Broadbanding
What is broadbanding?
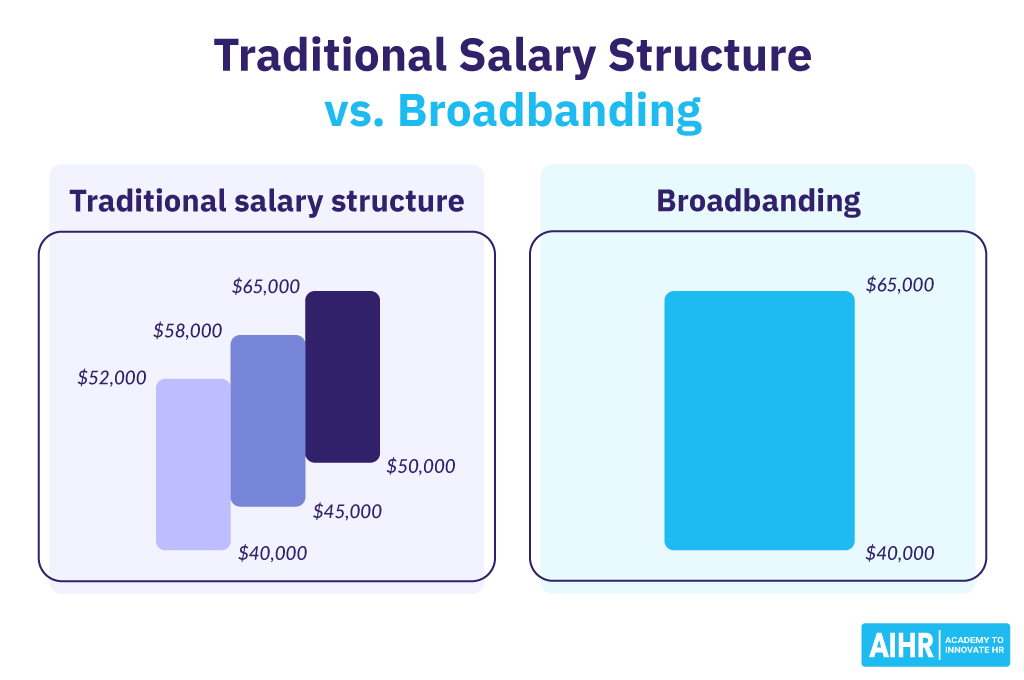
Broadbanding is a compensation approach consolidating a range of similar job classifications into a single pay band. This encompasses a much broader range of compensation levels than traditional salary structures and results in reducing the number of pay grades.
A traditional salary band usually has a range spread of 25-60% in its single-step grade structure, whereas a broadband structure often has an 80 to 300% in the low-end and high-end scales.
A broadband approach gives management a wider range and flexibility to pay employees.
What are the objectives of broadbanding?
HR and compensation & benefits teams implement broadbanding with the following objectives in mind:
- Offering flexibility in employee compensation
- Encouraging employees to acquire new skills to move higher within the pay range
- Reducing the need for pay band reclassification
Who uses broadbanding?
Broadbanding pay structure is more common in industries where employees tend to stay within the same companies and expand on their skills and training to move up within the same band. In other words, broadbanding makes it easier to reward employees for horizontal career growth.
Types of organizations broadbanding can work well for include:
- Healthcare and hospitals
- Startups
- IT
On the other hand, highly hierarchical organizations require different pay structures, as broadbanding de-emphasizes hierarchy. This type of pay structure might also not be suitable for scaling companies, as it is not easy to replicate across different locations.
An example of broadbanding
As a broadbanding example, a finance department might combine all of its jobs into a single entry “finance” band. This allows for compensation ranges for all roles to be from the least-skilled finance job to the highest-skilled job.
Let’s say the median salary is $60,000, and the range is 80% to 180% of the median. The minimum salary then is $48,000, and the range maximum is $108,000.
What are the advantages of broadbanding?
- It encourages internal mobility and lateral moves within the organization. Because an employee is likely to stay in a specific pay band for longer, it pushes them to take on new projects, learn new skills, and take on stretch tasks to receive a pay increase. Focusing on competencies and skills rather than on job titles, using broadband structure helps promote continuous learning and development.
- The hierarchy of an organization is streamlined. Broadbanding reduces the number of levels in an organization and creates space for lateral moves and horizontal career growth.
- It increases employee satisfaction, as some employees are deep specialists. Thus, further advancement into an employee’s career means they do not have to get promoted. They can achieve pay progression without the need to become a manager (which is not the desire of all employees).
- It is easier to administer. Broadbanding is flexible and gives managers a greater ability to reward their employees without the continuous need to promote them in order to provide more financial incentives.
What are the disadvantages of broadbanding?
- It does not always take into consideration external salary benchmarks and changes to external market conditions.
- It reduces the opportunities for promotion. Broadbanding might go against the work culture in some countries where employees tend to expect promotions more frequently than in other countries. Some employees may also lose motivation when they see fewer opportunities to earn a promotion.
- It can create (a perception of) pay inequity among employees. If you don’t set clear rules for rewarding similar work equally, broadbanding can result in pay differences that are difficult to justify.
How to move from traditional salary ranges to broadbanding
Here are the key elements to successfully implement broadbanding in your organization:
Review your current compensation structure. Evaluate the pay policies and strategies you have in place at the moment to determine how you could transition to a broadbanding pay structure.
Ensure that your job evaluation system is credible. This should happen before you implement broadbanding, so that when you classify jobs into bands, it is accurate and fair.
Put jobs of equal value in one band. This ensures consistency and a feeling of fairness in the organization. External auditors also regularly verify the bands, so it is a good idea to document them clearly.
Involve all relevant stakeholders. The compensation and benefits team should ensure to involve HR, management, and even employees when developing the bands. Communication is key, and explaining a broadband structure is easier when more people are involved in creating it.
Develop clear policies around your broadband structure. This policy could include information on how employees can earn a raise within their pay band, how moving from one broadband to another works, etc.
Broadbanding in HR: What to keep in mind
Explain the broadbanding pay structure in the selection and interview process. It will help you manage employee expectations about pay increases and career growth within your organization from the very beginning of the employee life cycle.