DEI Data: Use Data to Achieve Your DEI Objectives
DEI data builds the foundation of an effective DEI strategy. Gathering and evaluating DEI data is the best way to make decisions and measure and convey progress. The numbers reflect how well the initiatives are working and provide reference points for reaching DEI goals. This keeps you accountable and on track for success.
Contents
What is DEI data?
Why collect DEI data?
How to collect DEI data
What is DEI data?
DEI data is any information that can be linked to the areas of diversity, equity, and inclusion within an organization. These 3 types of data are explained as follows:
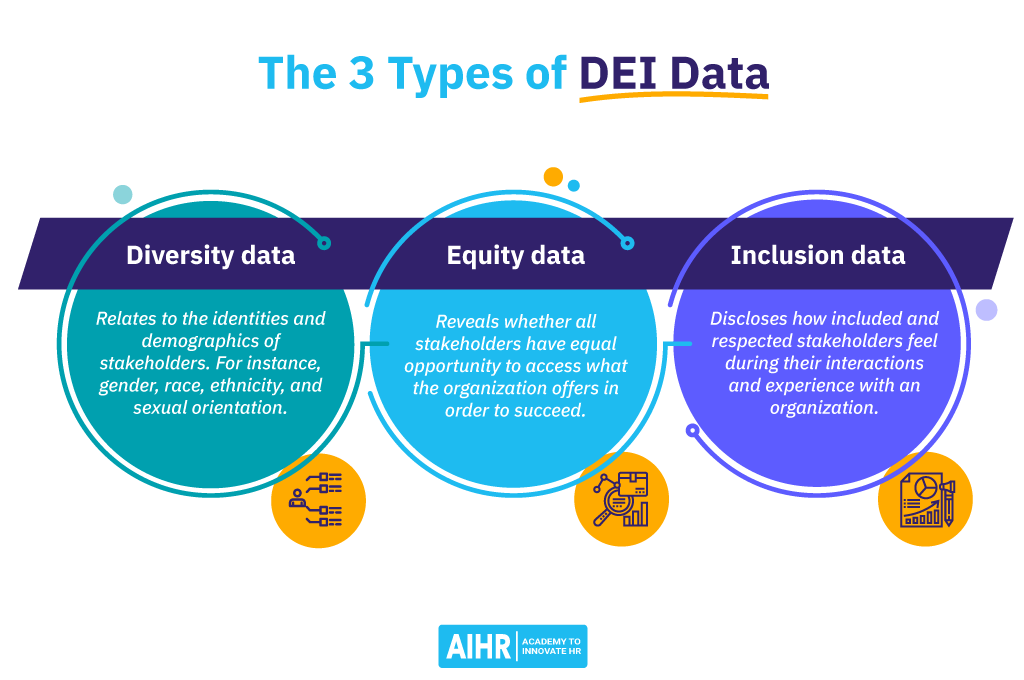
- Diversity data relates to the identities and demographics of stakeholders—for instance, gender, race, ethnicity, and sexual orientation.
- Equity data reveals whether all stakeholders have equal opportunity to access what the organization offers to succeed, such as employment, advancement, benefits, products, or services.
- Inclusion data discloses how included, and respected stakeholders feel during their interactions and experience with an organization.
With a data-driven approach, a DEI strategy can go from an item on HR’s checklist to a valuable program that makes a difference. DEI data provides a clear view of the demographics and sentiments of the people behind the organization and whether they can thrive in it. Then the data can be used for making decisions that promote progress.
Numerous successful businesses, such as global investment management company Schroder, are committed to leveraging data to enhance DEI efforts.
Why collect DEI data?
Data is the source for discovering the state of DEI in your organization and the effectiveness of your DEI strategy. It answers the questions you need to ask to evaluate your efforts and work toward a more diverse, equal, and inclusive environment.
Here are the key purposes of collecting DEI data:
Employee engagement
DEI data can give you a better understanding of the people who make up your workforce. Identifying and addressing biases or other issues will validate your commitment to improving the employee experience. This leads to keeping current employees engaged and attracting future talent who seek an employer that values DEI.
Transparency and authenticity
The ability to produce data related to DEI initiatives demonstrates an organization’s commitment to the process. It also maintains accountability while you strive to address the root causes of any inequalities in your workplace.
Awareness and accountability
Data can signal potential issues to address before they manifest into more significant problems or conflicts. It also gives you a means for establishing goals, setting benchmarks, and measuring progress.
Adherence to regulatory requirements
Governmental agencies and regulators have made workplace diversity a priority. DEI recommendations or regulations will likely be in place for your organization according to your industry and location. Collecting appropriate data means you are equipped to provide relevant information and be in compliance.
How to collect DEI data
There is a process for gathering DEI data that will make the most of your efforts. This is broken it down into the following 8 steps:
1. Form a working group with key stakeholders
A DEI data initiative should expand beyond HR and bring in the other parties necessary for support and execution. Pulling together a group of key stakeholders will help you cover all the bases for a more comprehensive DEI data collection process.
Consider including the following contributors on the front end of your DEI data program:
- Leadership: Organizational commitment to DEI needs to start at the top. Senior management must be fully aware of the DEI data-gathering process and be represented in any communications to employees. Leadership’s backing is also necessary to allocate resources and show solidarity with HR in overcoming possible challenges.
- IT/HR Systems: There is no DEI data without a system for collecting it. You will need to consult with your IT/HR systems team or work with external sources to establish the right structure and tools for your data collection needs.
- Data protection, legal, and compliance experts: DEI data is sensitive. Collection methods and usage of DEA data must be safe, legal, and in compliance with applicable regulations. This must be addressed with either your internal legal and data protection professionals or external consultants.
- Communications: Collaborate with your communications team early on to create an effective campaign that will engage employees. You can weave your DEI data collection strategy into various communication channels and networks to appeal to workers across the organization.
- Employees: The sooner you bring employees into the process the better. Opportunities such as surveys and focus groups allow them to provide their input and comfort level with sharing data. This gives them a voice and helps them feel included.
- Unions: In a union employment situation, it’s crucial to connect with union leaders and bring them into the loop. Be clear about the reasons for and value of DEI data collection. Eliminating their suspicions can get them on board with reinforcing the idea with the employees they represent.
2. Determine priorities and outcomes
There is more to a DEI strategy than just adhering to laws or signaling your organization’s commitment to diversity and inclusion. DEI considerations can solve problems. Business reasons for collecting DEI data will help you specify priorities and set goals.
For example, let’s say your organization is finding it increasingly difficult to fill entry-level positions. Does current DEI data shed any light on this problem? Is your workforce lacking diversity? The current recruiting process may not reach all the available demographics of potential talent.
- Business need: Fill open entry-level positions consistently.
- Goal: Grow staff diversity by 15% within one year by targeting untapped recruiting sources and talent pools.
- Outcome: Hiring more talent from under-represented groups to meet recruiting demands.
3. Identify legal and business considerations
Handling DEI data is complicated. As mentioned above, you must take legal considerations and technology capabilities into account:
- Legal: There are varying regulations and employment laws for collecting and processing DEI data. Organizations that operate in more than one region or country will have multiple policies and restrictions to navigate.
- You must be fully informed about current and developing requirements and conditions for managing DEI data. Depending on the size of your organization, this could be an extensive endeavor. You may need to delegate it to specialized data protection and legal professionals.
- Technology: The right system streamlines the DEI data collection process. You’ll need to assess whether your current technology will suit your needs or if new technology is required. Again, if you have larger, dispersed operations, you will need a more complex system or various tools.
4. Determine data collection types and methods
It’s possible to source more data than you need. Focus on what data are relevant and the best techniques for obtaining it.
DEI data that can be useful include:
- Age
- Race
- Ethnicity
- Sexual orientation
- Gender identity
- Disability/limitations
- Religious affiliation
- Military/veteran status
- Level of education
Data collection methods are based on your business needs and available resources. The following are typical avenues for DEI data:
- Self-reported employee demographics: Information provided voluntarily from employee profile questions.
- Employee engagement and experience surveys: DEI issues can drive how employees feel about their jobs and the organization.
- DEI survey: Questions about employees’ lived experiences that target areas often affecting underrepresented groups. This can be a section of your regular employee feedback surveys or a separate pulse survey.
5. Create a DEI data communications strategy
Since most DEI data is yielded voluntarily, you must get employees engaged to have a high percentage of participation. A well-thought-out communications strategy for DEI data collection is crucial because employees will approach the process with a wide range of perspectives.
Some will be skeptical about sharing sensitive information because they worry about how it will be used and if it will be safeguarded. Some will question the reasons behind the practice and hesitate to participate. Others will disregard DEI communications because they don’t think it pertains to them.
Be proactive in tackling this. Launch your communication strategy well ahead of implementing data collection. This starts with clearly defining the DEI data message and identifying your stakeholders.
Every facet of your organizational culture can communicate a message, so use every available channel to reach all employees and build their trust. You may need to adapt your communication style and refine the message to resonate with all different types of employee groups.
The crucial elements of a DEI data communications strategy include:
- Diverse voices and inclusive language and imagery.
- Transparency about exactly how the data will be collected and used.
- Assurance of how the data will be protected.
- Clear communication of positive outcomes the data will bring and accountability for putting it into action.
- Authenticity is demonstrated through visible support from leadership.
- Consistency of an ongoing message instead of a timed campaign.
- Opportunities for employees to engage by providing input and feedback in both open and confidential settings.
- Contact information for who fields employee questions and concerns
6. Collect data ethically
DEI data is sensitive and must be handled with vigilance. Employees have to feel respected and trust the reasons and methods for collecting the data. Otherwise, the noble intent of the process will be harmed by negative perceptions.
Here are some tips for how you can ensure that DEI data is managed ethically:
- Formulate policies and procedures that meet legal requirements and are consistently followed.
- Set strict parameters for who has access to the data.
- Be very transparent about the business needs for that data, what data will be collected, how it will be collected, and how it will be used.
- Explain that data will be kept confidential and protected. Then ensure that it is.
- Don’t collect unnecessary data.
7. Analyze data
DEI data analysis is how you determine how successful your DEI initiatives are. The insights you discover can help you see where you’re on the right track and which areas need attention.
Some of the DEI metrics you may choose to analyze include:
- General demographics: This will give you an overall picture of the different classifications represented in your workforce.
- Demographics breakdown: See how the demographics relate to location, manager, team, etc. Look for where the most diversity is and where it is lacking. Are there patterns?
- Attendance and performance: An uptick in unplanned absences or a decline in performance can indicate that employees are dissatisfied or frustrated. These can certainly be caused by various other issues unrelated to DEI, but they should be considered.
- Turnover: High turnover rates can signify that certain people don’t believe they have promising opportunities. Do you have more turnover with certain demographics?
- Exit interview feedback: People’s reasons for leaving their employment can indicate DEI struggles. Does a certain manager initiate a greater number of terminations? Do more people depart from a particular location?
- Employee engagement/satisfaction: Look at employee engagement and satisfaction scores by demographic. See how they correlate with overall engagement ratings.
Data analysis is a broad function that goes from relatively simple to highly complex. Let’s look at a few general tips for basic DEI data analytics:
- Be clear on your goals for what you want from the data. If you don’t know what you’re looking for, you won’t be able to find it.
- Choose the right tools. Excel or Google Sheets may be sufficient, or you might need a specialized analytics program.
- Organize and clean up the data by assembling it in one place, detecting errors, removing duplicates, and standardizing the format.
- Identify trends and patterns and compare current and past data.
- Examine any outliers that don’t support what you expected to find.
- Use visualization tools to summarize the data.
8. Take action and implement findings
The purpose of the DEI data you collect is to reveal insights about the state of DEI in your organization. What you learn from the data will empower you to make changes that will have a positive impact. This evidence-based approach will help you dispel myths, refine priorities, and generate better DEI strategy decisions and actions.
Putting the data to work may involve educating employees on DEI, using new recruiting methods, reforming organizational structures, revising compensation or other policies, or providing coaching.
You can select the types of interventions you need based on the reflections revealed by the data, such as:
- Types of DEI situations experienced by employees.
- How employees perceive DEI in the workplace.
- If employees believe they are valued and can be themselves at work.
- Current hotspots and barriers to DEI.
- Perception of leadership support for DEI.
Be sure to inform employees the data was used for these actions and then gauge whether the impact is meaningful to them.
Key takeaways
- HR needs a data-driven approach to DEI: Instead of relying on assumptions or preconceptions, data provide direct evidence.
- DEI data must be handled carefully: Sensitive information must be protected and used appropriately.
- DEI data collection requires a strong communication strategy: Employees must understand and trust the process in order to participate.
- Targeted DEI interventions come from data: Data reveals the specific areas that need attention.
Weekly update
Stay up-to-date with the latest news, trends, and resources in HR
Learn more
Related articles
Are you ready for the future of HR?
Learn modern and relevant HR skills, online