Disciplinary Infraction
What is a disciplinary infraction?
A disciplinary infraction is a breach of conduct within an organization involving violating employer rules, procedures, or general standards of behavior.
While less serious than gross employee misconduct, it can result in disciplinary action if not appropriately addressed. Some examples may include repeatedly arriving late, failing to follow management instructions or neglecting assigned duties.
A disciplinary infraction is documented through a verbal or written warning to clearly record the offense and serve as notice that corrective action must be taken. Mandatory additional training may also be required to ensure the employee understands workplace policies and procedures fully. Sometimes, a performance improvement plan is put in place to closely monitor conduct and address issues over a set time period.
What is a minor infraction?
Unlike gross employee misconduct, which can lead to immediate dismissal, a minor infraction is typically a first-time breach or inadvertent offense that can be addressed through coaching or additional training. For instance, a verbal reminder of company policy would suffice for an employee who occasionally uses the office printer for personal documents if the policy prohibits its use without authorization.
Another example is an employee who wears sneakers in a company that only allows formal dressing. A friendly reminder of the expected dress code would remedy such a minor infraction.
Does disciplinary infraction mean fired?
A disciplinary infraction on its own does not automatically lead to termination. It formally documents issues and applies appropriate punitive measures short of a dismissal. Firing is often a last resort if repeated infractions show that the employee is unwilling or unable to meet conduct standards despite warnings and support.
Firing someone also requires due process to avoid unfair dismissal claims. It’s crucial to follow internal termination policies and engage appropriate levels of management approval before termination. Notifying the employee in writing, including reasons and their right to appeal, helps demonstrate fairness. Without due process, even a repeat offender may successfully argue that they were dismissed arbitrarily without a fair chance to remedy issues.
In the U.S., cell phone policies in the workplace are diverse, with some companies (like Amazon and FedEx) enforcing strict rules that can lead to disciplinary actions if violated. While phones are crucial in certain jobs, they pose security risks and distractions in others. About 52% of individuals don’t secure their phones, increasing the risk of information leaks in workplaces.
Disciplinary infraction examples in the workplace
Disciplinary infractions in the workplace can take various forms, and it’s important for both employers and employees to understand these to maintain a professional and productive work environment. Here are some common disciplinary infraction examples:
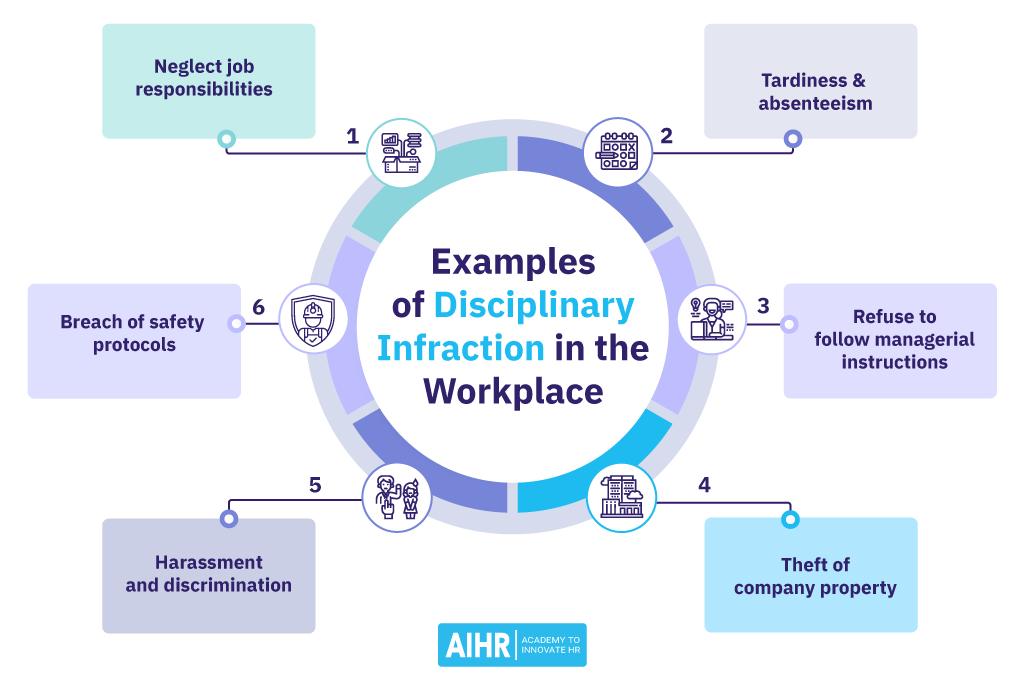
1. Neglecting job responsabilities
This occurs when an employee fails to complete their assigned duties or does not meet the expected standards of their role. It could be due to missing deadlines, leaving tasks unfinished, producing poor quality work, or needing frequent correction.
Additionally, neglect can be seen in employees who show little to no effort in addressing problems or improving their performance after feedback, or those who carry out personal activities during work hours.
2. Tardiness and absenteeism
Repeatedly arriving late to work without a valid reason can be seen as a disciplinary infraction. This includes arriving late to work or meetings on a regular basis, missing work without prior notification, and excessive use of sick days, especially without medical documentation.
The consequences of such behavior are serious, as they can disrupt workflow, burden colleagues who may have to cover the absent employee’s duties, and negatively impact business operations.
3. Insubordination
Insubordination happens when an employee willfully disobeys or disregards managerial instructions or shows disrespect to someone in a position of authority. It can take the form of deliberately refusing to complete a task related to the job, publicly challenging or criticizing management decisions, or consistently ignoring requests from meetings, updates, or feedback sessions.
4. Theft of company property
This involves any act of unauthorized taking, use, or misappropriation of company assets, resources, or property, as well as other colleagues’ personal belongings. It can range from relatively minor items like office supplies to more significant thefts such as embezzling company funds, stealing confidential information, or taking high-value physical assets.
Theft also encompasses stealing intellectual property, where an employee might illegally copy or distribute proprietary company data, software, or trade secrets.
5. Harassment and discrimination
Harassment refers to any unwanted behavior that makes someone feel intimidated, dangreaded, humiliated, or offended, and it can be seen as a serious disciplinary infraction. This type of misconduct can be physical, verbal, or nonverbal and might include actions like making derogatory remarks, spreading malicious rumors, or engaging in aggressive behavior.
Anti-harassment policies must be clearly defined to set expectations and ensure understanding around inappropriate behaviors.
6. Breach of safety protocols
This occurs when an employee violates established safety rules and procedures, such as not wearing required protective equipment or bypassing safety checks on machinery. It also includes actions that put others at risk, like leaving hazardous materials improperly stored.
Breaching safety protocols can have severe consequences, including the risk of accidents and injuries, legal liabilities, and potential harm to the company’s reputation.
What HR can do to manage disciplinary infractions
Employee disciplinary infractions can be one of the most challenging aspects of HR, as they play a central role in ensuring fairness, consistency, and compliance with legal and organizational policies. Here are some tips to get your team started:
- Conduct a fair investigation into the matter to ensure all sides are heard, so HR can evaluate the facts objectively. Witness accounts may be collected through interviews and evidence reviewed impartially. Even for clear-cut infractions, taking time for a dialogue shows respect and can provide helpful context.
- Formally document the infraction and disciplinary action taken to establish a performance baseline in case issues reoccur or escalate. Employees also need transparency about consequences to handle the process seriously.
- Establish clear performance improvement plans for minor first-time infractions. This gives staff an opportunity to correct their behavior within a specified timeframe, under guidance, before more severe measures are considered.
- Regular follow-ups are essential to assess the success of any remedial actions. This also shows the employee that the management is advocating for their success rather than setting them up for failure.
- Allow employees the right to appeal disciplinary decisions, especially in cases that involve severe repercussions like suspension or termination.
HR tip
To prevent disciplinary infractions and employee misconduct, HR should ensure workplace policies are clear to all employees. This involves providing all staff with accessible policy documents and conducting regular refresher sessions to answer questions and address any gaps in understanding. HR must also consistently enforce policies to demonstrate their importance.
FAQ
The term ‘infraction’ refers to employees breaking organizational rules or regulations covered under HR guidelines, employee handbooks, code of conduct policies, or through employment agreements. Infractions are typically categorized based on their severity and the impact they have on the workplace environment, colleagues, or the business itself. For example, a minor infraction might be something like a failure to adhere to a dress code, while a more serious infraction could involve breaches of safety protocols or ethical guidelines.
A major disciplinary infraction is a serious violation of a company’s rules or policies. These infractions are considered more severe due to their potential impact on the business, employees, clients, or the company’s reputation. Examples are theft, harassment, substance abuse, and discrimination, among others. Such infractions often result in immediate and serious disciplinary action, which can range from suspension to termination of employment.
Disciplinary action refers to the measures taken by an employer against an employee who has violated company policies, rules, or standards of conduct. The nature and severity of disciplinary actions can vary widely depending on the seriousness of the infraction, the employee’s history, and the company’s policies.
Disciplinary action against an employee starts with less severe measures like verbal warnings and write-ups for minor infractions, escalating to more serious consequences for repeated or severe misconduct. The escalation can include performance improvement plans, suspension, and ultimately, termination of employment in cases of gross misconduct or when other measures fail.