Delegative Leadership
What is delegative leadership?
Delegative leadership is a style of management in which a leader delegates tasks and responsibilities to their team while enabling autonomy to make decisions and take ownership of the project.
Sometimes, it’s referred to as laissez-faire leadership; however, there can be subtle differences. Laissez-faire leadership can imply a leader’s complete hands-off approach, while delegative leadership might involve a leader who is more involved but still allows significant autonomy.
The delegative leadership style
Delegative leadership is all about giving team members the power to make decisions and take ownership of tasks. Leaders can provide guidance and support, but the ultimate decisions are left up to employees.
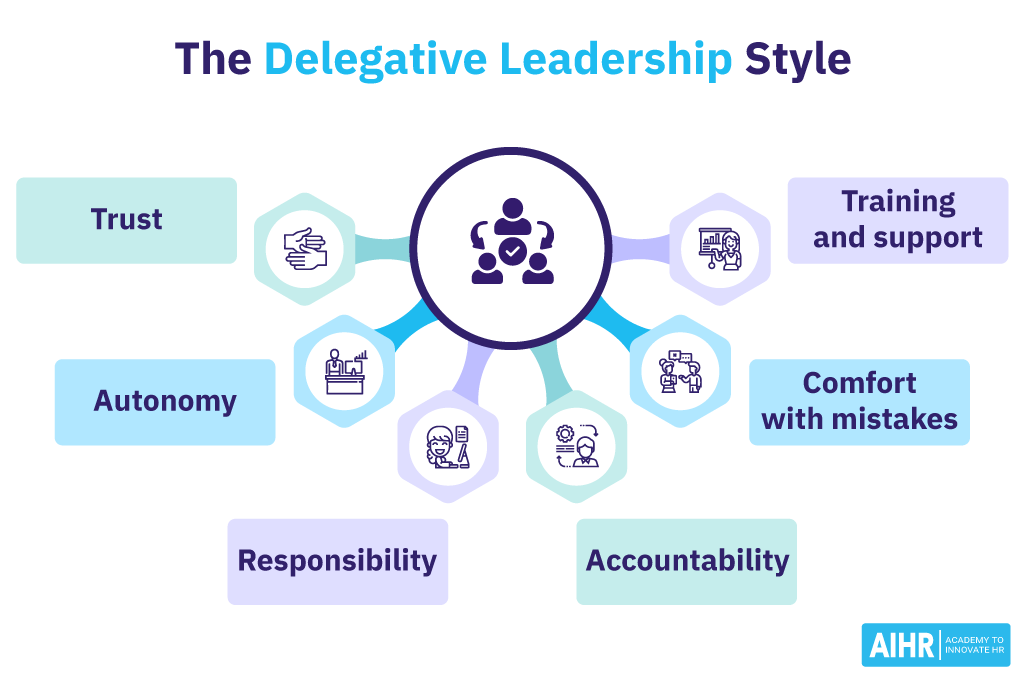
Below is a closer look at the key characteristics that define the delegative leadership style.
- Trust: Leaders must trust their team members to make decisions and take ownership of tasks.
- Autonomy: Team members have the freedom to make decisions without interference from the leader.
- Responsibility: Employees are held responsible for their own decisions and actions.
- Accountability: Team members are held accountable for their work and results, encouraging them to take ownership and initiative.
- Comfort with mistakes: Mistakes are seen as a part of learning and growing, so team members are encouraged to take risks and learn from any mistakes they make.
- Sufficient training and support: Leaders must provide adequate training and support to ensure team members have the skills to make decisions and complete tasks.
Delegative leadership pros and cons in the workplace
As with all leadership styles, delegative leadership has both advantages and disadvantages. Here are some pros and cons to consider when using this management style in the workplace.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| • Increased motivation: Employees have autonomy and decision-making power, which can increase their motivation to complete tasks. • Improved creativity: Team members can get creative with their ideas, enhancing innovation and problem-solving. • Boosted morale: Employees feel empowered and valued, leading to increased confidence and job satisfaction. | • Lack of control: Leaders may lack the required control over employees, resulting in a lack of accountability and structure. • Potential for disaster: Without proper guidance or training, team members may make mistakes that could have disastrous results. |
Real-life examples of delegative leaders
There are many successful delegative leaders in the world today. Some of the most notable include:
Steve Jobs
Combined with facilitative leadership encouraging collaboration, the late Apple CEO believed in empowering his team and giving them autonomy to make decisions, resulting in some of the most innovative products in history. For example, Jobs famously allowed his team to take risks and make mistakes, which led to the creation of the iPod.
One of his famous quotes even emphasizes this belief: “It doesn’t make sense to hire smart people and then tell them what to do; we hire smart people so they can tell us what to do.”
Ronald Reagan
Apart from the business world, delegative leadership also has a place in other fields, such as politics.
While Ronald Reagan was initially criticized for his lack of experience in daily politics and government management when starting his role as US president in 1981, he compensated by appointing industry leaders from Wall Street to crucial economic positions. He also delegated significant power to his Chief of Staff and other secretaries.
Despite controversies surrounding his administration, his impact as a delegative leader remains noteworthy.
Warren Buffet
The billionaire investor is known for his delegative approach to management, trusting his team to make decisions and allowing them the freedom to take initiative. This has resulted in significant successes, such as the acquisition of Heinz and Kraft.
HR tip
As an HR expert, you should encourage leaders to take a more delegative approach by emphasizing the benefits of this leadership style. Help them understand that it’s essential to trust employees and give them autonomy, leading to improved morale, creativity, and results. Ensure they know it’s not about giving up control—it’s about trusting their team members and equipping them with the resources to succeed.
Industries and situations ideal for the delegative leadership style
The laissez-faire leadership style doesn’t work in every situation but can be highly effective in specific industries and scenarios. Here are some examples:
- Startups: Startup companies typically require a lot of creativity and innovation to get off the ground, so delegative leadership is ideal for giving employees autonomy to make decisions and take risks.
- Research and development: This type of leadership works well in research and development roles, where teams need to think outside the box and develop new ideas.
- Technology: Delegative leadership allows for the freedom and autonomy needed in technology roles, where innovation is critical.
- Project-based teams: This leadership style works well for teams working on short-term projects, as it allows team members to take initiative and make decisions without waiting for approval from the leader.
- Creative fields: Working in creative fields like advertising, design, and writing requires high-level skills, motivation, and creativity, which is best achieved when team members are empowered to make decisions and take risks.