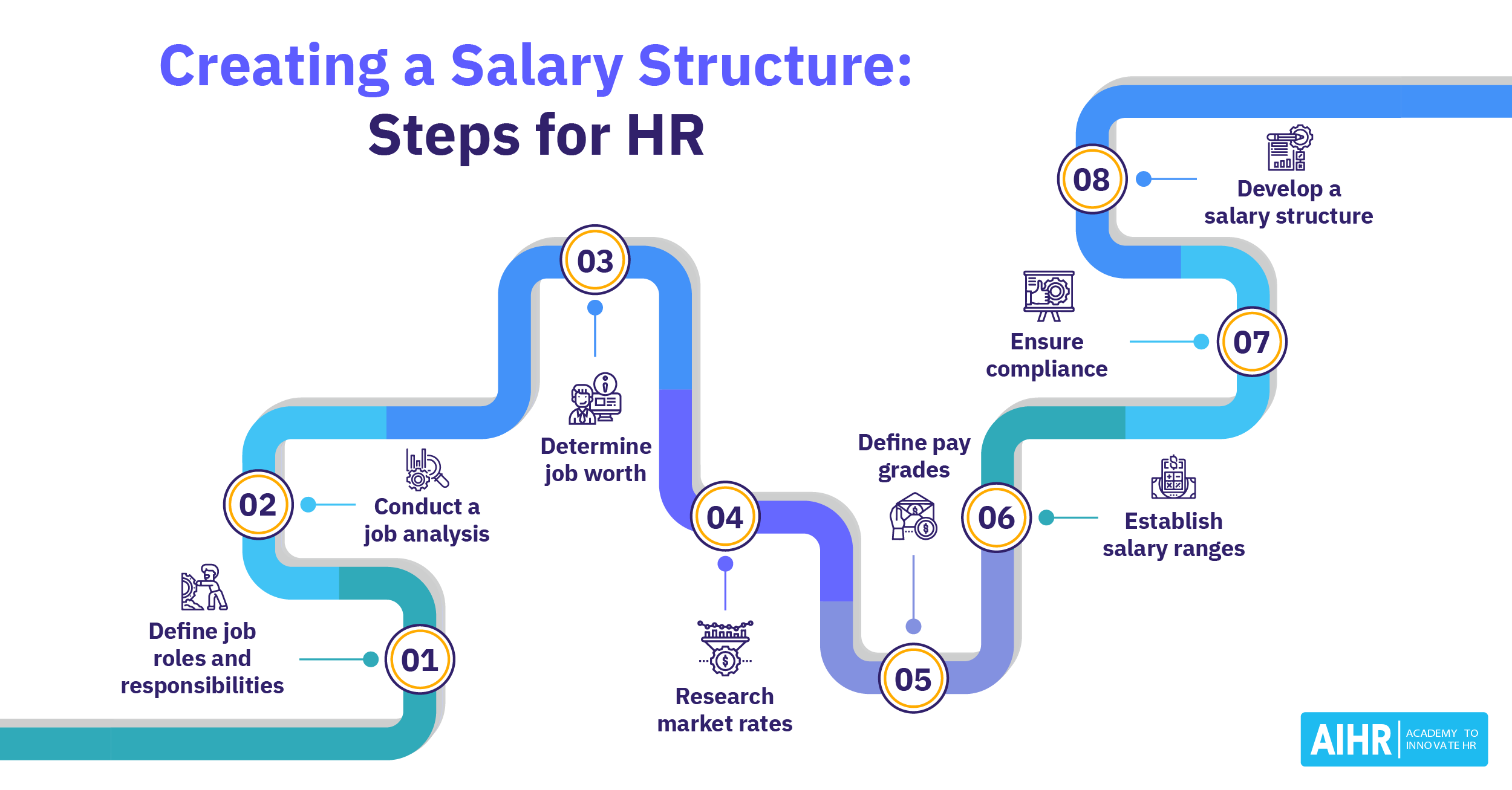
Job Pricing
What is job pricing?
Job pricing refers to the process of determining the appropriate compensation level for a specific job within an organization. This involves assessing the job’s responsibilities, required skills, and its value to the organization, as well as comparing it against similar roles in the job market. The primary goal is to set a competitive, fair salary that attracts and retains talent while aligning with the company’s budget and compensation strategy.
The importance of job pricing
Job pricing is important for several reasons, particularly for fair compensation and organizational efficiency.
Here are some reasons why job pricing is essential:
- Fair compensation: This helps ensure that employees are paid fairly for their work. By assessing the responsibilities, skills required, and effort of each job, organizations can establish a compensation structure that pays employees in proportion to the value of their contributions.
- Budgeting and financial planning: Understanding the value of different jobs helps make informed budgetary decisions and ensures that salary allocations align with business objectives.
- Organizational structure and development: Job pricing is critical in designing an organizational structure that aligns with the company’s goals. It assists in clarifying job roles, expectations, and career paths.
- Enhances negotiation power: With a clear understanding of the value of each job, HR professionals and managers are better equipped to negotiate salaries and benefits, both with existing employees and new hires.
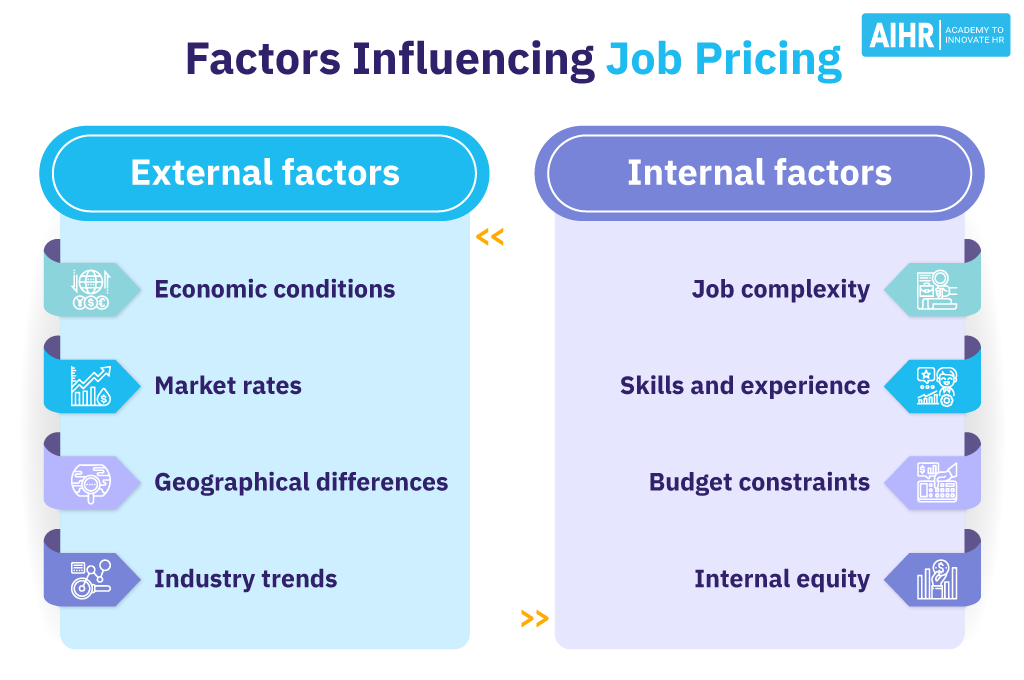
Factors influencing job pricing
Understanding the factors influencing job pricing can help organizations attract and retain talent while ensuring fairness and competitiveness.
External factors
External factors are those that exist outside the organization and typically influence industry-wide compensation standards. These include:
- Economic conditions: The economy’s overall health can significantly impact job pricing. In a strong economy, businesses may offer higher salaries due to increased demand for goods and services, whereas in a recession, salary increments may be lower or stagnant.
- Market rates: The supply and demand for specific skills in the labor market can drive salaries up or down. High demand for scarce skills can lead to higher pay, while many candidates with similar skills might lower salaries for those positions.
- Geographical differences: The cost of living and prevailing wage rates in different regions affect job pricing. For example, jobs in urban areas typically pay more than similar roles in rural areas due to the higher cost of living.
- Trends in the industry: Sector-specific trends can also influence job pricing. For instance, emerging technologies might lead to higher pay in the tech industry due to the need for advanced skills and expertise.
Internal factors
Internal factors are controlled within the organization and can vary widely from one company to another based on their strategies, policies, and practices:
- Job complexity and responsibilities: The level of responsibility, the complexity of tasks, and the required skill set for a job typically correlate with higher pay.
- Skills and experience required: Positions requiring rare skills or high levels of experience tend to be priced higher to reflect the limited availability of suitable candidates.
- Budget constraints: An organization’s financial health and budget allocations can limit how much they can afford to pay their employees.
- Internal equity: This refers to the fairness of pay within the organization. Maintaining internal equity makes sure that employees in similar roles and responsibilities receive comparable pay.
Job pricing example
Let’s say a company is hiring for a marketing manager position. After conducting market research and evaluating the job responsibilities, required skills, and qualifications, they determined that the market salary range for this position is $70,000 to $90,000.
Based on the internal equity principle, the company ensures that its current marketing manager is already paid within this range. They also consider the candidate’s experience and qualifications during salary negotiations and offer a final salary of $85,000.
HR strategies for determining job pricing
HR plays an essential role in determining job pricing to ensure fair compensation and align organizational goals with employee rewards. Here are some effective strategies to put into practice:
- Conduct comprehensive job evaluations and analysis: Analyze and evaluate job responsibilities and complexities to understand and rank each position’s value within the organization.
- Benchmark against the market: Use salary surveys and benchmarking against similar positions in the industry to ensure competitive compensation.
- Establish pay grades and salary ranges: Create structured pay grades that group similar jobs within defined pay ranges and ensure regular updates to these structures.
- Ensure internal equity: Maintain internal equity by ensuring similar job roles are compensated fairly and consistently.
- Consider total compensation: Factor in all forms of compensation, including base salary, bonuses, and benefits, to provide a complete package that is attractive to current and prospective employees.
- Factor in organizational strategy and goals: Align job pricing with the organization’s strategic objectives, ensuring that compensation structures support overall business goals and encourage desired outcomes.
HR tip
Streamline job pricing with specialized compensation management software. These tools can automate data collection and analysis, help maintain up-to-date market pricing, track compensation trends, and ensure compliance with budget and equity policies. Embracing technology saves time, boosts accuracy, and enhances efficiency in compensation management.
FAQ
Job market pricing is the process of establishing a salary based on the compensation rates for similar positions in the external labor market. It involves using data from salary surveys and industry reports to ensure competitive and equitable pay rates.
To price a job position effectively:
• Conduct a detailed job analysis to define job responsibilities and requirements.
• Use salary surveys to benchmark against similar roles in the industry.
• Consider factors like location, company size, and industry sector.
• Align salary data with the organization’s compensation strategy and ensure internal equity.
• Adjust the total compensation package, including base salary, benefits, and incentives, to attract suitable candidates.