, and privacy of employees and customers.
- Monitoring quality and accuracy: Having a policy prompts organizations and employees to regularly evaluate and validate AI outputs. This mitigates misinformation, poor decisions, and subpar outputs.
- Promoting accountability and responsibility: A clear AI policy defines a path of accountability and responsibility to effectively and quickly handle situations where AI makes mistakes or causes harm, which helps prevent internal disputes or legal challenges.
- Fostering employee trust: By transparently communicating the purpose and limitations of AI tools, the policy reassures employees, mitigating fears of replacement or excessive monitoring, and upholding organizational morale.
Effective regulation and oversight of AI use in the workplace through a generative AI policy can help mitigate these risks, ensuring that the technology is used responsibly and ethically.
Examples of companies implementing generative AI policies
Samsung bans AI use after spotting ChatGPT data leak
In May 2023, Samsung banned its employees from using generative AI tools like ChatGPT. The ban came after the company discovered that their staff uploaded sensitive code to these AI platforms.
Samsung was concerned that data sent to AI platforms like ChatGPT is stored on external servers, making it hard to retrieve and delete, and that this data could potentially be disclosed to other users. All inputs are part of the technology’s learning protocol, making the act an issue of intellectual property.
Expedia deploys ChatGPT widely
Expedia Group is using AI to simplify the travel experience for travelers and B2B partners. The travel company says three critical elements are required for generative AI to be successful – a solid tech platform, high-quality data, and an AI-first culture.
The organization integrated OpenAI’s ChatGPT into the Expedia app to provide conversational trip planning. They also simplified air credit redemption, making it easier for travelers to book flights and use their air credits.
Powered by natural language processing, its Virtual Agent helps travelers resolve queries and has saved significant operational costs. The investment in tech transformation and AI has delivered value by enabling rapid product development, efficiency, creativity, and growth.
Expedia keeps a close watch on governance, ethics, and privacy considerations on sharing any of its information. The focus is on working together as a concrete community to use AI for good and make sure best practices are applied across the industry.
Salesforce combines AI models with CRM data
Salesforce’s Einstein GPT is an AI tool integrated within the Salesforce platform. It combines public and private AI models with CRM data, allowing users to ask natural-language prompts and receive AI-generated content. Real-time data is fed into these models from Salesforce clouds and the Salesforce Data Cloud to unify customer data.
The Einstein GPT Trust Layer ensures data privacy and security by preventing sensitive customer data from being retained by large-language models (LLMs). This has set a new industry standard for trusted enterprise AI – offering the benefits of generative AI while providing data privacy and data security.
How to develop a generative AI policy
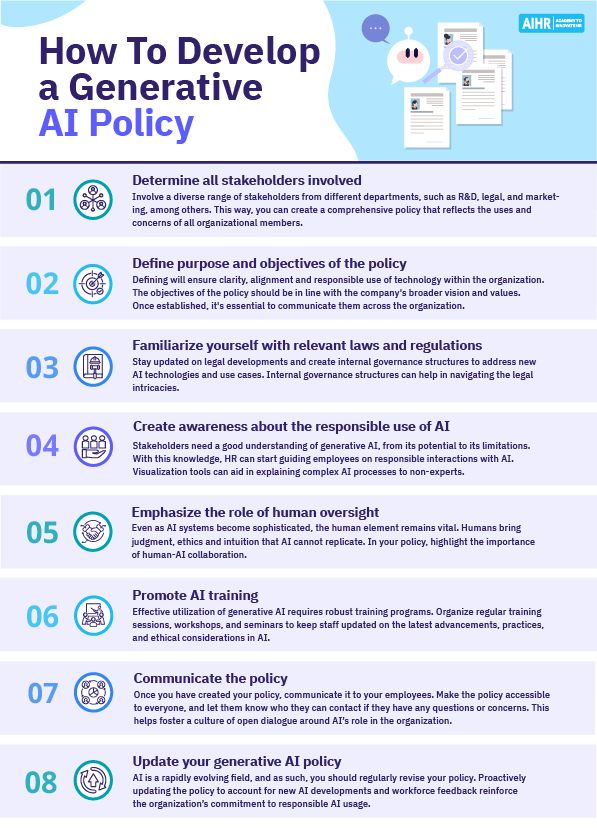
Creating a generative AI policy for your workforce is a complex task with many considerations to be made. Here are 8 steps you can follow to successfully implement the new policy:
1. Determine all stakeholders involved
Engaging a diverse range of stakeholders allows you to create a policy that’s comprehensive and aligned with organizational goals as well as global trends and regulations.
Determine who will be impacted by the policy, such as employees from different departments, contractors, and leadership. You need to understand what your stakeholders use generative AI for to determine clear user guidelines.
Engage representatives from all parts of the organization, including AI research & development, risk and compliance, legal, communications, marketing, and sales.
Tip: Regularly convene this group to gather feedback and review the policy. This helps you keep the policy relevant and up-to-date in the rapidly evolving AI landscape.
2. Define purpose and objectives of the policy
Defining the purpose and objectives of a generative AI policy serves as its foundational pillar, determining its direction and guiding principles. This ensures clarity, alignment, and responsible use of the technology within your organization.
Objectives are the actionable goals that your organization aims to achieve through the policy. They offer specific, measurable outcomes or principles that guide the implementation and application of the technology.
The objectives of the policy should be in line with the company’s broader vision and values. Once established, it’s essential to communicate them across the organization.
Tip: When drafting specific objectives, consider ethical AI use, transparency, data privacy, security, oversight, and continuous learning.
3. Familiarize yourself with relevant laws and regulations
A crucial factor you need to consider when determining how your workforce will use generative AI are the laws and regulations your organization needs to comply with. For example, you might include restrictions on what your employees cannot use AI for.
Privacy laws, both in the US and internationally, impose requirements on data collection, use, and sharing related to AI systems. These privacy laws include:
- The right to opt out of automated profiling
- Public disclosures of automated profiling and inferences
- Consent to use
- Restrictions on sharing with third-party AI platforms
- Chatbot disclosure laws
- Rights to delete, access, and correct personal data
Principles such as purpose limitation, data minimization, and avoiding dark patterns are also relevant to AI system use cases.
Consider how these laws and regulations will impact the users of generative AI at your organization. Then, you can address this in your policy.
Tip: Stay updated on legal developments and create internal governance structures to address new AI technologies and use cases.
4. Create awareness about the responsible use of AI
Your stakeholders need a good understanding of generative AI, its capabilities, potential use cases, risks, and benefits to use it responsibly.
The models are trained to recognize small-scale and overarching patterns and relationships in datasets that come from all kinds of sources, including the internet, books, image libraries, and more.
Generative AI and ChatGPT models are ‘black-box’ – they don’t provide any explanation for how they’ve arrived at a conclusion. Not even the companies behind them can fully explain how exactly they work.
By fostering this foundational knowledge, HR can start guiding employees on responsible interactions with AI.
Tip: Use visualization tools that can represent how AI models generate results in a simplified form. This makes complex AI operations more accessible and easier to understand for non-experts.
5. Emphasize the role of human oversight
Even as generative AI systems become increasingly sophisticated, the human element remains irreplaceable in responsible AI deployment. Human involvement offers a layer of judgment, ethics, and intuition that AI, regardless of its complexity, cannot replicate.
In your generative AI policy, highlight the importance of human-AI collaboration.
Humans can discern context, cultural nuances, and subtle implications in ways that AI can’t. By including human oversight in using AI, your organization can mitigate risks, uphold ethical considerations, and guarantee that decisions align with organizational values and societal norms.
You also need to put accountability mechanisms in place. They should establish clear lines of responsibility to address and rectify any issues when AI systems errors produce unintended outcomes.
Tip: Implement a “red teaming” approach, where a dedicated team regularly challenges and tests AI outputs, much like a devil’s advocate. This encourages a culture of scrutiny and can identify unforeseen flaws or biases in the AI system. That way, you’re empowering your teams to make decisions that are both data-informed and ethically sound.
6. Promote AI training
Proper training around using generative AI allows team members across various departments to better appreciate and utilize its potential. You should also make this a point in your policy.
Only 14% of employees are reporting receiving training on using AI tools, while 86% say they need such upskilling.
Consider putting together an awareness session to highlight the broader societal implications, biases, and concerns related to AI. You need your employees to be not just technically proficient but also ethically aware.
Organize regular training sessions, workshops, and seminars to keep staff updated on the latest advancements, best practices, and ethical considerations in AI. Cater to a broad audience, from technical teams directly working with AI to non-technical staff who might interact with or be impacted by AI outputs.
Tip: Implement a digital badge or certification system for AI training within your organization. This not only incentivizes employees to participate actively, but also tracks and showcases their AI proficiency.
7. Communicate the policy
Once you’ve created your generative AI policy, it’s time to put it to use. Communicate to your employees and leadership what the main objectives of the policy are, what it covers, and where they can find it.
Make the policy accessible to everyone in the company. For instance, you can upload it to your organization’s intranet or internal wiki and then share a company-wide update with a link. You can also ask managers to remind their team members about the new or updated policy.
Let employees know who they can contact if they have any questions or concerns. This helps you foster a culture of open dialogue around AI’s role in the organization.
Tip: Use different multimedia tools, such as infographics, to make the policy communication more engaging and easier to understand. This can help ensure better retention and comprehension by employees.
8. Update your generative AI policy regularly
Your generative AI policy is not a static document. With rapid developments in the world of AI, you need to regularly revisit the policy to make sure that it stays aligned with the latest AI developments, emerging ethical considerations, and feedback from the workforce.
Such proactive updates reinforce the organization’s commitment to responsible AI usage. They also instill confidence in employees, assuring them that their interactions with AI are governed by a contemporary and responsive framework.
Tip: Set up a review cycle for the policy and include a diverse group of stakeholders in the review process. This ensures that multiple perspectives are considered during updates.
Generative AI usage policy template
To sum up
Developing a generative AI policy is essential if you want to make sure that your employees use ChatGPT and other AI technologies in a responsible and ethical way. Such a policy sets clear guidelines for using AI at work for your workforce and helps employees navigate the complexities of the technology.
By creating a comprehensive and transparent policy, organizations can harness the power of AI while reducing the risks of misuse and ethical challenges.
Weekly update
Stay up-to-date with the latest news, trends, and resources in HR
Learn more
Related articles
Are you ready for the future of HR?
Learn modern and relevant HR skills, online