2024 Guide to Developing Employee Training Materials (With Examples)
The “secret sauce” for increased employee retention includes one simple ingredient — training. In fact, 76% of employees are more inclined to stay with an employer if they offer training and development.

The development of a company’s training initiatives plays a critical role in an organization’s growth — including the development of employee training materials.
Training lays the foundation for increased employee productivity, competence, and even job satisfaction. It empowers employees by providing them with the necessary tools and resources to perform their work more efficiently and effectively. A robust training program has short- and long-term benefits, including increased employee engagement and retention rates, mitigating compliance risks, and encouraging creative thinking.
According to LinkedIn, approximately 94% of employees say they would stay with an organization longer if it invested more in employee training and learning.
Contents
What are employee training materials?
The importance of employee training materials
What to include in your employee training materials
Examples of employee training materials
7 steps to create engaging training materials for employees
What are employee training materials?
Employee training materials are the resources used to train, educate, and develop an employee’s knowledge and skills. It’s a broad term and includes a variety of delivery methods, tools, resources, and documentation.
Employee training resources can come in many formats, including digital or printed materials. Each piece of content has a specific learning goal or desired outcome.
The importance of employee training materials
Employee training tools are essential for several reasons, including:
- Skills development and competence: Training materials are important for helping employees develop their skills and ensuring they have the proper tools and resources to meet their job expectations.
- Employee retention: Employees who are trained effectively are more likely to remain with their employer for longer. It’s expensive for a company to replace and retrain new staff. So, from a financial perspective, it’s beneficial for a company to provide adequate and relevant training to its employees.
- Consistency and clarity: Well-crafted training materials provide a consistent and clear source of information for employees, which results in a more uniform learning experience for all. This consistency is vital for maintaining quality standards, regulation compliance, and operational efficiency. On the other hand, inconsistent training materials can lead to confusion and a lack of understanding. This may result in an employee not knowing how or when to use the correct processes or procedures.
- Reference material: Employee training materials are an important resource that employees can refer back to when they need to refresh their knowledge.
What to include in your employee training materials
HR must consider what content needs to be included before creating employee training resources. HR can consult with management or other key players to gather input.
Here are some of the main elements that employee training materials should cover:
- Learning objectives: Be clear and specific about desired training objectives, outcomes, and expectations.
- Table of contents: Develop a table of contents that provides an overview of the topics covered in the training. Employees can use this as a quick reference after the training.
- Detailed instructions: Make sure any training instructions are clear and easy to follow. Include step-by-step instructions when appropriate.
- Visual aids: Include photos, videos, charts, graphs, or other visual aids that will enhance the learning experience.
- Organizational charts: Organizational charts reflect how a department is structured and functions. Including charts in employee training tools can help them better understand where they fit in the organization and how their work contributes to the overall company goals and strategy.
- Practice activities: Develop interactive and engaging opportunities that include “real-life” examples for employees to practice and apply the skills and concepts they learned in the training.
- Assessments and knowledge check questions: Include questions throughout the training to check for comprehension and understanding. This can help gauge whether objectives have been met. HR can analyze the results over the long term to determine if training needs are being satisfied or if revisions to the training need to be made.
- Glossary of terms: Include a list of terms and definitions that were included in the training that employees can refer back to.
- Additional relevant resources: Provide some additional links, training, or reference materials that complement the training so employees can expand their knowledge even further.
- Accessibility considerations: Be mindful about making employee training materials accessible to all participants, including those with disabilities, by using accessible formats and learning styles.
Finally, keep training materials updated. Keeping training materials current is essential so employees are provided with the most relevant information.
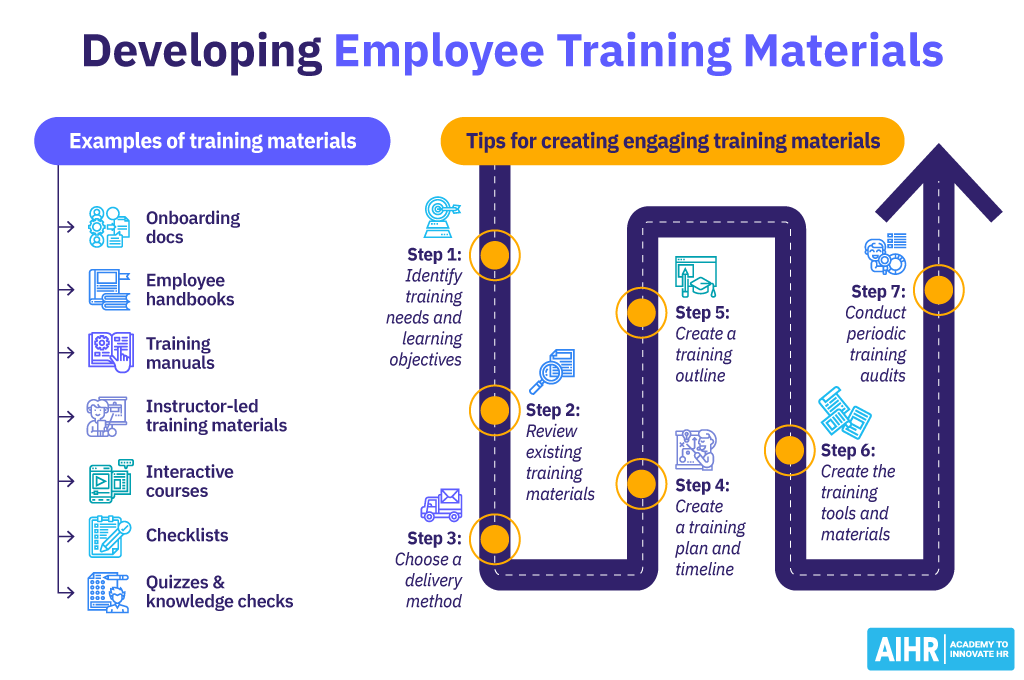
Examples of employee training materials
Employee training materials can be developed, used, and delivered in a variety of methods, such as instructor-led training, e-learning, or self-paced learning, depending on a company’s needs. Below are some training materials examples:
Employee handbooks
Employee handbooks contain structured information on company policies, procedures, safety and compliance information, standard operating procedures, and even step-by-step instructions for specific tasks or use of equipment.
→ Uses: Serves as a reference tool that employees can consult on a regular basis. Ideal for training new employees during the onboarding process.
Training manuals
Training manuals are usually a smaller version of an employee handbook in that they include information or instructions on a specific process, job, or body of work.
→ Uses: These manuals are effective for training employees on a specific topic or task.
Instructor-led training materials
Instructor-led in-person or virtual training includes more of a classroom setting where a facilitator leads the employees through a series of lessons, exercises, and discussions.
The training tools provided typically include PowerPoint presentations, worksheets or workbooks, and other related resources. These resources can be given as handouts or distributed electronically. They also provide consistency as all the employees being trained receive the same materials.
→ Uses: Distributed training materials are an excellent method to quickly and effectively communicate information. Employees can use and refer back to these materials for future reference.
Interactive courses
Interactive training tools include video or in-person training courses that engage the employees by including simulations or role-playing scenarios, video vignettes, etc.
→ Uses: Engaging the employee in interactive training allows for active learning and helps employees apply and retain the skills and concepts learned.
Checklists
Checklists are typically simple, easy-to-read lists that include the necessary actions/steps that need to be completed for the task at hand.
→ Uses: Checklists can help employees stay organized, keep track of their progress, and ensure that all steps of a process are completed.
Quizzes and knowledge checks
Incorporate knowledge checks or quizzes that are placed throughout the training. Keep the knowledge checks brief and simple but still allow for measuring the level of content mastery.
→ Uses: These assessment tools allow HR and the employee to gauge the employee’s comprehension and progress. HR can use this data to make any future revisions or enhancements to the training.
7 steps to create engaging training materials for employees
Now that we’ve looked at examples of training materials, let’s dive deeper into how to create the actual employee training materials.
Step 1: Identify training needs and learning objectives
Training needs and learning objectives go hand-in-hand and serve as the foundation of the learning and development process. It helps determine the type of training content needed.
Consider the following:
- Who is the audience and what should those employees achieve by the end of the training?
- What skills gap needs to be addressed?
- What company-specific or compliance information needs to be included?
- What is the most effective delivery method to achieve the best results?
Be clear and specific about what employees are expected to know or be able to do once they’ve completed the training. Materials need to be relevant to an employee’s overall role and responsibilities.
While training materials on company policies and procedures will be the same for all employees, job-related training needs and delivery methods may vary by role and job function. For example, the training content for marketing or sales jobs may vastly differ from training content for engineers or information technology roles.
Step 2: Review existing training materials
Does your company already have certain training materials available? If so, review any existing materials to determine if the content is still relevant and what may need updating. Existing training materials will help save the company time and resources if it doesn’t need to be completely developed from scratch.
Step 3: Choose a delivery method
The training delivery method impacts the type of training material that needs to be developed. There are various training delivery methods, including:
- In-person training
- Written training manuals
- Asynchronous computer-based training
- Live webinars
- Slide decks
- Online classes.
HR can decide on the training delivery method based on the training needs and business operations. For example, a small company may decide on in-person training. A larger organization with various locations might find it more effective to conduct online training – which requires less coordination and saves time and travel costs.
Get input from management or other key players when deciding on the most effective training delivery method, g. If a company uses an outside vendor to deliver training, the vendor will usually provide the training materials.
Step 4: Create a training plan and timeline
Create a training plan and timeline. This helps define how training will be delivered, how long it will take to develop training materials, and determine a target training and completion end date.
Include specific steps in the process, such as identifying the resources that will be needed, costs, time commitments, and communications related to the training schedule, delivery, and requirements. After identifying those main steps, a training schedule can be developed.
Also, include a tracking mechanism so the completion of training can be tracked and documented. Factor in makeup classes/training should unexpected or last-minute conflicts that arise.
Step 5: Develop a training outline
Prior to developing the training content, create an outline or “lesson plan” to help identify all the main topics. This will help break down the content into the necessary sections and topics.
Step 6: Create the training tools and materials
Employees need to absorb the information they learn in the training. The training should be tailored so that employees can easily absorb the necessary information without being overburdened or confused by too many details.
Developing high-quality and effective training material takes thought, time, and effort. Once the outline is developed, focus on defining the training content. Add visuals and interactive activities to keep learners engaged, which will help them retain what they learned in the long term.
Step 7: Conduct periodic training audits
Training needs and methods will change over time based on business needs. So, it’s essential to conduct training reviews and analyze previous training assessments to understand what needs improvement.
HR tip
Test the training with a pilot group prior to rolling it out across the organization. Select a group of employee “testers” from different departments of the company and gather their feedback. This will help you gain valuable insight from various perspectives and identify issues in the content, such as unclear language or information overload.
Questions to ask employee testers include:
- Is the learning material interesting and engaging?
- Is the content clear and easy to understand?
- Are the training materials relevant to daily work?
- Did the training offer opportunities to apply what was learned?
- How can the training material be improved?
To sum up
Training and development are essential to the employee experience and can even be the difference between employee retention and turnover. Developing and delivering effective employee training materials, tools, and resources are a major component of a company’s training initiatives.
Properly trained employees are a “win-win” for both the employee and the company. Retention tends to increase when employees feel engaged and feel that the company is investing in them. In turn, this helps the company’s bottom line and contributes towards building a strong and positive work environment for employees at all levels of the organization.
Weekly update
Stay up-to-date with the latest news, trends, and resources in HR
Learn more
Related articles
Are you ready for the future of HR?
Learn modern and relevant HR skills, online